Abstract
Introduction/Objectives:
The protein delta homolog 1 (DLK1) has been reported to have an important role as inhibitor of adipogenesis. Understanding its mode of action can be a promising approach to cope with the formation of obesity. However, data on DLK1 signaling are not consistent, and especially its role as negative regulator of Notch receptors is discussed controversially.
Methods:
DLK1 effects have been investigated in differentiated 3T3-L1 cells by Adipokine Profiler Array, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR). In vivo effects of DLK1 on adipogenesis have been studied by the DLK1 treatment of pregnant C57BL/6NTac mice and the phenotypical characterization of the offspring fed on chow or high-fat diet (HFD). Furthermore, gene expression of key adipogenesis genes in adipose tissue (AT) samples was observed by qRT-PCR.
Results:
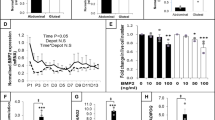
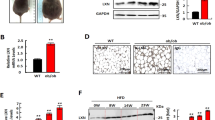
In 3T3-L1 cells, DLK1 was found to be an inhibitor of Notch1 signaling. Gene expression of Notch1 and Hes1 was lowered by 53% and 65%, respectively, and the expression of protein target PAI-1 was decreased by 51%. The offspring of DLK1-treated pregnant mice were fed chow or HFD starting from week 4. At week 18, a larger proportion of visceral AT was determined on HFD after DLK1 treatment (P=0.011), whereas adipocyte size was reduced (P=0.007 for maximal size). This was affiliated to an upregulation of adipocyte differentiation. The underlying mechanism was found in an increased expression of the Notch1 receptor gene and protein in AT of the offsprings independently of the diet. However, feeding a chow diet resulted in a decreased expression of Notch1 target genes Hes1 and RBP-Jκ, whereas under HFD these genes were upregulated.
Conclusions:
Treatment of mice with recombinant human DLK1 during pregnancy has significant effects on AT of the offspring. This can be associated with counter-regulatory changes in the Notch1 signaling cascade.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
WHO. Factsheet obesity and overweight, January 2015. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs311/en/ (last accessed 17 February 2015).
Spalding KL, Arner E, Westermark PO, Bernard S, Buchholz BA, Bergmann O et al. Dynamics of fat cell turnover in humans. Nature 2008; 453: 783–787.
Knittle JL, Timmers K, Ginsberg-Fellner F, Brown RE, Katz DP . The growth of adipose tissue in children and adolescents. Cross-sectional and longitudinal studies of adipose cell number and size. J Clin Invest 1979; 63: 239–246.
Rolland-Cachera MF, Deheeger M, Guilloud-Bataille M, Avons P, Patois E, Sempe M . Tracking the development of adiposity from one month of age to adulthood. Ann Hum Biol 1987; 14: 219–229.
Gesta S, Tseng YH, Kahn CR . Developmental origin of fat: tracking obesity to its source. Cell 2007; 131: 242–256.
Hudak CS, Gulyaeva O, Wang Y, Park SM, Lee L, Kang C et al. Pref-1 marks very early mesenchymal precursors required for adipose tissue development and expansion. Cell Rep 2014; 8: 678–687.
Smas CM, Sul HS . Pref-1, a protein containing EGF-like repeats, inhibits adipocyte differentiation. Cell 1993; 73: 725–734.
Cao Z, Umek RM, McKnight SL . Regulated expression of three C/EBP isoforms during adipose conversion of 3T3-L1 cells. Genes Dev 1991; 5: 1538–1552.
Farmer SR . Regulation of PPARgamma activity during adipogenesis. Int J Obes (Lond) 2005; 29: S13–S16.
Boutet E, Lieberherr D, Tognolli M, Schneider M, Bairoch A . UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot. Methods Mol Biol 2007; 406: 89–112.
Wang Y, Sul HS . Ectodomain shedding of preadipocyte factor 1 (Pref-1) by tumor necrosis factor alpha converting enzyme (TACE) and inhibition of adipocyte differentiation. Mol Cell Biol 2006; 26: 5421–5435.
Yevtodiyenko A, Schmidt JV . Dlk1 expression marks developing endothelium and sites of branching morphogenesis in the mouse embryo and placenta. Dev Dyn 2006; 235: 1115–1123.
Su AI, Wiltshire T, Batalov S, Lapp H, Ching KA, Block D et al. A gene atlas of the mouse and human protein-encoding transcriptomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 6062–6067.
