Abstract
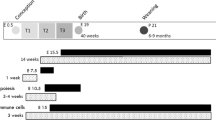
Maternal obesity is associated with an increased risk of developing gestational diabetes mellitus and it also results in an increased risk of giving birth to a large baby with increased fat mass. Furthermore, it is also contributes to an increased risk of obesity and insulin resistance in the offspring in childhood, adolescence and adult life. It has been proposed that exposure to maternal obesity may therefore result in an ‘intergenerational cycle’ of obesity and insulin resistance. There is significant interest in whether exposure to maternal obesity around the time of conception alone contributes directly to poor metabolic outcomes in the offspring and whether dieting in the obese mother before pregnancy or around the time of conception has metabolic benefits for the offspring. This review focusses on experimental and clinical studies that have investigated the specific impact of exposure to maternal obesity during the periconceptional period alone or extending beyond conception on adipogenesis, lipogenesis and on insulin signalling pathways in the fat, liver and muscle of the offspring. Findings from these studies highlight the need for a better evidence base for the development of dietary interventions in obese women before pregnancy and around the time of conception to maximize the metabolic benefits and minimize the metabolic costs for the next generation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kumanyika SK, Obarzanek E, Stettler N, Bell R, Field AE, Fortmann SP et al. Population-based prevention of obesity: the need for comprehensive promotion of healthful eating, physical activity, and energy balance: a scientific statement from American Heart Association Council on Epidemiology and Prevention, Interdisciplinary Committee for prevention (formerly the expert panel on population and prevention science). Circulation 2008; 118: 428–464.
Ogden CL, Yanovski SZ, Carroll MD, Flegal KM . The epidemiology of obesity. Gastroenterology 2007; 132: 2087–2102.
Catalano PM, Ehrenberg HM . The short- and long-term implications of maternal obesity on the mother and her offspring. BJOG 2006; 113: 1126–1133.
Zhang S, Rattanatray L, Morrison JL, Nicholas LM, Lie S, McMillen IC . Maternal obesity and the early origins of childhood obesity: weighing up the benefits and costs of maternal weight loss in the periconceptional period for the offspring. Exp Diabetes Res 2011; 2011: 585749.
Oteng-Ntim E, Varma R, Croker H, Poston L, Doyle P . Lifestyle interventions for overweight and obese pregnant women to improve pregnancy outcome: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med 2012; 10: 47.
Rooney K, Ozanne SE . Maternal over-nutrition and offspring obesity predisposition: targets for preventative interventions. Int J Obes (Lond) 2011; 35: 883–890.
Ryan D . Obesity in women: a life cycle of medical risk. Int J Obes (Lond) 2007; 31 (Suppl 2): S3–S7.
Freinkel N . Of pregnancy and progeny. Diabetes 1980; 29: 1023–1035.
Lawlor DA, Relton C, Sattar N, Nelson SM . Maternal adiposity—a determinant of perinatal and offspring outcomes? Nat Rev Endocrinol 2012; 8: 679–688.
Smith GD, Leary S, Ness A, Lawlor DA . Challenges and novel approaches in the epidemiological study of early life influences on later disease. Adv Exp Med Biol 2009; 646: 1–14.
Whitaker RC, Wright JA, Pepe MS, Seidel KD, Dietz WH . Predicting obesity in young adulthood from childhood and parental obesity. N Engl J Med 1997; 337: 869–873.
Yu Z, Han S, Zhu J, Sun X, Ji C, Guo X . Pre-pregnancy body mass index in relation to infant birth weight and offspring overweight/obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One 2013; 8: e61627.
Isganaitis E, Rifas-Shiman SL, Oken E, Dreyfuss JM, Gall W, Gillman MW et al. Associations of cord blood metabolites with early childhood obesity risk. Int J Obes (Lond) 2015; 39: 1041–1048.
Petitt DJ, Baird HB, Aleck KA . Excessive obesity in offspring of Pima Indian women with diabetes during pregnancy. N Engl J Med 1983; 308: 242–245.
