Abstract
Objectives:
To review child and adolescent obesity prevention programmes to determine whether they have included the Social Marketing Benchmark Criteria (BC). In addition, we analysed whether there was a relationship between the presence of the criteria and the effectiveness of the programme.
Methods:
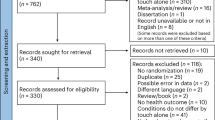
Interventions had to be aimed at preventing obesity through behaviour changes relating to diet, physical activity, lifestyle and social support, separately or in combination. A total of 41 interventions were identified in PubMed and Embase that fulfilled the inclusion criteria.
Results:
The more recent the studies, the greater the number of the BC that seem to have been used. However, regarding behaviour changes, we found the most effective period to be 1997–2002, with 100% of the interventions resulting in behaviour changes (9/9). In addition, almost all interventions resulted in improvements in body composition variables: 5 of 6 for body mass index or overweight/obesity prevalence and 6 of 6 for skin-folds.
Conclusions:
The presence of a higher number of BC does not assure higher effectiveness. Further research is required in this field. At the moment, studies aimed at preventing obesity in children and adolescents have not included social marketing aspects in their interventions in a comprehensive manner.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gracia-Marco L, Vicente-Rodríguez G, Rey-López J, España-Romero V, Moreno L . Energy metabolism and childhood obesity development. In: Child Nutrition Physiology. Nova Biomedical: New York 2009; pp 245–255.
Dietz WH . Health consequences of obesity in youth: childhood predictors of adult disease. Pediatrics 1998; 101 (3 Part 2): 518–525.
Troiano RP, Berrigan D, Dodd KW, Masse LC, Tilert T, McDowell M . Physical activity in the United States measured by accelerometer. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2008; 40: 181–188.
Summerbell CD, Waters E, Edmunds LD, Kelly S, Brown T, Campbell KJ . Interventions for preventing obesity in children. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2005; 20: CD001871.
Doak CM, Visscher TL, Renders CM, Seidell JC . The prevention of overweight and obesity in children and adolescents: a review of interventions and programmes. Obes Rev 2006; 7: 111–136.
Kotler P, Zaltman G . Social marketing: an approach to planned social change. J Mark 1971; 35: 3–12.
Henley N, Raffin S . Social marketing to prevent childhood obesity: The EPODE Program. In: Waters E, Swinburn B, Seidell J, Uauy R (eds). Wiley-Blackwell: Chichester 2010. pp 243–252.
Donovan R, Henley N . Social Marketing: Principles and Practice. IP Communications: Melbourne, 2003.
Hastings G . Ten promises to Terry: towards a social marketing manifesto. Soc Mar Q 2006; 12: 59–62.
Hastings G, Saren M . The critical contribution of social marketing. Mar Theory 2003; 3: 305–322.
Stead M, Hastings G, McDermott L . The meaning, effectiveness and future of social marketing. Obes Rev 2007; 8 (Suppl 1): 189–193.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Communication at CDC, Practice Areas: Social Marketing, [WWW document] In Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2005, USA (Accessed August 2009).
Department of Health. Choosing health. Making Healthier Choices Easier. In: Public Health White Paper, Series No. CM 6374. The Stationery Office: London, 2004.
Change4Life Campaign. Available from http://www.nhs.uk/Change4life/Pages/Default.aspx (Accessed February 2010).
French J, Blair-Stevens C . Social Marketing National Benchmark Criteria. UK National Social Marketing Centre: UK, 2006.
Westley H . Thin living. BMJ 2007; 335: 1236–1237.
Romon M, Lommez A, Tafflet M, Basdevant A, Oppert JM, Bresson JL et al. Downward trends in the prevalence of childhood overweight in the setting of 12-year school- and community-based programmes. Public Health Nutr 2009; 12: 1735–1742.
Andreasen A . Social marketing in the social change marketplace. J Publ Pol Market 2002; 21: 3–13.
Tamir D, Feurstein A, Brunner S, Halfon ST, Reshef A, Palti H . Primary prevention of cardiovascular diseases in childhood: changes in serum total cholesterol, high density lipoprotein, and body mass index after 2 years of intervention in Jerusalem schoolchildren age 7–9 years. Prev Med 1990; 19: 22–30.
Flores R . Dance for health: improving fitness in African American and Hispanic adolescents. Public Health Rep 1995; 110: 189–193.
Vandongen R, Jenner DA, Thompson C, Taggart AC, Spickett EE, Burke V et al. A controlled evaluation of a fitness and nutrition intervention program on cardiovascular health in 10- to 12-year-old children. Prev Med 1995; 24: 9–22.
Donnelly JE, Jacobsen DJ, Whatley JE, Hill JO, Swift LL, Cherrington A et al. Nutrition and physical activity program to attenuate obesity and promote physical and metabolic fitness in elementary school children. Obes Res 1996; 4: 229–243.