Moon YS, Smas CM, Lee K, Villena JA, Kim KH, Yun EJ et al. Mice lacking paternally expressed Pref-1/Dlk1 display growth retardation and accelerated adiposity. Mol Cell Biol 2002; 22: 5585–5592.
Wang Y, Kim KA, Kim JH, Sul HS . Pref-1, a preadipocyte secreted factor that inhibits adipogenesis. J Nutr 2006; 136: 2953–2956.
Villena JA, Choi CS, Wang Y, Kim S, Hwang YJ, Kim YB et al. Resistance to high-fat diet-induced obesity but exacerbated insulin resistance in mice overexpressing preadipocyte factor-1 (Pref-1): a new model of partial lipodystrophy. Diabetes 2008; 57: 3258–3266.
Yanai H, Nakamura K, Hijioka S, Kamei A, Ikari T, Ishikawa Y et al. Dlk-1, a cell surface antigen on foetal hepatic stem/progenitor cells, is expressed in hepatocellular, colon, pancreas and breast carcinomas at a high frequency. J Biochem 2010; 148: 85–92.
Begum A, Kim Y, Lin Q, Yun Z . DLK1, delta-like 1 homolog (Drosophila), regulates tumor cell differentiation in vivo. Cancer Lett 2012; 318: 26–33.
Zhang W, Shao Z, Fu R, Wang H, Li L, Yue L . Effect of DLK1 on tumorigenesis in CD34CD38 bone marrow cells in myelodysplastic syndromes. Oncol Lett 2013; 6: 203–206.
Andersen DC, Laborda J, Baladron V, Kassem M, Sheikh SP, Jensen CH . Dual role of delta-like 1 homolog (DLK1) in skeletal muscle development and adult muscle regeneration. Development 2013; 140: 3743–3753.
Waddell JN, Zhang P, Wen Y, Gupta SK, Yevtodiyenko A, Schmidt JV et al. Dlk1 is necessary for proper skeletal muscle development and regeneration. PLoS One 2010; 5: e15055.
Shin S, Suh Y, Zerby HN, Lee K . Membrane-bound delta-like 1 homolog (Dlk1) promotes while soluble Dlk1 inhibits myogenesis in C2C12 cells. FEBS Lett 2014; 588: 1100–1108.
Tanaka M, Okabe M, Suzuki K, Kamiya Y, Tsukahara Y, Saito S et al. Mouse hepatoblasts at distinct developmental stages are characterized by expression of EpCAM and DLK1: drastic change of EpCAM expression during liver development. Mech Dev 2009; 126: 665–676.
Puertas-Avendano RA, Gonzalez-Gomez MJ, Ruvira MD, Ruiz-Hidalgo MJ, Morales-Delgado N, Laborda J et al. Role of the non-canonical notch ligand delta-like protein 1 in hormone-producing cells of the adult male mouse pituitary. J Neuroendocrinol 2011; 23: 849–859.
Lai EC . Notch signaling: control of cell communication and cell fate. Development 2004; 131: 965–973.
Lobry C, Oh P, Aifantis I . Oncogenic and tumor suppressor functions of Notch in cancer: it's NOTCH what you think. J Exp Med 2011; 208: 1931–1935.
Louvi A, Artavanis-Tsakonas S . Notch and disease: a growing field. Semin Cell Dev Biol 2012; 23: 473–480.
Kilian T-M, Beck-Sickinger AG . Recombinant expression and characterization of biologically active protein delta homolog 1. Protein Expr Purif 2015; 110: 72–78.
Kloting N, Graham TE, Berndt J, Kralisch S, Kovacs P, Wason CJ et al. Serum retinol-binding protein is more highly expressed in visceral than in subcutaneous adipose tissue and is a marker of intra-abdominal fat mass. Cell Metab 2007; 6: 79–87.
Kloting N, Koch L, Wunderlich T, Kern M, Ruschke K, Krone W et al. Autocrine IGF-1 action in adipocytes controls systemic IGF-1 concentrations and growth. Diabetes 2008; 57: 2074–2082.
Krowczynska AM, Coutts M, Makrides S, Brawerman G . The mouse homologue of the human acidic ribosomal phosphoprotein PO: a highly conserved polypeptide that is under translational control. Nucleic Acids Res 1989; 17: 6408.