Pettitt DJ, Bennett PH, Knowler WC . Gestational diabetes mellitus and impaired glucose tolerance during pregnancy. Long-term effects on obesity and glucose tolerance in the offspring. Diabetes 1985; 34: 119–122.
Boney CM, Verma A, Tucker R, Vohr BR . Metabolic syndrome in childhood: association with birth weight, maternal obesity, and gestational diabetes mellitus. Pediatrics 2005; 115: e290–e296.
Parsons TJ, Power C, Manor O . Fetal and early life growth and body mass index from birth to early adulthood in 1958 British cohort: Longitudinal. BMJ 2001; 323: 1331–1335.
Kubo A, Ferrara A, Windham GC, Greenspan LC, Deardorff J, Hiatt RA et al. Maternal hyperglycemia during pregnancy predicts adiposity of the offspring. Diabetes Care 2014; 37: 2996–3002.
Buckley AJ, Keserü B, Briody J, Thompson M, Ozanne SE, Thompson CH . Altered body composition and metabolism in the male offspring of high fat-fed rats. Metabolism 2005; 54: 500–507.
Cerf ME, Williams K, Nkomo XI, Muller CJ, Du Toit DF, Louw J et al. Islet cell response in the neonatal rat after exposure to a high-fat diet during pregnancy. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2005; 288: R1122–R1128.
Nivoit P, Morens C, Van Assche FA, Jansen E, Poston L, Remacle C et al. Established diet-induced obesity in female rats leads to offspring hyperphagia, adiposity and insulin resistance. Diabetologia 2009; 52: 1133–1142.
Samuelsson AM, Matthews PA, Argenton M, Christie MR, McConnell JM, Jansen EH et al. Diet-induced obesity in female mice leads to offspring hyperphagia, adiposity, hypertension, and insulin resistance: a novel murine model of developmental programming. Hypertension 2008; 51: 383–392.
Shankar K, Harrell A, Liu X, Gilchrist JM, Ronis MJJ, Badger TM . Maternal obesity at conception programs obesity in the offspring. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2008; 294: R528–R538.
Taylor PD, McConnell J, Khan IY, Holemans K, Lawrence KM, Asare-Anane H et al. Impaired glucose homeostasis and mitochondrial abnormalities in offspring of rats fed a fat-rich diet in pregnancy. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2005; 288: R134–R139.
Volpato AM, Schultz A, Magalhães-da-Costa E, MLdG Correia, Águila MB, Mandarim-de-Lacerda CA . Maternal high-fat diet programs for metabolic disturbances in offspring despite leptin sensitivity. Neuroendocrinology 2012; 96: 272–284.
Frayn KN . Visceral fat and insulin resistance—causative or correlative? Br J Nutr 2000; 83 (Suppl 1): S71–S77.
Murabayashi N, Sugiyama T, Zhang L, Kamimoto Y, Umekawa T, Ma N et al. Maternal high-fat diets cause insulin resistance through inflammatory changes in fetal adipose tissue. Eur J Obstetr Gynecol Reprod Biol 2013; 169: 39–44.
Balagopal PB, de Ferranti SD, Cook S, Daniels SR, Gidding SS, Hayman LL et al. Nontraditional risk factors and biomarkers for cardiovascular disease: mechanistic, research, and clinical considerations for youth: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2011; 123: 2749–2769.
Antuna-Puente B, Feve B, Fellahi S, Bastard JP . Adipokines: the missing link between insulin resistance and obesity. Diabetes Metab 2008; 34: 2–11.
Yamauchi T, Kamon J, Minokoshi Y, Ito Y, Waki H, Uchida S et al. Adiponectin stimulates glucose utilization and fatty-acid oxidation by activating AMP-activated protein kinase. Nat Med 2002; 8: 1288–1295.
Zhang Y, Proenca R, Maffei M, Barone M, Leopold L, Friedman JM . Positional cloning of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue. Nature 1994; 372: 425–432.
Ahima RS, Flier JS . Leptin. Annu Rev Physiol 2000; 62: 413–437.