Harrell JS, McMurray RG, Bangdiwala SI, Frauman AC, Gansky SA, Bradley CB . Effects of a school-based intervention to reduce cardiovascular disease risk factors in elementary-school children: the Cardiovascular Health in Children (CHIC) study. J Pediatr 1996; 128: 797–805.
Luepker RV, Perry CL, McKinlay SM, Nader PR, Parcel GS, Stone EJ et al. Outcomes of a field trial to improve children's dietary patterns and physical activity. The Child and Adolescent Trial for Cardiovascular Health. CATCH collaborative group. JAMA 1996; 275: 768–776.
Webber LS, Osganian SK, Feldman HA, Wu M, McKenzie TL, Nichaman M et al. Cardiovascular risk factors among children after a 2 1/2-year intervention-The CATCH Study. Prev Med 1996; 25: 432–441.
Stolley MR, Fitzgibbon ML . Effects of an obesity prevention program on the eating behavior of African American mothers and daughters. Health Educ Behav 1997; 24: 152–164.
Mo-suwan L, Pongprapai S, Junjana C, Puetpaiboon A . Effects of a controlled trial of a school-based exercise program on the obesity indexes of preschool children. Am J Clin Nutr 1998; 68: 1006–1011.
Nader PR, Stone EJ, Lytle LA, Perry CL, Osganian SK, Kelder S et al. Three-year maintenance of improved diet and physical activity: the CATCH cohort. Child and Adolescent Trial for Cardiovascular Health. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 1999; 153: 695–704.
Robinson TN . Reducing children's television viewing to prevent obesity: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 1999; 282: 1561–1567.
Manios Y, Kafatos A, Mamalakis G . The effects of a health education intervention initiated at first grade over a 3 year period: physical activity and fitness indices. Health Educ Res 1998; 13: 593–606.
Gortmaker SL, Peterson K, Wiecha J, Sobol AM, Dixit S, Fox MK et al. Reducing obesity via a school-based interdisciplinary intervention among youth: Planet Health. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 1999; 153: 409–418.
Epstein LH, Gordy CC, Raynor HA, Beddome M, Kilanowski CK, Paluch R . Increasing fruit and vegetable intake and decreasing fat and sugar intake in families at risk for childhood obesity. Obes Res 2001; 9: 171–178.
McKenzie TL, Stone EJ, Feldman HA, Epping JN, Yang M, Strikmiller PK et al. Effects of the CATCH physical education intervention: teacher type and lesson location. Am J Prev Med 2001; 21: 101–109.
Muller MJ, Asbeck I, Mast M, Langnase K, Grund A . Prevention of obesity—more than an intention. Concept and first results of the Kiel Obesity Prevention Study (KOPS). Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2001; 25 (Suppl 1): S66–S74.
Rodgers DV, Johnson SR, Tschann JM, Chesterman EA, Mellin LM . The evaluation of a school-based obesity program. Research Just for Kids. Balboa Publishing Corporation: San Anselmo, CA, USA, 2001.
Sahota P, Rudolf MC, Dixey R, Hill AJ, Barth JH, Cade J . Randomised controlled trial of primary school based intervention to reduce risk factors for obesity. BMJ 2001; 323: 1029–1032.
Sahota P, Rudolf MC, Dixey R, Hill AJ, Barth JH, Cade J . Evaluation of implementation and effect of primary school based intervention to reduce risk factors for obesity. BMJ 2001; 323: 1027–1029.
McMurray RG, Harrell JS, Bangdiwala SI, Bradley CB, Deng S, Levine A . A school-based intervention can reduce body fat and blood pressure in young adolescents. J Adolesc Health 2002; 31: 125–132.
Caballero B, Clay T, Davis SM, Ethelbah B, Rock BH, Lohman T . et al. Pathways: a school-based, randomized controlled trial for the prevention of obesity in American Indian schoolchildren. Am J Clin Nutr 2003; 78: 1030–1038.
Baranowski T, Baranowski JC, Cullen KW, Thompson DI, Nicklas T, Zakeri IE et al. The Fun, Food, and Fitness Project (FFFP): the Baylor GEMS pilot study. Ethn Dis 2003; 13 (1 Suppl 1): S30–S39.
Beech BM, Klesges RC, Kumanyika SK, Murray DM, Klesges L, McClanahan B et al. Child- and parent-targeted interventions: the Memphis GEMS pilot study. Ethn Dis 2003; 13 (1 Suppl 1): S40–S53.
Harvey-Berino J, Rourke J . Obesity prevention in preschool native-American children: a pilot study using home visiting. Obes Res 2003; 11: 606–611.
Neumark-Sztainer D, Story M, Hannan PJ, Rex J . New Moves: a school-based obesity prevention program for adolescent girls. Prev Med 2003; 37: 41–51.
