Abstract
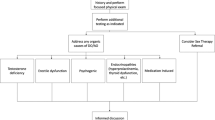
To estimate the prevalence of erectile dysfunction (ED) and the level of psychological distress and to assess the inter-associations of them among type 2 diabetic men, a cross-sectional observational study of 335 men with type 2 diabetes and 284 men without diabetes from a hospital in Hefei city, Anhui province, China, was conducted. The erectile function was assessed using the five-item version of the International Index of Erectile Function scale (IIEF-5). The evaluation of psychological distress was completed using a self-administered questionnaire, the Symptom Checklist 90–Revised (SCL-90-R). In this study, ED was more prevalent in type 2 diabetic men than that in the control group (58.51% vs 26.76%, P<0.001). All subscale scores of SCL-90-R were significantly higher in the group with type 2 diabetes (N=335) than those in the group without type 2 diabetes (N=284). All scores of SCL-90-R subscales were inversely correlated with IIEF-5 score. ED and psychological distress were strongly correlated in type 2 diabetic patients. Clinicians should be aware of the association between ED and psychological distress when treating men with type 2 diabetes.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 8 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $32.38 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wild S, Roglic G, Green A, Sicree R, King H . Global prevalence of diabetes: estimates for the year 2000 and projections for 2030. Diabetes Care 2004; 27: 1047–1053.
NIH Consensus Conference. Impotence. NIH Consensus Development Panel on Impotence. JAMA 1993; 270: 83–90.
Defeudis G, Gianfrilli D, Di Emidio C, Pofi R, Tuccinardi D, Palermo A et al. Erectile dysfunction and its management in patients with diabetes mellitus. Rev Endocr Metab Disord 2015; 16: 1–19.
Malavige LS, Jayaratne SD, Kathriarachchi ST, Sivayogan S, Fernando DJ, Levy JC . Erectile dysfunction among men with diabetes is strongly associated with premature ejaculation and reduced libido. J Sex Med 2008; 5: 2125–2134.
Feldman HA, Goldstein I, Hatzichristou DG, Krane RJ, McKinlay JB . Impotence and its medical and psychosocial correlates: results of the Massachusetts Male Aging Study. J Urol 1994; 151: 54–61.
Corona G, Mannucci E, Mansani R, Petrone L, Bartolini M, Giommi R et al. Organic, relational and psychological factors in erectile dysfunction in men with diabetes mellitus. Eur Urol 2004; 46: 222–228.
Egede LE, Dismuke CE . Serious psychological distress and diabetes: a review of the literature. Curr Psychiatry Rep 2012; 14: 15–22.
Domingo AK, Asmal L, Seedat S, Esterhuizen TM, Laurence C, Volmink J . Investigating the association between diabetes mellitus, depression and psychological distress in a cohort of South African teachers. S Afr Med J 2015; 105: 1057–1060.
Shin JK, Chiu YL, Choi S, Cho S, Bang H . Serious psychological distress, health risk behaviors, and diabetes care among adults with type 2 diabetes: the California Health Interview Survey 2007. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2012; 95: 406–414.
Dismuke CE, Hernandez-Tejada MA, Egede LE . Relationship of serious psychological distress to quality of life in adults with diabetes. Int J Psychiatry Med 2014; 48: 135–146.
Rubin RR, Peyrot M . Quality of life and diabetes. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 1999; 15: 205–218.
Sadovsky R . The role of the primary care clinician in the management of erectile dysfunction. Rev Urol 2002; 4 (Suppl 3): S54–S63.
Malavige LS, Jayaratne SD, Kathriarachchi ST, Sivayogan S, Ranasinghe P, Levy JC . Erectile dysfunction is a strong predictor of poor quality of life in men with Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabet Med 2014; 31: 699–706.
Schiavi RC, Stimmel BB, Mandeli J, Schreiner-Engel P, Ghizzani A . Diabetes, psychological function and male sexuality. J Psychosom Res 1995; 39: 305–314.
De Berardis G, Pellegrini F, Franciosi M, Belfiglio M, Di Nardo B, Greenfield S et al. Identifying patients with type 2 diabetes with a higher likelihood of erectile dysfunction: the role of the interaction between clinical and psychological factors. J Urol 2003; 169: 1422–1428.
De Berardis G, Pellegrini F, Franciosi M, Belfiglio M, Di Nardo B, Greenfield S et al. Clinical and psychological predictors of incidence of self-reported erectile dysfunction in patients with type 2 diabetes. J Urol 2007; 177: 252–257.