Matsuda J, Yokota I, Iida M, Murakami T, Naito E, Ito M et al. Serum leptin concentration in cord blood: Relationship to birth weight and gender. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1997; 82: 1642–1644.
Tapanainen P, Leinonen E, Ruokonen A, Knip M . Leptin concentrations are elevated in newborn infants of diabetic mothers. Horm Res 2001; 55: 185–190.
Steppan CM, Bailey ST, Bhat S, Brown EJ, Banerjee RR, Wright CM et al. The hormone resistin links obesity to diabetes. Nature 2001; 409: 307–312.
Reilly MP, Lehrke M, Wolfe ML, Rohatgi A, Lazar MA, Rader DJ . Resistin is an inflammatory marker of atherosclerosis in humans. Circulation 2005; 111: 932–939.
Sun Q, Kiernan UA, Shi L, Phillips DA, Kahn BB, Hu FB et al. Plasma retinol-binding protein 4 (RBP4) levels and risk of coronary heart disease: a prospective analysis among women in the nurses' health study. Circulation 2013; 127: 1938–1947.
Deng Y, Scherer PE . Adipokines as novel biomarkers and regulators of the metabolic syndrome. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2010; 1212: E1–E19.
Bringhenti I, Moraes-Teixeira JA, Cunha MR, Ornellas F, Mandarim-de-Lacerda CA, Aguila MB . Maternal obesity during the preconception and early life periods alters pancreatic development in early and adult life in male mouse offspring. PLoS One 2013; 8: 1.
Shelley P, Martin-Gronert MS, Rowlerson A, Poston L, Heales SJR, Hargreaves IP et al. Altered skeletal muscle insulin signaling and mitochondrial complex II-III linked activity in adult offspring of obese mice. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2009; 297: R675–R681.
Ainge H, Thompson C, Ozanne SE, Rooney KB . A systematic review on animal models of maternal high fat feeding and offspring glycaemic control. Int J Obes 2011; 35: 325–335.
Du M, Yan X, Tong JF, Zhao J, Zhu MJ . Maternal obesity, inflammation, and fetal skeletal muscle development. Biol Reprod 2010; 82: 4–12.
Sen S, Simmons RA . Maternal antioxidant supplementation prevents adiposity in the offspring of Western diet-fed rats. Diabetes 2010; 59: 3058–3065.
Tong JF, Yan X, Zhu MJ, Ford SP, Nathanielsz PW, Du M . Maternal obesity downregulates myogenesis and beta-catenin signaling in fetal skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2009; 296: E917–E924.
Lewis DS, Bertrand HA, McMahan CA . Preweaning food intake influences the adiposity of young adult baboons. J Clin Invest 1986; 78: 899–905.
DiGiacomo JE, Hay WW Jr . Effect of hypoinsulinemia and hyperglycemia on fetal glucose utilization. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 1990; 259: E506–E512.
Ford SP, Tuersunjiang N . Maternal obesity: How big an impact does it have on offspring prenatally and during postnatal life? Expert Rev Endocrinol Metab 2013; 8: 261–273.
Hay Jr WW, DiGiacomo JE, Meznarich HK, Hirst K, Zerbe G . Effects of glucose and insulin on fetal glucose oxidation and oxygen consumption. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 1989; 256: E704–E713.
Anthony RV, Scheaffer AN, Wright CD, Regnault TR . Ruminant models of prenatal growth restriction. Reprod Suppl 2003; 61: 183–194.
Long NM, Rule DC, Zhu MJ, Nathanielsz PW, Ford SP . Maternal obesity upregulates fatty acid and glucose transporters and increases expression of enzymes mediating fatty acid biosynthesis in fetal adipose tissue depots. J Anim Sci 2012; 90: 2201–2210.
Ford SP, Zhang L, Zhu M, Miller MM, Smith DT, Hess BW et al. Maternal obesity accelerates fetal pancreatic β-cell but not α-cell development in sheep: Prenatal consequences. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2009; 297: R835–R843.
