Abstract
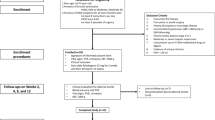
We evaluated the clinical efficacy and safety of the coadministration of a PDE5 inhibitor and an α-adrenergic blocker in patients with both benign prostatic hyperplasia/lower urinary tract symptoms (BPH-LUTS) and ED using mirodenafil 50 mg (Mvixx) once daily (OD) in patients already receiving stable α-blocker therapy. This study was a prospective, multicenter, open-label trial. We selected 147 patients undergoing stable (longer than 4 weeks) α-blocker therapy for BPH-LUTS as recipients of the additive mirodenafil 50 mg OD for 8 weeks. The coprimary measures were the International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS) and the International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF-5). The key secondary measures were peak flow rate (Qmax) and postvoiding residual (PVR) volume. Safety was assessed by evaluating cardiovascular parameters and the participant-reported treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs). The additional administration of mirodenafil 50 mg OD significantly improved IPSS results (18.70–14.30 at 4 weeks and 18.70–13.72 at 8 weeks; P<0.001). The IIEF-5 score was improved at 8 weeks (10.94–16.16; P<0.001). There was no significant change in systolic blood pressure/diastolic blood pressure (124.8 mm Hg/78.6 mm Hg–122.0 mm Hg/79.6 mm Hg; P=0.638) and heart rates (78.8 per min to 80.2 per min; P=0.452). The most common TEAEs were hot flashes (10.9%) and headache (8.1%). The combination of mirodenafil with an α-blocker did not significantly improve PVR; however, Qmax was improved at 8 weeks (14.51–16.80 ml s−1; P=0.026). Mirodenafil 50 mg OD in combination with an α-blocker appeared to have few adverse effects, to improve BPH-LUTS and restore sexual function.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 8 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $32.38 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hoesl CE, Woll EM, Burkart M, Altwein JE . Erectile dysfunction (ED) is prevalent, bothersome and underdiagnosed in patients consulting urologists for benign prostatic syndrome (BPS). Eur Urol 2005; 47: 511–517.
Rosen R, Altwein J, Boyle P, Kirby RS, Lukacs B, Meuleman E et al. Lower urinary tract symptoms and male sexual dysfunction: the multinational survey of the aging male (MSAM-7). Eur Urol 2003; 44: 637–649.
Braun M, Wassmer G, Klotz T, Reifenrath B, Mathers M, Engelmann U . Epidemiology of erectile dysfunction: results of the 'Cologne Male Survey'. Int J Impot Res 2000; 12: 305–311.
Kohler TS, McVary KT . The relationship between erectile dysfunction and lower urinary tract symptoms and the role of phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors. Eur Urol 2009; 55: 38–48.
Lewis RW, Fugl-Meyer KS, Corona G, Hayes RD, Laumann EO, Moreira ED et al. Definitions/epidemiology/risk factors for sexual dysfunction. J Sex Med 2010; 7: 1598–1607.
Deedwania PC . Mechanisms of endothelial dysfunction in the metabolic syndrome. Curr Diab Rep 2003; 3: 289–292.
Khan MA, Thompson CS, Dashwood MR, Mumtaz FH, Morgan RJ, Mikhailidis DP . Endothelin-1 and nitric oxide in the pathogenesis of urinary tract disorders secondary to bladder outlet obstruction. Curr Vasc Pharmacol 2003; 1: 27–31.
Uckert S, Oelke M, Stief CG, Andersson KE, Jonas U, Hedlund P . Immunohistochemical distribution of cAMP- and cGMP-phosphodiesterase (PDE) isoenzymes in the human prostate. Eur Urol 2006; 49: 740–745.
McVary KT, Roehrborn CG, Avins AL, Barry MJ, Bruskewitz RC, Donnell RF et al. Update on AUA guideline on the management of benign prostatic hyperplasia. J Urol 2011; 185: 1793–1803.
American Urological Association. AUA Guideline. Management of erectile dysfunction. Arch Esp Urol 2011; 64: 4.
Wespes E, Amar E, Hatzichristou D, Hatzimouratidis K, Montorsi F, Pryor J et al. EAU Guidelines on erectile dysfunction: an update. Eur Urol 2006; 49: 806–815.
Chung BH, Lee JY, Kim CI, Kim CS, Oh CY, Lee SW et al. Sexuality and the management of BPH with alfuzosin (SAMBA) trial. Int J Impot Res 2009; 21: 68–73.
Egerdie RB, Auerbach S, Roehrborn CG, Costa P, Garza MS, Esler AL et al. Tadalafil 2.5 or 5 mg administered once daily for 12 weeks in men with both erectile dysfunction and signs and symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia: results of a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study. J Sex Med 2012; 9: 271–281.