Pangrazi RP, Beighle A, Vehige T, Vack C . Impact of Promoting Lifestyle Activity for Youth (PLAY) on children's physical activity. J Sch Health 2003; 73: 317–321.
Robinson TN, Killen JD, Kraemer HC, Wilson DM, Matheson DM, Haskell WL et al. Dance and reducing television viewing to prevent weight gain in African-American girls: the Stanford GEMS pilot study. Ethn Dis 2003; 13 (1 Suppl 1): S65–S77.
Sallis JF, McKenzie TL, Conway TL, Elder JP, Prochaska JJ, Brown M et al. Environmental interventions for eating and physical activity: a randomized controlled trial in middle schools. Am J Prev Med 2003; 24: 209–217.
Story M, Sherwood NE, Himes JH, Davis M, Jacobs Jr DR, Cartwright Y et al. An after-school obesity prevention program for African-American girls: the Minnesota GEMS pilot study. Ethn Dis 2003; 13 (1 Suppl 1): S54–S64.
Warren JM, Henry CJ, Lightowler HJ, Bradshaw SM, Perwaiz S . Evaluation of a pilot school programme aimed at the prevention of obesity in children. Health Promot Int 2003; 18: 287–296.
Dennison BA, Russo TJ, Burdick PA, Jenkins PL . An intervention to reduce television viewing by preschool children. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 2004; 158: 170–176.
James J, Thomas P, Cavan D, Kerr D . Preventing childhood obesity by reducing consumption of carbonated drinks: cluster randomised controlled trial. BMJ 2004; 328: 1237.
Kain J, Uauy R, Albala, Vio F, Cerda R, Leyton B . School-based obesity prevention in Chilean primary school children: methodology and evaluation of a controlled study. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2004; 28: 483–493.
Johnson SL, Bellows L, Beckstrom L, Anderson J . Evaluation of a social marketing campaign targeting preschool children. Am J Health Behav 2007; 31: 44–55.
Evans WD, Necheles J, Longjohn M, Christoffel KK . The 5-4-3-2-1 go! Intervention: social marketing strategies for nutrition. J Nutr Educ Behav 2007; 39 (2 Suppl): S55–S59.
Bellows L, Anderson J, Gould SM, Auld G . Formative research and strategic development of a physical activity component to a social marketing campaign for obesity prevention in preschoolers. J Community Health 2008; 33: 169–178.
Eisenmann JC, Gentile DA, Welk GJ, Callahan R, Strickland S, Walsh M et al. SWITCH: rationale, design, and implementation of a community, school, and family-based intervention to modify behaviors related to childhood obesity. BMC Public Health 2008; 8: 223.
Foster GD, Sherman S, Borradaile KE, Grundy KM, Vander Veur SS, Nachmani J et al. A policy-based school intervention to prevent overweight and obesity. Pediatrics 2008; 121: e794–e802.
Price SM, Huhman M, Potter LD . Influencing the parents of children aged 9–13 years: findings from the VERB campaign. Am J Prev Med 2008; 34 (6 Suppl): S267–S274.
Sanigorski AM, Bell AC, Kremer PJ, Cuttler R, Swinburn BA . Reducing unhealthy weight gain in children through community capacity-building: results of a quasi-experimental intervention program, Be Active Eat Well. Int J Obes (Lond) 2008; 32: 1060–1067.
Acknowledgements
EPODE European Network Study Group: Zaragoza University (Spain), Proteines (France), Free University of Amsterdam (The Netherlands), Gent University (Belgium), Lille 2 University (France) and Fleurbaix Laventie Ville Santé NGO (France). Grants: Directorate General for Health and Consumers (European Commission, Agreement 2007 327). EEN Private Partners: Ferrero International, Mars, Nestlé S.A, Orangina-Schweppes Group.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gracia-Marco, L., Vicente-Rodríguez, G., Borys, J. et al. Contribution of social marketing strategies to community-based obesity prevention programmes in children. Int J Obes 35, 472–479 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2010.221
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2010.221
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Community coalition efforts to prevent childhood obesity: two-year results of the Shape Up Under 5 study
BMC Public Health (2023)
-
Tools for a systematic appraisal of integrated community-based approaches to prevent childhood obesity
BMC Public Health (2018)
-
A youth-led social marketing intervention to encourage healthy lifestyles, the EYTO (European Youth Tackling Obesity) project: a cluster randomised controlled0 trial in Catalonia, Spain
BMC Public Health (2015)
-
Design of CIAO, a research program to support the development of an integrated approach to prevent overweight and obesity in the Netherlands
BMC Obesity (2014)
-
Effects of an intervention aimed at reducing the intake of sugar-sweetened beverages in primary school children: a controlled trial
International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity (2014)