Abstract
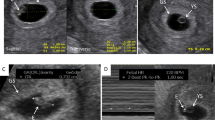
The objective of this study was to anatomically describe the relationship of penile intracavernosal pillars to penile surgery, specifically corporal dilation during penile prosthesis placement. Corpora cavernosa from four embalmed male cadavers were dissected and subjected to probe dilation. Corpora were cross-sectioned and examined for the gross presence and location of pillars and dilated spaces. Infrapubic penile prosthesis insertion was performed on one fresh-frozen cadaveric male pelvis, followed by cross-sectioning. A single patient had intracavernosal pillars examined intraoperatively during Peyronie’s plaque excision and penile prosthesis insertion. Intracavernosal pillars were identified in all cadavers and one surgical patient, passing obliquely from the dorsolateral tunica albuginea across the sinusoidal space to the ventral intercorporal septum. This delineated each corpus into two potential compartments for dilation: dorsomedial and ventrolateral. Dorsal dilation seated instruments and prosthetics satisfactorily in the dorsal mid glans and provided additional tissue coverage over weak ventral areas of the tunica albuginea, while ventrolateral dilation appeared to result in ventral seating and susceptibility to perforation. Intracavernosal pillars are an important anatomic consideration during penile prosthesis placement. Dorsal dilation appears to result in improved distal seating of cylinder tips, which may be protective against tip malposition, perforation or subsequent erosion.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 8 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $32.38 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hsu G, Brock G, Martinez-Pineiro L, Nunes L, von Heyden B, Lue T . The three-dimensional structure of the tunica albuginea: anatomical and ultrastructural levels. Int J Impot Res 1992; 4: 117–129.
Hsu GL, Hsieh CH, Wen HS, Hsu WL, Wu CH, Fong TH et al. Anatomy of the human penis: the relationship of the architecture between skeletal and smooth muscles. J Androl 2004; 25: 426–431.
Udelson D, Nehra A, Hatzichristou DG, Azadzoi K, Moreland RB, Krane J et al. Engineering analysis of penile hemodynamic and structural-dynamic relationships: Part I–Clinical implications of penile tissue mechanical properties. Int J Impot Res 1998; 10: 15–24.
Udelson D, Nehra A, Hatzichristou DG, Azadzoi K, Moreland RB, Krane RJ et al. Engineering analysis of penile hemodynamic and structural-dynamic relationships: Part III–clinical considerations of penile hemodynamic and rigidity erectile responses. Int J Impot Res 1998; 10: 89–99.
Udelson D, Nehra A, Hatzichristou DG, Azadzoi K, Moreland RB, Krane RJ et al. Engineering analysis of penile hemodynamic and structural-dynamic relationships: Part II–clinical implications of penile buckling. Int J Impot Res 1998; 10: 25–35.
Hsu GL, Brock G, von Heyden B, Nunes L, Lue TF, Tanagho EA . The distribution of elastic fibrous elements within the human penis. Br J Urol 1994; 73: 566–571.
Brock G, Hsu GL, Nunes L, von Heyden B, Lue TF . The anatomy of the tunica albuginea in the normal penis and Peyronie's disease. J Urol 1997; 157: 276–281.
Graham SD, Keane TE, Glenn JF . Glenn's Urologic Surgery, 7th edn. Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2010.
Egydio PH, Kuehhas FE . Penile lengthening and widening without grafting according to a modified 'sliding' technique. BJU Int 2015; 116: 965–972.
Egydio PH, Kuehhas FE, Valenzuela RJ . Modified sliding technique (MoST) for penile lengthening with insertion of inflatable penile prosthesis. J Sex Med 2015; 12: 1100–1104.
Valenzuela R . IPP insertion and vasectomy using a single sub-coronal incision. Video J Prosthetic Urol 2015; 2: 046.
Hakky TS, Wang R, Henry GD . The evolution of the inflatable penile prosthetic device and surgical innovations with anatomical considerations. Curr Urol Rep 2014; 15: 410.
Hakky TS, Ferguson D, Spiess PE, Bradley P, Lue TF, Carrion RE . Three-dimensional mapping and comparative analysis of the distal human corpus cavernosum and the inflatable penile prosthesis. Asian J Androl 2013; 15: 567–570.
Hsu GL, Brock G, Martinez-Pineiro L, von Heyden B, Lue TF, Tanagho EA . Anatomy and strength of the tunica albuginea: its relevance to penile prosthesis extrusion. J Urol 1994; 151: 1205–1208.
Wilson SK . Postoperative pitfalls and their solutions In: Pearls, Perils and Pitfalls of Prosthetic Urology. Calvert McBride Publishing: Fort Smith, AR, USA, 2008 pp 45.
Wein AJ, Kavoussi LR, Campbell MF (eds). Campbell-Walsh Urology. 10th edn. Elsevier Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2012.
Bettocchi C, Ditonno P, Palumbo F, Lucarelli G, Garaffa G, Giammusso B et al. Penile prosthesis: what should we do about complications? Adv Urol 2008; 573560.
Sadeghi-Nejad H . Penile prosthesis surgery: a review of prosthetic devices and associated complications. J Sex Med 2007; 4: 296–309.
Carson CC, Noh CH . Distal penile prosthesis extrusion: treatment with distal corporoplasty or Gortex windsock reinforcement. Int J Impot Res 2002; 14: 81–84.
Carson CC . Repair of distal extrusion of a penile prosthesis. Contemp Urol 1998; 10: 13–17.
Mulcahy JJ . Distal corporoplasty for lateral extrusion of penile prosthesis cylinders. J Urol 1999; 161: 193–195.
Henry GD, Laborde E . A review of surgical techniques for impending distal erosion and intraoperative penile implant complications: part 2 of a three-part review series on penile prosthetic surgery. J Sex Med 2012; 9: 927–936.
Mulhall JP, Kim FJ . Reconstructing penile supersonic transporter (SST) deformity using glanulopexy (glans fixation). Urology 2001; 57: 1160–1162.
Morey AF . Reconstructing penile supersonic transporter (SST) deformity using glanulopexy (glans fixation). J Urol 2005; 174: 969.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank our illustrator, Vanessa Dudley, for significant contributions to this work. No research support or funding was received in connection with this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
No research support or funding was received in connection with this study. Drs Pagano, Weinberg, Deibert, Alukal, Zhao, Egydio and Mr Hernandez have no conflict of interest. Dr Wilson reports consultation fees and non-financial support from Abreon, Boston Scientific Corp., Coloplast Corp., Neotract and Sontec Instruments outside of the submitted work. Dr Valenzuela reports consultation fees and non-financial support from Boston Scientific Corp., Coloplast Corp. and Neotract outside of the submitted work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pagano, M., Weinberg, A., Deibert, C. et al. Penile intracavernosal pillars: lessons from anatomy and potential implications for penile prosthesis placement. Int J Impot Res 28, 114–119 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijir.2016.12
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijir.2016.12
This article is cited by
-
Anatomic considerations of inflatable penile prosthetics: lessons gleaned from surgical body donor workshops
International Journal of Impotence Research (2023)
-
Evolution of techniques for aesthetic penile enlargement during prosthesis placement: a chronicle of the Egydio non-grafting strategy
International Journal of Impotence Research (2023)