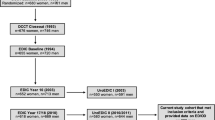
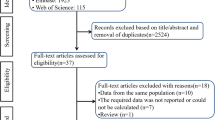
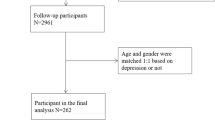
Abstract
In several studies of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, a positive association between depressive symptoms and erectile dysfunction (ED) has been reported. No evidence exists, however, regarding the association between depressive symptoms and ED among Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Thus, we examined this issue among Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Study subjects were 469 male Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, aged 19 years or over. ED, moderate to severe ED and severe ED were defined as present when a subject had a Sexual Health Inventory for Men score <22, <12 and <8, respectively. Depressive symptoms were defined as present when a subject had a Self-Rating Depression Scale (SDS) score >49. Adjustment was made for age, body mass index, waist, duration of type 2 diabetes, current smoking, current drinking, hypertension, dyslipidemia, coronary artery disease, stroke, glycated hemoglobin and diabetic neuropathy. The prevalence values of depressive symptoms, moderate to severe ED and severe ED were 15.1%, 64.2% and 51.0%, respectively. Depressive symptoms were independently positively associated with moderate to severe ED and severe ED (adjusted odds ratios were 2.23 (95% confidence interval (CI): 1.17–4.43) and 1.86 (95% CI: 1.04–3.41), respectively). In Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, depressive symptoms may be associated with ED.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 8 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $32.38 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson RJ, Freedland KE, Clouse RE, Lustman PJ . The prevalence of comorbid depression in adults with diabetes: a meta-analysis. Diabetes Care 2001; 24: 1069–1078.
Malavige LS, Levy LC . Erectile dysfunction in diabetes mellitus. J Sex Med 2009; 6: 1232–1247.
Egede LE, Ellis C . Diabetes and depression: global perspectives. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2010; 87: 302–312.
Penson DF, Latini DM, Lubeck DP, Wallace KL, Henning JM, Lue TF et al. Do impotent men with diabetes have more severe erectile dysfunction and worse quality of life than the general population of impotent patients? Results from the Exploratory Comprehensive Evaluation of Erectile Dysfunction (ExCEED) database. Diabetes Care 2003; 26: 1093–1099.
Song HJ, Lee EJ, Bergstrom N, Kang DH, Lee DH, Koh G et al. Lower urinary tract symptoms and erectile dysfunction in men with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int Neurourol J 2013; 17: 180–185.
Shiri R, Ansari M, Falah Hassani K . Association between comorbidity and erectile dysfunction in patients with diabetes. Int J Impot Res 2006; 18: 348–353.
Niraula K, Kohrt BA, Flora MS, Thapa N, Mumu SJ, Pathak R et al. Prevalence of depression and associated risk factors among persons with type 2 diabetes mellitus without a prior psychiatric history: a cross-sectional study in clinical setting in urban Nepal. BMC Psychiatry 2013; 13: 309.
Giugliano F, Maiorino M, Bellastella G, Gicchino M, Giugliano D, Esposito K . Determinants of erectile dysfunction in type 2 diabetes. Int J Impot Res 2010; 22: 204–209.
Corona G, Giorda CB, Cucinotta D, Guida P, Nada E, SUBITO-DE study group. The SUBITO-DE study: sexual dysfunction is newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes male patients. J Endcocrinol Invest 2013; 36: 864–868.
Derosa G, Romano D, Tinelli C, D’Angelo A, Maffioli P . Prevalence and associations of erectile dysfunction in a sample of Italian male with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2015; 108: 329–335.
Furukawa S, Sakai T, Niiya T, Miyaoka H, Yamamoto S, Maruyama K et al. Nocturia and prevalence of erectile dysfunction in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: the Dogo Study. J Diabetes Investig 2016; 7: 786–790.
Furukawa S, Sakai T, Niiya T, Miyaoka H, Yamamoto S, Maruyama K et al. Microvasuclar complicaiions and prevalence of urgency incontinence in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: the Dogo Study. Neurourol Urodyn 2015; 35: 1024–1027.
Furukawa S, Sakai T, Niiya T, Miyaoka H, Yamamoto S, Maruyama K et al. Microvasuclar complicaiions and prevalence of nocturia in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: the Dogo Study. Urology 2016; 93: 147–151.
Haneda M, Utsunomiya K, Koya D, Babazono T, Moriya T, Makino H et al. A new classification of diabetic nephropathy 2014: a report from joint committee on diabetic nephropathy. J Diabetes Investig 2014; 6: 242–246.
