Abstract
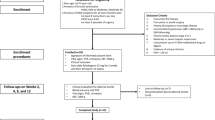
Results are reported from the first two adequate trials of the PDE-5 inhibitor vardenafil using a stopwatch to precisely measure erection duration in men with ED. Two randomized, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials were conducted: a crossover 4-week treatment in men with ED (ENDURANCE) and a parallel group, 12-week treatment in men with ED and dyslipidemia (the dyslipidemia study). Stopwatch-assessed duration of erection leading to successful intercourse measured by Sexual Encounter Profile question-3 (SEP-3) was the primary end point in ENDURANCE and one of the secondary end points in the dyslipidemia study. Other efficacy end points included responses to SEP-2, SEP-3 and International Index of Erectile Function–Erectile Function (IIEF–EF) domain scores. Adverse events were recorded. Duration of erection (least squares mean±s.e.) leading to successful intercourse was statistically superior in men receiving vardenafil versus placebo (12.8±1.0 versus 5.5±1.0 min; p<0.001 in ENDURANCE and 10.0±0.8 versus 3.4±0.8; p<0.001 in the dyslipidemia study), with a difference of 7.4 and 6.6 min, respectively, between treatment groups. Results for SEP-2, SEP-3 and IIEF–EF domain scores were consistent across studies and with stopwatch-assessed measures for duration of erection. Vardenafil was well tolerated. Duration of erection leading to successful intercourse is an important indicator of the efficacy of ED treatment. The stopwatch approach offers an alternative, precise and reproducible measure of efficacy. We propose this approach as a potential new paradigm for assessing the efficacy of ED treatments.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 8 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $32.38 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
McKinlay JB . The worldwide prevalence and epidemiology of erectile dysfunction. Int J Impot Res 2000; 12: S6–S11.
Ayta IA, McKinlay JB, Krane RJ . The likely worldwide increase in erectile dysfunction between 1995 and 2025 and some possible policy consequences. BJU Int 1999; 84: 50–56.
Haczynksi J, Lew-Starowicz Z, Darewicz B, Krajka K, Piotrowicz R, Ciesielska B et al. The prevalence of erectile dysfunction in men visiting outpatient clinics. Int J Impot Res 2006; 18: 359–363.
Baldwin K, Ginsberg P, Harkaway RC . Under-reporting of erectile dysfunction among men with unrelated urologic conditions. Int J Impot Res 2003; 15: 87–89.
Solomon H, deBusk RF, Jackson G . Erectile dysfunction: the need to be evaluated, the right to be treated. Am Heart J 2005; 150: 620–626.
Kubin M, Wagner G, Fugl-Meyer AR . Epidemiology of erectile dysfunction. Int J Impot Res 2003; 15: 63–71.
Rosen RC, Fisher WA, Eardley I, Niederberger C, Nadel A, Sand M . The multinational Men's Attitudes to Life Events and Sexuality (MALES) study: I. Prevalence of erectile dysfunction and related health concerns in the general population. Curr Med Res Opin 2004; 20: 607–617.
Kapur V, Schwarz ER . The relationship between erectile dysfunction and cardiovascular disease. Part I: pathophysiology and mechanisms. Rev Cardiovasc Med 2007; 8: 214–219.
DeBusk R, Drory Y, Goldstein I, Jackson G, Kaul S, Kimmel SE et al. Management of sexual dysfunction in patients with cardiovascular disease: recommendations of the Princeton Consensus Panel. Am J Cardiol 2000; 86: 175–181.
Solomon HMJ, Martin E, Jackson G . Erectile dysfunction is a marker of asymptomatic peripheral vascular disease. Int J Impot Res 2002; 14: S20.
Solomon H, Man JW, Wierzbicki AS, Jackson G . Relation of erectile dysfunction to angiographic coronary artery disease. Am J Cardiol 2003; 91: 230–231.
Kostis JB, Jackson G, Rosen R, Barrett-Connor E, Billups K, Burnett AL et al. Sexual dysfunction and cardiac risk (the Second Princeton Consensus Conference). Am J Cardiol 2005; 96: 313–321.
Miner MM . Erectile dysfunction and the ‘window of curability’: a harbinger of cardiovascular events. Mayo Clin Proc 2009; 84: 102–104.
Ma RC, So WY, Yang X, Yu LW, Kong AP, Ko GT et al. Erectile dysfunction predicts coronary artery disease in type 2 diabetes. J Am Coll Cardiol 2008; 4: 2045–2050.
Inman BA, St Sauver JL, Jacobson DJ, McGree ME, Nehra A, Lieber MM et al. A population-based longitudinal study of erectile dysfunction and future coronary artery disease. Mayo Clin Proc 2009; 84: 108–113.
Jackson G, Rosen RC, Kloner RA, Kostis JB . The second Princeton consensus on sexual dysfunction and cardiac risk: new guidelines for sexual medicine. J Sex Med 2006; 3: 28–36.
Thompson IM, Tangen CM, Goodman PJ, Probstfield JL, Moinpour CM, Coltman CA . Erectile dysfunction and subsequent cardiovascular disease. JAMA 2005; 294: 2996–3002.
Miner MM, Kuritzky L . Erectile dysfunction: a sentinel marker for cardiovascular disease in primary care. Cleve Clin J Med 2007; 74 (Suppl 3): S30–S37.
Kirby M, Jackson G, Simonsen U . Endothelial dysfunction links erectile dysfunction to heart disease. Int J Clin Pract 2005; 59: 225–229.
Seftel AD, Sun P, Swindle R . The prevalence of hypertension, hyperlipidemia, diabetes mellitus and depression in men with erectile dysfunction. J Urol 2004; 171 (6, Part 1): 2341–2345.
