Abstract
Objective:
The expanding overweight and obesity epidemic notwithstanding, little is known about their long-term effect on health-related quality of life (HRQoL). The main objective of this study was to investigate whether overweight (body mass index (BMI) 25 to <30 kg m−2) and obese (BMI ⩾30 kg m−2) young adults have poorer HRQoL 20 years later.
Methods:
We studied 3014 participants in the Coronary Artery Risk Development in Young Adults (CARDIA) study, a longitudinal, community-dwelling, biracial cohort from four cities. BMI was measured at baseline and 20 years later. HRQoL was assessed by the Physical Component Summary (PCS) and the Mental Component Summary (MCS) scores of the Medical Outcomes Study 12-Item Short-Form Health Survey at year 20. Higher PCS or MCS scores indicate better HRQoL.
Results:
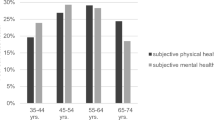
Mean year 20 PCS score was 52.2 for normal weight participants at baseline, 50.3 for overweight and 46.4 for obese (P-trend <0.001). This relation persisted after adjustment for baseline demographics, general health, and physical and behavioral risk factors and after further adjustment for 20-year changes in risk factors. No association was observed for MCS scores (P-trend 0.43).
Conclusion:
Overweight and obesity in early adulthood are adversely associated with self-reported physical HRQoL, but not mental HRQoL 20 years later.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others

References
Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Curtin LR, McDowell MA, Tabak CJ, Flegal KM . Prevalence of overweight and obesity in the United States, 1999–2004. JAMA 2006; 295: 1549–1555.
Flegal KM . Epidemiologic aspects of overweight and obesity in the United States. Physiol Behav 2005; 86: 599–602.
Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Ogden CL, Johnson CL . Prevalence and trends in obesity among US adults, 1999–2000. JAMA 2002; 288: 1723–1727.
Kopelman P . Health risks associated with overweight and obesity. Obes Rev 2007; 8 (Suppl): 13–17.
Mokdad AH, Ford ES, Bowman BA, Dietz WH, Vinicor F, Bales VS et al. Prevalence of obesity, diabetes, and obesity-related health risk factors, 2001. JAMA 2003; 289: 76–79.
Flegal KM, Graubard BI, Williamson DF, Gail MH . Excess deaths associated with underweight, overweight, and obesity. JAMA 2005; 293: 1861–1867.
Finkelstein E, Ruhm C, Kosa K . Economic causes and consequences of obesity. Annu Rev Public Health 2005; 26: 239–257.
Medicine Io. Crossing the Quality Chasm: A New Health System for the 21st Century. National Academy Press: Washington, DC, 2001.
Fontaine KR, Cheskin LJ, Barofsky I . Health-related quality of life in obese persons seeking treatment. J Fam Pract 1996; 43: 265–270.
Damush TM, Stump TE, Clark DO . Body-mass index and 4-year change in health-related quality of life. J Aging Health 2002; 14: 195–210.
Ferraro KF, Su YP, Gretebeck RJ, Black DR, Badylak SF . Body mass index and disability in adulthood: a 20-year panel study. Am J Public Health 2002; 92: 834–840.
Daviglus ML, Liu K, Yan LL, Pirzada A, Garside DB, Schiffer L et al. Body mass index in middle age and health-related quality of life in older age: the Chicago Heart Association Detection Project in Industry Study. Arch Intern Med 2003; 163: 2448–2455.
Friedman GD, Cutter GR, Donahue RP, Hughes GH, Hulley SB, Jacobs Jr DR et al. CARDIA: study design, recruitment, and some characteristics of the examined subjects. J Clin Epidemiol 1988; 41: 1105–1116.
Ware Jr J, Kosinski M, Keller SD . A 12-Item Short-Form Health Survey: construction of scales and preliminary tests of reliability and validity. Med Care 1996; 34: 220–233.
National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism. Helping Patients Who Drink Too Much: A Clinician's Guide. National Institutes of Health: Rockville, MD, 2005.
Jacobs Jr DR, Hahn L, Haskell W, Pirie P, Sidney S . Validity and reliability of short physical activity history: CARDIA and the Minnesota Heart Health Program. J Cardiopulm Rehabil 1989; 9: 448–459.
Robins J, Rotnitzky A, Zhao L . Analysis of semiparametric regression models for repeated outcomes in the presence of missing data. J Am Stat Assoc 1995; 90: 106–129.
Yancy Jr WS, Olsen MK, Westman EC, Bosworth HB, Edelman D . Relationship between obesity and health-related quality of life in men. Obes Res 2002; 10: 1057–1064.
Larsson U, Karlsson J, Sullivan M . Impact of overweight and obesity on health-related quality of life—a Swedish population study. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2002; 26: 417–424.
Hopman WM, Berger C, Joseph L, Barr SI, Gao Y, Prior JC et al. The association between body mass index and health-related quality of life: data from CaMos, a stratified population study. Qual Life Res 2007; 16: 1595–1603.
Singer MA, Hopman WM, MacKenzie TA . Physical functioning and mental health in patients with chronic medical conditions. Qual Life Res 1999; 8: 687–691.
Lopez-Garcia E, Banegas Banegas JR, Gutierrez-Fisac JL, Perez-Regadera AG, Ganan LD, Rodriguez-Artalejo F . Relation between body weight and health-related quality of life among the elderly in Spain. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord Jun 2003; 27: 701–709.
Acknowledgements
Dr Andrea Kozak's work on this article was supported in part by the National Institutes of Health T32 Postdoctoral Fellowship in Cardiovascular Epidemiology and Prevention (5-T32-HL069771-04). The work of Cheeling Chan and Dr Martha Daviglus, Dr Kiang Liu, Dr Catarina Kiefe and Dr David Jacobs was supported in part by National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute contracts N01-HC-48047, N01-HC-48048, N01-HC-48049, N01-HC-48050 and N01-HC-95095 (CARDIA study).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kozak, A., Daviglus, M., Chan, C. et al. Relationship of body mass index in young adulthood and health-related quality of life two decades later: the Coronary Artery Risk Development in Young Adults study. Int J Obes 35, 134–141 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2010.120
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2010.120
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Night eating syndrome subtypes: differences in binge eating and food addiction symptoms
Eating and Weight Disorders - Studies on Anorexia, Bulimia and Obesity (2023)
-
Project STARLIT: protocol of a longitudinal study of habitual sleep trajectories, weight gain, and obesity risk behaviors in college students
BMC Public Health (2019)
-
Sleep, Depressive/Anxiety Disorders, and Obesity in Puerto Rican Youth
Journal of Clinical Psychology in Medical Settings (2017)
-
Overweight and obesity epidemic in Ghana—a systematic review and meta-analysis
BMC Public Health (2016)
-
Population-based survey of overweight and obesity and the associated factors in peri-urban and rural Eastern Uganda
BMC Public Health (2015)