Tamimi NA, Mincik I, Haughie S, Lamb J, Crossland A, Ellis P . A placebo-controlled study investigating the efficacy and safety of the phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor UK-369,003 for the treatment of men with lower urinary tract symptoms associated with clinical benign prostatic hyperplasia. BJU Int 2010; 106: 674–680.
Chung BH, Lee JY, Lee SH, Yoo SJ, Lee SW, Oh CY . Safety and efficacy of the simultaneous administration of udenafil and an alpha-blocker in men with erectile dysfunction concomitant with BPH-LUTS. Int J Impot Res 2009; 21: 122–128.
Kaplan SA, Gonzalez RR, Te AE . Combination of alfuzosin and sildenafil is superior to monotherapy in treating lower urinary tract symptoms and erectile dysfunction. Eur Urol 2007; 51: 1717–1723.
Lee JY, Cho SY, Oh CY, Ha US, Lee SH, Park SY et al. Efficacy and safety of combination therapy with mirodenafil and alpha1-blocker for benign prostatic hyperplasia-induced lower urinary tract symptoms accompanied by erectile dysfunction: a multicenter, open-label, prospective study. Int J Impot Res 2011; 23: 249–256.
Paick JS, Ahn TY, Choi HK, Chung WS, Kim JJ, Kim SC et al. Efficacy and safety of mirodenafil, a new oral phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor, for treatment of erectile dysfunction. J Sex Med 2008; 5: 2672–2680.
Lee YS, Choi YH, Kim TK, Ryu KH, Lee BY, Lee MG . Pharmacokinetics of mirodenafil and its two metabolites, SK3541 and SK3544, after intravenous and oral administration of mirodenafil to streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus rats. Xenobiotica 2010; 40: 129–137.
Yang CS, Kim SC . The Influence of Treatment-emergent Adverse Reactions on Selecting Phosphodiesterase Type 5 Inhibitors. Korean J Urol AID 2006; 47: 272–278.
Andersson KE, de Groat WC, McVary KT, Lue TF, Maggi M, Roehrborn CG et al. Tadalafil for the treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms secondary to benign prostatic hyperplasia: pathophysiology and mechanism(s) of action. Neurourol Urodyn 2011; 30: 292–301.
Broderick GA, Brock GB, Roehrborn CG, Watts SD, Elion-Mboussa A, Viktrup L . Effects of tadalafil on lower urinary tract symptoms secondary to benign prostatic hyperplasia in men with or without erectile dysfunction. Urology 2010; 75: 1452–1458.
Porst H, Kim ED, Casabe AR, Mirone V, Secrest RJ, Xu L et al. Efficacy and safety of tadalafil once daily in the treatment of men with lower urinary tract symptoms suggestive of benign prostatic hyperplasia: results of an international randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Eur Urol 2011; 60: 1105–1113.
Oh CY, Lee SH, Yoo SJ, Chung BH . Korean urologist's view of practice patterns in diagnosis and management of benign prostatic hyperplasia: a nationwide survey. Yonsei Med J 2010; 51: 248–252.
Hatzimouratidis K, Amar E, Eardley I, Giuliano F, Hatzichristou D, Montorsi F et al. Guidelines on male sexual dysfunction: erectile dysfunction and premature ejaculation. Eur Urol 2010; 57: 804–814.
Lee J, Yoo HH, Rhim KJ, Sohn DR, Kim DH . Metabolism and excretion of 5-ethyl-2-{5-[4-(2-hydroxyethyl)piperazine-1-sulfonyl]-2-propoxyphenyl}-7-propyl-3,5-dihydropyrrolo[3,2-d]-pyrimidin-4-one (SK3530) in rats. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 2007; 21: 1139–1149.
Warde N . Therapy: Two birds, one stone: tadalafil is an effective treatment for men with both BPH-LUTS and ED. Nat Rev Urol 2011; 8: 643.
Martinez-Salamanca JI, Carballido J, Eardley I, Giuliano F, Gratzke C, Rosen R et al. Phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors in the management of non-neurogenic male lower urinary tract symptoms: critical analysis of current evidence. Eur Urol 2011; 60: 527–535.
van Dijk MM, de la Rosette JJ, Michel MC . Effects of alpha(1)-adrenoceptor antagonists on male sexual function. Drugs 2006; 66: 287–301.
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by SK chemicals Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bang, W., Oh, C., Yoo, C. et al. Efficacy and safety of the simultaneous administration of mirodenafil and an α-blocker in men with BPH-LUTS: a multicenter open-label prospective study. Int J Impot Res 25, 149–154 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijir.2012.44
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijir.2012.44
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Management of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: Role of Phosphodiesterase-5 Inhibitors
Drugs & Aging (2014)