Zhang L, Long NM, Hein SM, Ma Y, Nathanielsz PW, Ford SP . Maternal obesity in ewes results in reduced fetal pancreatic β-cell numbers in late gestation and decreased circulating insulin concentration at term. Domest Anim Endocrinol 2011; 40: 30–39.
Long NM, George LA, Uthlaut AB, Smith DT, Nijland MJ, Nathanielsz PW et al. Maternal obesity and increased nutrient intake before and during gestation in the ewe results in altered growth, adiposity, and glucose tolerance in adult offspring. J Anim Sci 2010; 88: 3546–3553.
Li J, Huang J, Li JS, Chen H, Huang K, Zheng L . Accumulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress and lipogenesis in the liver through generational effects of high fat diets. J Hepatol 2012; 56: 900–907.
Masuyama H, Hiramatsu Y . Effects of a high-fat diet exposure in utero on the metabolic syndrome-like phenomenon in mouse offspring through epigenetic changes in adipocytokine gene expression. Endocrinology 2012; 153: 2823–2830.
Strakovsky RS, Zhang X, Zhou D, Pan YX . Gestational high fat diet programs hepatic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene expression and histone modification in neonatal offspring rats. J Physiol 2011; 589: 2707–2717.
Graus-Nunes F, Dalla Corte Frantz E, Lannes WR, da Silva Menezes MC, Mandarim-de-Lacerda CA, Souza-Mello V . Pregestational maternal obesity impairs endocrine pancreas in male F1 and F2 progeny. Nutrition 2015; 31: 380–387.
Adamo KB, Ferraro ZM, Goldfield G, Keely E, Stacey D, Hadjiyannakis S et al. The Maternal Obesity Management (MOM) Trial Protocol: a lifestyle intervention during pregnancy to minimize downstream obesity. Contemp Clin Trials 2013; 35: 87–96.
Nohr EA, Vaeth M, Baker JL, Sørensen TIA, Olsen J, Rasmussen KM . Combined associations of prepregnancy body mass index and gestational weight gain with the outcome of pregnancy. Am J Clin Nutr 2008; 87: 1750–1759.
Smith J, Cianflone K, Biron S, Hould FS, Lebel S, Marceau S et al. Effects of maternal surgical weight loss in mothers on intergenerational transmission of obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2009; 94: 4275–4283.
Jensen DM, Damm P, Sørensen B, Mølsted-Pedersen L, Westergaard JG, Ovesen P et al. Pregnancy outcome and prepregnancy body mass index in 2459 glucose-tolerant Danish women. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2003; 189: 239–244.
Van Der Steeg JW, Steures P, Eijkemans MJC, Habbema JDF, Hompes PGA, Burggraaff JM et al. Obesity affects spontaneous pregnancy chances in subfertile, ovulatory women. Hum Reprod 2008; 23: 324–328.
Hochner H, Friedlander Y, Calderon-Margalit R, Meiner V, Sagy Y, Avgil-Tsadok M et al. Associations of maternal prepregnancy body mass index and gestational weight gain with adult offspring cardiometabolic risk factors: the Jerusalem Perinatal Family Follow-up Study. Circulation 2012; 125: 1381–1389.
Oostvogels AJ, Stronks K, Roseboom TJ, van der Post JA, van Eijsden M, Vrijkotte TG . Maternal prepregnancy BMI, offspring's early postnatal growth, and metabolic profile at age 5–6 years: the ABCD Study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2014; 99: 3845–3854.
Maftei O, Whitrow MJ, Davies MJ, Giles LC, Owens JA, Moore VM . Maternal body size prior to pregnancy, gestational diabetes and weight gain: associations with insulin resistance in children at 9-10 years. Diabet Med 2015; 32: 174–180.
Minge CE, Bennett BD, Norman RJ, Robker RL . Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α agonist rosiglitazone reverses the adverse effects of diet-induced obesity on oocyte quality. Endocrinology 2008; 149: 2646–2656.
Wu LL, Russell DL, Wong SL, Chen M, Tsai TS, St John JC et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction in oocytes of obese mothers: transmission to offspring and reversal by pharmacological endoplasmic reticulum stress inhibitors. Development 2015; 142: 681–691.