Matsuo S, Imai E, Horio M, Yasuda Y, Tomita K, Nitta K et al. Revised equations for estimated GFR from serum creatinine in Japan. Am J Kidney Dis 2009; 53: 982–992.
Yasuda H, Sanada M, Kitada K, Terashima T, Kim H, Sakaue Y et al. Rationale and usefulness of newly devised abbreviated diagnostic criteria and staging for diabetic polyneuropathy. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2007; 77: S178–S183.
Zung WW . A self-rating depression scale. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1965; 12: 63–70.
Rosen RC, Cappelleri JC, Smith MD, Lipsky J, Peña BM . Development and evaluation of an abridged, 5-item version of the International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF-5) as a diagnostic tool for erectile dysfunction. Int J Impot Res 1999; 11: 319–326.
Araujo AB, Durante R, Feldman HA, Goldstein I, Mckinlay JB . The relationship between depression symptoms and male erectile dysfunction: cross-sectional results from the Massachusetts Male Aging Study. Psychosom Med 1998; 60: 458–465.
Nicolosi A, Moreira ED Jr, Shirai M, Bin Mohd Tambi MI, Glasser DB . Epidemiology of erectile dysfunction in four countries: Cross-national study of the prevalence and correlates of erectile dysfunction. Urology 2003; 61: 201–206.
Okulate G, Olayinka O, Dongunro AS . Erectile dysfunction; prevalence and relationship to depression, alcohol abuse and panic disorder. Gen Hosp Psychiatry 2003; 25: 209–213.
Shiri R, Ansari M, Hassani KF . Association between comorbidity and erectile dysfunction in patients with diabetes. Int J Impot Res 2006; 18: 348–353.
Moreira ED Jr, Abdo CH, Torres EB, Lôbo CF, Fittipaldi JA . Prevalence and correlates of erectile dysfunction: results of the Brazilian study of sexual behaviour. Urology 2001; 58: 583–588.
Sugimori H, Yoshida K, Tanaka T, Baba K, Nishida T, Nakazawa R . Relationship between erectile dysfunction, depression, and anxiety in Japanese subjects. J Sex Med 2005; 2: 390–396.
Seidman SN, Roose SP . The relationship between depression and erectile dysfunction. Curr Psychiatry Rep 2000; 2: 201–205.
Corona G, Giorda CB, Cucinotta D, Guida P, Nada E, SUBITO-DE study group. Sexual dysfunction at the onset of type 2 diabetes: the intetplay of depression, hormonal and cardiovascular factors. J Sex Med 2014; 11: 2065–2073.
Shiri R, Koskimäki J, Tammela TL, Häkkinen J, Auvinen A, Hakama M . Bidirectional relationship between depression and erectile dysfunction. J Urol 2007; 177: 669–673.
Corona G, Rastrelli G, Filippi S, Vignozzi L, Mannucci E, Maggi M . Erectile dysfunction and central obesity: an Italian perspective. Asian J Androl 2014; 16: 581–591.
Fukui M, Tanaka M, Okada H, Iwase H, Mineoka Y, Senmaru T et al. Five-item version of the international index of erectile function correlated with albuminuria and subclinical atherosclerosis in men with type 2 diabetes. J Atheroscler Thromb 2011; 18: 991–997.
Acknowledgements
We thank Keiko Kikuchi and Tomo Kogama from Ehime University and Eri Furukawa from the Furukawa Clinic. This study was funded by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) KAKENHI Grants (21790583 and 23790697).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Furukawa, S., Sakai, T., Niiya, T. et al. Depressive symptoms and prevalence of erectile dysfunction in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: the Dogo Study. Int J Impot Res 29, 57–60 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijir.2016.45
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijir.2016.45
This article is cited by
-
Prevalence of sexual dysfunction and pursuit of sexual medicine evaluation among male physicians—a survey
International Journal of Impotence Research (2024)
-
Association between bowel movement frequency and erectile dysfunction in patients with ulcerative colitis: a cross-sectional study
International Journal of Impotence Research (2024)
-
Association between erectile dysfunction and subjective well-being in primary care patients with type 2 diabetes
Diabetology International (2024)
-
The Italian Society of Andrology and Sexual Medicine (SIAMS), along with ten other Italian Scientific Societies, guidelines on the diagnosis and management of erectile dysfunction
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation (2023)
-
Effect of testosterone replacement therapy on sexual function and glycemic control among hypogonadal men with type 2 diabetes mellitus
International Journal of Impotence Research (2019)