American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 2005; 28 (Suppl 1): S37–S42.
Rosen RC, Cappelleri JC, Smith MD, Lipsky J, Pena BM . Development and evaluation of an abridged, 5-item version of the International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF-5) as a diagnostic tool for erectile dysfunction. Int J Impot Res 1999; 11: 319–326.
Bloom CA, Labato MA, Hazarika S, Court MH . Preliminary pharmacokinetics and cardiovascular effects of fenoldopam continuous rate infusion in six healthy dogs. J Vet Pharmacol Ther 2012; 35: 224–230.
Ruis C, van den Berg E, van Stralen HE, Huenges Wajer IM, Biessels GJ, Kappelle LJ et al. Symptom Checklist 90-Revised in neurological outpatients. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol 2014; 36: 170–177.
Derogatis LR, Rickels K, Rock AF . The SCL-90 and the MMPI: a step in the validation of a new self-report scale. Br J Psychiatry 1976; 128: 280–289.
Tan H, Lan XM, Yu NL, Yang XC . Reliability and validity assessment of the revised Symptom Checklist 90 for alopecia areata patients in China. J Dermatol 2015; 42: 975–980.
Yu LW, Kong AP, Tong PC, Tam C, Ko GT, Ho CS et al. Evaluation of erectile dysfunction and associated cardiovascular risk using structured questionnaires in Chinese type 2 diabetic men. Int J Androl 2010; 33: 853–860.
Kirby M, Jackson G, Simonsen U . Endothelial dysfunction links erectile dysfunction to heart disease. Int J Clin Pract 2005; 59: 225–229.
Mota M, Lichiardopol C, Mota E, Panus C, Panus A . Erectile dysfunction in diabetes mellitus. Rom J Intern Med 2003; 41: 163–177.
Sasaki H, Yamasaki H, Ogawa K, Nanjo K, Kawamori R, Iwamoto Y et al. Prevalence and risk factors for erectile dysfunction in Japanese diabetics. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2005; 70: 81–89.
Zheng H, Fan W, Li G, Tam T . Predictors for erectile dysfunction among diabetics. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2006; 71: 313–319.
Lustman PJ, Griffith LS, Clouse RE, Cryer PE . Psychiatric illness in diabetes mellitus. Relationship to symptoms and glucose control. J Nerv Ment Dis 1986; 174: 736–742.
Ali S, Stone MA, Peters JL, Davies MJ, Khunti K . The prevalence of co-morbid depression in adults with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabet Med 2006; 23: 1165–1173.
McDade-Montez EA, Watson D . Examining the potential influence of diabetes on depression and anxiety symptoms via multiple sample confirmatory factor analysis. Ann Behav Med 2011; 42: 341–351.
Gao J, Zhang X, Su P, Liu J, Shi K, Hao Z et al. Relationship between sexual dysfunction and psychological burden in men with infertility: a large observational study in China. J Sex Med 2013; 10: 1935–1942.
Aghighi A, Grigoryan VH, Delavar A . Psychological determinants of erectile dysfunction among middle-aged men. Int J Impot Res 2015; 27: 63–68.
Mallis D, Moysidis K, Nakopoulou E, Papaharitou S, Hatzimouratidis K, Hatzichristou D . Psychiatric morbidity is frequently undetected in patients with erectile dysfunction. J Urol 2005; 174: 1913–1916.
Siddiqui MA, Peng B, Shanmugam N, Yeo W, Fook-Chong S, Li Tat JC et al. Erectile dysfunction in young surgically treated patients with lumbar spine disease: a prospective follow-up study. Spine 2012; 37: 797–801.
Shamloul R, Ghanem H . Erectile dysfunction. Lancet 2013; 381: 153–165.
Zavoreo I, Madzar Z, Demarin V, Kes VB . Vascular cognitive impairment in diabetes mellitus: are prevention and treatment effective? Acta Clin Croat 2014; 53: 326–333.
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Fund 81501244.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, S., Peng, D., Xu, X. et al. Assessment of erectile dysfunction and associated psychological distress in Chinese men with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int J Impot Res 29, 210–214 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijir.2017.25
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijir.2017.25
This article is cited by
-
Association between erectile dysfunction and subjective well-being in primary care patients with type 2 diabetes
Diabetology International (2024)
-
Effects of ozone treatment on penile erection capacity and nitric oxide synthase levels in diabetic rats
International Journal of Impotence Research (2021)
-
The Complex Relationship Between Erectile Dysfunction and Hypogonadism in Diabetes Mellitus
Current Sexual Health Reports (2019)