Nicholas LM, Morrison JL, Rattanatray L, Ozanne SE, Kleemann DO, Walker SK et al. Differential effects of exposure to maternal obesity or maternal weight loss during the periconceptional period in the sheep on insulin signalling molecules in skeletal muscle of the offspring at 4 months of age. PLoS One 2013; 8: e84594.
Nicholas LM, Rattanatray L, Maclaughlin SM, Ozanne SE, Kleemann DO, Walker SK et al. Differential effects of maternal obesity and weight loss in the periconceptional period on the epigenetic regulation of hepatic insulin-signaling pathways in the offspring. FASEB J 2013; 27: 3786–3796.
Nicholas LM, Rattanatray L, Morrison JL, Kleemann DO, Walker SK, Zhang S et al. Maternal obesity or weight loss around conception impacts hepatic fatty acid metabolism in the offspring. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2014; 22: 1685–1693.
Rattanatray L, MacLaughlin SM, Kleemann DO, Walker SK, Muhlhausler BS, McMillen IC . Impact of maternal periconceptional overnutrition on fat mass and expression of adipogenic and lipogenic genes in visceral and subcutaneous fat depots in the postnatal lamb. Endocrinology 2010; 151: 5195–5205.
Zhang S, Rattanatray L, MacLaughlin SM, Cropley JE, Suter CM, Molloy L et al. Periconceptional undernutrition in normal and overweight ewes leads to increased adrenal growth and epigenetic changes in adrenal IGF2/H19 gene in offspring. FASEB J 2010; 24: 2772–2782.
Catalano PM, Nizielski SE, Shao J, Preston L, Qiao L, Friedman JE . Downregulated IRS-1 and PPARγ in obese women with gestational diabetes: relationship to FFA during pregnancy. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2002; 282: E522–E533.
Greenfield JR, Campbell LV . Insulin resistance and obesity. Clin Dermatol 2004; 22: 289–295.
Savage DB, Petersen KF, Shulman GI . Disordered lipid metabolism and the pathogenesis of insulin resistance. Physiol Rev 2007; 87: 507–520.
Li X, Monks B, Ge Q, Birnbaum MJ . Akt/PKB regulates hepatic metabolism by directly inhibiting PGC-1α transcription coactivator. Nature 2007; 447: 1012–1016.
Ozanne SE, Jensen CB, Tingey KJ, Storgaard H, Madsbad S, Vaag AA . Low birthweight is associated with specific changes in muscle insulin-signalling protein expression. Diabetologia 2005; 48: 547–552.
Ozanne SE, Olsen GS, Hansen LL, Tingey KJ, Nave BT, Wang CL et al. Early growth restriction leads to down regulation of protein kinase C zeta and insulin resistance in skeletal muscle. J Endocrinol 2003; 177: 235–241.
Postic C, Dentin R, Girard J . Role of the liver in the control of carbohydrate and lipid homeostasis. Diabetes Metab 2004; 30: 398–408.
Angulo P . Medical progress: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. N Engl J Med 2002; 346: 1221–1231.
Marchesini G, Brizi M, Blanchi G, Tomassetti S, Bugianesi E, Lenzi M et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a feature of the metabolic syndrome. Diabetes 2001; 50: 1844–1850.
McCurdy CE, Bishop JM, Williams SM, Grayson BE, Smith MS, Friedman JE et al. Maternal high-fat diet triggers lipotoxicity in the fetal livers of nonhuman primates. J Clin Invest 2009; 119: 323–335.
Oben JA, Mouralidarane A, Samuelsson AM, Matthews PJ, Morgan ML, McKee C et al. Maternal obesity during pregnancy and lactation programs the development of offspring non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice. J Hepatol 2010; 52: 913–920.
Isagawa T, Nagae G, Shiraki N, Fujita T, Sato N, Ishikawa S et al. DNA methylation profiling of embryonic stem cell differentiation into the three germ layers. PLoS One 2011; 6 6: e26052.