Kern M, Kosacka J, Hesselbarth N, Bruckner J, Heiker JT, Flehmig G et al. Liver-restricted Repin1 deficiency improves whole-body insulin sensitivity, alters lipid metabolism, and causes secondary changes in adipose tissue in mice. Diabetes 2014; 63: 3295–3309.
Ross DA, Hannenhalli S, Tobias JW, Cooch N, Shiekhattar R, Kadesch T . Functional analysis of Hes-1 in preadipocytes. Mol Endocrinol 2006; 20: 698–705.
Nueda ML, Baladron V, Sanchez-Solana B, Ballesteros MA, Laborda J . The EGF-like protein dlk1 inhibits notch signaling and potentiates adipogenesis of mesenchymal cells. J Mol Biol 2007; 367: 1281–1293.
Rodriguez P, Higueras MA, Gonzalez-Rajal A, Alfranca A, Fierro-Fernandez M, Garcia-Fernandez RA et al. The non-canonical NOTCH ligand DLK1 exhibits a novel vascular role as a strong inhibitor of angiogenesis. Cardiovasc Res 2012; 93: 232–241.
Wang YH, Zhao L, Smas C, Sul HS . Pref-1 interacts with fibronectin to inhibit adipocyte differentiation. Mol Cell Biol 2010; 30: 3480–3492.
Kim KA, Kim JH, Wang Y, Sul HS . Pref-1 (preadipocyte factor 1) activates the MEK/extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway to inhibit adipocyte differentiation. Mol Cell Biol 2007; 27: 2294–2308.
Hudak CS, Sul HS . Pref-1, a gatekeeper of adipogenesis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2013; 4: 79.
Wang Y, Sul HS . Pref-1 regulates mesenchymal cell commitment and differentiation through Sox9. Cell Metab 2009; 9: 287–302.
Juhan-Vague I, Alessi MC . PAI-1, obesity, insulin resistance and risk of cardiovascular events. Thromb Haemost 1997; 78: 656–660.
Garces C, Ruiz-Hidalgo MJ, Font de Mora J, Park C, Miele L, Goldstein J et al. Notch-1 controls the expression of fatty acid-activated transcription factors and is required for adipogenesis. J Biol Chem 1997; 272: 29729–29734.
Nichols AM, Pan Y, Herreman A, Hadland BK, De Strooper B, Kopan R et al. Notch pathway is dispensable for adipocyte specification. Genesis 2004; 40: 40–44.
Hatakeyama J, Kageyama R . Notch1 expression is spatiotemporally correlated with neurogenesis and negatively regulated by Notch1-independent Hes genes in the developing nervous system. Cereb Cortex 2006; 16: i132–i137.
Swiatek PJ, Lindsell CE, del Amo FF, Weinmaster G, Gridley T . Notch1 is essential for postimplantation development in mice. Genes Dev 1994; 8: 707–719.
Bachmann E, Krogh TN, Hojrup P, Skjodt K, Teisner B . Mouse fetal antigen 1 (mFA1), the circulating gene product of mdlk, pref-1 and SCP-1: isolation, characterization and biology. J Reprod Fertil 1996; 107: 279–285.
Ansell PJ, Zhou Y, Schjeide BM, Kerner A, Zhao J, Zhang X et al. Regulation of growth hormone expression by Delta-like protein 1 (Dlk1). Mol Cell Endocrinol 2007; 271: 55–63.
Carlsson C, Tornehave D, Lindberg K, Galante P, Billestrup N, Michelsen B et al. Growth hormone and prolactin stimulate the expression of rat preadipocyte factor-1/delta-like protein in pancreatic islets: molecular cloning and expression pattern during development and growth of the endocrine pancreas. Endocrinology 1997; 138: 3940–3948.
Acknowledgements
We thank Kristin Löbner for assistance in cell culture and Eva Böge as well as Bella Bohnstedt for support in animal experiments. This project was financially supported by a grant from Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft SFB1052/1 and BMBF IFB K7-18 Adi KO5b to NK.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on International Journal of Obesity website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kilian, T., Klöting, N., Blüher, M. et al. Prenatal notch1 receptor blockade by protein delta homolog 1 (DLK1) modulates adipocyte size in vivo. Int J Obes 40, 698–705 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2015.227
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2015.227
This article is cited by
-
Enlarged adipocytes from subcutaneous vs. visceral adipose tissue differentially contribute to metabolic dysfunction and atherogenic risk of patients with obesity
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
DLK proteins modulate NOTCH signaling to influence a brown or white 3T3-L1 adipocyte fate
Scientific Reports (2018)