Duque-Guimarães DE, Ozanne SE . Nutritional programming of insulin resistance: Causes and consequences. Trends Endocrinol Metab 2013; 24: 525–535.
Morgan HD, Santos F, Green K, Dean W, Reik W . Epigenetic reprogramming in mammals. Hum Mol Genet 2005; 14: R47–R58.
Jiménez-Chillarón JC, Díaz R, Martínez D, Pentinat T, Ramón-Krauel M, Ribó S et al. The role of nutrition on epigenetic modifications and their implications on health. Biochimie 2012; 94: 2242–2263.
Margueron R, Reinberg D . Chromatin structure and the inheritance of epigenetic information. Nat Rev Genet 2010; 11: 285–296.
Semple RK, Chatterjee VK, O'Rahilly S . PPAR gamma and human metabolic disease. J Clin Invest 2006; 116: 581–589.
Waterland RA, Travisano M, Tahiliani KG, Rached MT, Mirza S . Methyl donor supplementation prevents transgenerational amplification of obesity. Int J Obes 2008; 32: 1373–1379.
He A, Zhu L, Gupta N, Chang Y, Fang F . Overexpression of micro ribonucleic acid 29, highly up-regulated in diabetic rats, leads to insulin resistance in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Mol Endocrinol 2007; 21: 2785–2794.
Trajkovski M, Hausser J, Soutschek J, Bhat B, Akin A, Zavolan M et al. MicroRNAs 103 and 107 regulate insulin sensitivity. Nature 2011; 474: 649–653.
Jordan SD, Krüger M, Willmes DM, Redemann N, Wunderlich FT, Brönneke HS et al. Obesity-induced overexpression of miRNA-143 inhibits insulin-stimulated AKT activation and impairs glucose metabolism. Nat Cell Biol 2011; 13: 434–448.
Taniguchi CM, Emanuelli B, Kahn CR . Critical nodes in signalling pathways: insights into insulin action. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2006; 7: 85–96.
Hulsmans M, Holvoet P . MicroRNAs as early biomarkers in obesity and related metabolic and cardiovascular diseases. Curr Pharm Des 2013; 19: 5704–5717.
Mühlhäusler BS, Adam CL, Findlay PA, Duffield JA, McMillen IC . Increased maternal nutrition alters development of the appetite-regulating network in the brain. FASEB J 2006; 20: 1257–1259.
Mühlhäusler BS, Duffield JA, McMillen IC . Increased maternal nutrition stimulates peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-γ, adiponectin, and leptin messenger ribonucleic acid expression in adipose tissue before birth. Endocrinology 2007; 148: 878–885.
Mühlhäusler BS, Roberts CT, Yuen BSJ, Marrocco E, Budge H, Symonds ME et al. Determinants of fetal leptin synthesis, fat mass, and circulating leptin concentrations in well-nourished ewes in late pregnancy. Endocrinology 2003; 144: 4947–4954.
Mühlhäusler BS, Duffield JA, McMillen IC . Increased maternal nutrition increases leptin expression in perirenal and subcutaneous adipose tissue in the postnatal lamb. Endocrinology 2007; 148: 6157–6163.
Rattanatray L, Muhlhausler BS, Nicholas LM, Morrison JL, McMillen IC . Impact of maternal overnutrition on gluconeogenic factors and methylation of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase promoter in the fetal and postnatal liver. Pediatr Res 2014; 75: 14–21.
Kral JG . Preventing and treating obesity in girls and young women to curb the epidemic. Obes Res 2004; 12: 1539–1546.
Birdsall KM, Vyas S, Khazaezadeh N, Oteng-Ntim E . Maternal obesity: a review of interventions. Int J Clin Pract 2009; 63: 494–507.
Dodd JM, Crowther CA, Robinson JS . Dietary and lifestyle interventions to limit weight gain during pregnancy for obese or overweight women: a systematic review. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2008; 87: 702–706.
Ronnberg AK, Nilsson K . Interventions during pregnancy to reduce excessive gestational weight gain: a systematic review assessing current clinical evidence using the Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) system. BJOG 2010; 117: 1327–1334.
Sui Z, Dodd JM . Exercise in obese pregnant women: positive impacts and current perceptions. Int J Womens Health 2013; 5: 389–398.
Patti ME . Reducing maternal weight improves offspring metabolism and alters (or modulates) methylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2013; 110: 12859–12860.
Dalfrà MG, Busetto L, Chilelli NC, Lapolla A . Pregnancy and foetal outcome after bariatric surgery: a review of recent studies. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2012; 25: 1537–1543.
Barisione M, Carlini F, Gradaschi R, Camerini G, Adami GF . Body weight at developmental age in siblings born to mothers before and after surgically induced weight loss. Surg Obes Relat Dis 2012; 8: 387–391.
Kral JG, Biron S, Simard S, Hould FS, Lebel S, Marceau S et al. Large maternal weight loss from obesity surgery prevents transmission of obesity to children who were followed for 2 to 18 years. Pediatrics 2006; 118: e1644–e1649.
Guénard F, Deshaies Y, Cianflone K, Kral JG, Marceau P, Vohl MC . Differential methylation in glucoregulatory genes of offspring born before vs. after maternal gastrointestinal bypass surgery. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2013; 110: 11439–11444.
Zambrano E, Martínez-Samayoa PM, Rodríguez-González GL, Nathanielsz PW . Dietary intervention prior to pregnancy reverses metabolic programming in male offspring of obese rats. J Physiol 2010; 588: 1791–1799.
Vega CC, Reyes-Castro LA, Bautista CJ, Larrea F, Nathanielsz PW, Zambrano E . Exercise in obese female rats has beneficial effects on maternal and male and female offspring metabolism. Int J Obes (Lond) 2015; 39: 712–719.
Raipuria M, Bahari H, Morris MJ . Effects of maternal diet and exercise during pregnancy on glucose metabolism in skeletal muscle and fat of weanling rats. PLoS One 2015; 10: e0120980.
De Rooij SR, Painter RC, Phillips DIW, Osmond C, Michels RPJ, Godsland IF et al. Impaired insulin secretion after prenatal exposure to the Dutch famine. Diabetes Care 2006; 29: 1897–1901.
Smith NA, McAuliffe FM, Quinn K, Lonergan P, Evans ACO . The negative effects of a short period of maternal undernutrition at conception on the glucose-insulin system of offspring in sheep Anim Reprod Sci 121: 94–100.
Todd SE, Oliver MH, Jaquiery AL, Bloomfield FH, Harding JE . Periconceptional undernutrition of ewes impairs glucose tolerance in their adult offspring. Pediatr Res 2009; 65: 409–413.
Lee RSF, Depree KM, Davey HW . The sheep (Ovis aries) H19 gene: genomic structure and expression patterns, from the preimplantation embryo to adulthood. Gene 2002; 301: 67–77.
Stanford KI, Lee MY, Getchell KM, So K, Hirshman MF, Goodyear LJ . Exercise before and during pregnancy prevents the deleterious effects of maternal high-fat feeding on metabolic health of male offspring. Diabetes 2014; 64: 427–433.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nicholas, L., Morrison, J., Rattanatray, L. et al. The early origins of obesity and insulin resistance: timing, programming and mechanisms. Int J Obes 40, 229–238 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2015.178
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2015.178
This article is cited by
-
The impact of social determinants of health on obesity and diabetes disparities among Latino communities in Southern California
BMC Public Health (2023)
-
PFAS concentrations in early and mid-pregnancy and risk of gestational diabetes mellitus in a nested case-control study within the ethnically and racially diverse PETALS cohort
BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth (2023)
-
Maternal cardiovascular disorders before and during pregnancy and offspring cardiovascular risk across the life course
Nature Reviews Cardiology (2023)
-
Frühkindliche Einflüsse auf das Körpergewicht
Info Diabetologie (2023)
-
Parental high-fat high-sugar diet programming and hypothalamus adipose tissue axis in male Wistar rats
European Journal of Nutrition (2022)