Levitra [package insert]. West Haven, CT: Bayer Healthcare Pharmaceuticals; Research Triangle Park, NC: GlaxoSmithKline; Kenilworth, NJ: Schering-Plough Corporation, 2008.
Viagra [package insert]. New York, NY: Pfizer Inc, 2008.
Cialis [package insert]. Indianapolis, IN: Eli Lilly and Company, 2008.
American Urological Association. Management of erectile dysfunction. Available at http://www.auanet.org, 2009.
Wespes E, Amar E, Hatzichristou D, Hatzimouratidis K, Montorsi F, Pryor J et al. EAU Guidelines on erectile dysfunction: an update. Eur Urol 2006; 49: 806–815.
Padma-Nathan H, Christ C, Adaikan G, Becher E, Brock G, Carrier S et al. Pharmacotherapy for erectile dysfunction. J Sex Med 2004; 1: 128–140.
Fink HA, Mac Donald R, Rutks IR, Nelson DB, Wilt TJ . Sildenafil for male erectile dysfunction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Intern Med 2002; 162: 1349–1360.
Brock GB, McMahon CG, Chen KK, Costigan T, Shen W, Watkins V et al. Efficacy and safety of tadalafil for the treatment of erectile dysfunction: results of integrated analyses. J Urol 2002; 168 (4, Part 1): 1332–1336. Erratum in: J Urol 2005; 173: 664.
Hellstrom WJ, Gittelman M, Karlin G, Segerson T, Thibonnier M, Taylor T et al. Vardenafil for the treatment of men with erectile dysfunction: efficacy and safety in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Androl 2002; 23: 763–771.
Goldstein I, Kim E, Steers WD, Pryor JL, Wilde DW, Natanegara F et al. High prevalence of significant comorbid conditions in men with erectile dysfunction: momentus trial demonstrates efficacy and safety of tadalafil in this group. J Urol 2005; 173: 238 (abstract 875).
Soler JM, Previnaire JG, Denys P, Chartier-Kastler E . Phosphodiesterase inhibitors in the treatment of erectile dysfunction in spinal cord-injured men. Spinal Cord 2007; 45: 169–173.
Ziegler D, Merfort F, van Ahlen H, Yassin A, Reblin T, Neureither M . Efficacy and safety of flexible-dose vardenafil in men with type 1diabetes and erectile dysfunction. J Sex Med 2006; 3: 883–891.
Stuckey BG, Jadzinsky MN, Murphy LJ, Montorsi F, Kadioglu A, Fraige F et al. Sildenafil citrate for treatment of erectile dysfunction in men with type 1 diabetes: results of a randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Care 2003; 26: 279–284.
Saenz de Tejada I, Anglin G, Knight JR, Emmick JT . Effects of tadalafil on erectile dysfunction in men with diabetes. Diabetes Care 2002; 25: 2159–2164.
Fonseca V, Seftel A, Denne J, Fredlund P . Impact of diabetes mellitus on the severity of erectile dysfunction and response to treatment: analysis of data from tadalafil clinical trials. Diabetologia 2004; 47: 1914–1923.
Valiquette L, Montorsi F, Auerbach S, Vardenafil Study Group. First-dose success with vardenafil in men with erectile dysfunction and associated comorbidities: RELY I. Int J Clin Pract 2006; 60: 1378–1385.
Miner M, Billups KL . Erectile dysfunction and dyslipidemia: relevance and role of phosphodiesterase type-5 inhibitors and statins. J Sex Med 2008; 5: 1066–1067.
Rosenberg MT, Adams PL, McBride TA, Roberts JN, McCallum SW . Improvement in duration of erection following phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor therapy with vardenafil in men with erectile dysfunction: the ENDURANCE study. Int J Clin Pract 2009; 63: 27–34.
Miner M, Gilderman L, Bailen J, Cook D, Dawson K, Stanislaus M et al. Vardenafil in men with stable statin therapy and dyslipidemia. J Sex Med 2008; 5: 1455–1467.
Shaw JW, Reardon G, Sandor DW, Rosen RC, Ferguson DM . Validation of stopwatch measurements of erection duration against responses to the sexual encounter profile and international index of erectile function in patients treated with a phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor. J Sex Med 2010; 7: 1147–1159.
Herrmann HC, Chang G, Klugherz BD, Mahoney PD . Hemodynamic effects of sildenafil in men with severe coronary artery disease. N Eng J Med 2000; 342: 1622–1626.
Goldwasser B, Carson III CC, Braun SD, McCann RL . Impotence due to the pelvic steal syndrome: treatment by iliac transluminal angioplasty. J Urol 1985; 133: 860–862.
National Institutes of Health. NIH Consensus Conference. Impotence. NIH Consensus Development Panel on Impotence. JAMA 1993; 270: 83–90.
Corty EW, Guardiani J . Canadian and American sex therapists’ perceptions of normal and abnormal ejaculatory latencies: how long should intercourse last? J Sex Med 2008; 5: 1251–1256.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Jacqueline Lanoix, PhD, for editorial assistance (funded by Schering-Plough and GlaxoSmithKline) in the preparation of this manuscript, and Ridwan Shabsigh, MD, for additional review and commentary. Dr Shabsigh did not receive any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Dr Rosenberg has been a consultant, speaker or advisor for the following: Abbott, Allergan, Astellas, Forest, GlaxoSmithKline, Novartis, Ortho-McNeil, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi-aventis, Shionogi and Solvay. Dr Miner receives research support from GlaxoSmithKline, and is a consultant for Auxilium. Ms Barnes and Dr Janning are employees of GlaxoSmithKline.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rosenberg, M., Miner, M., Barnes, A. et al. Stopwatch-assessed duration of erection: a new measure of the efficacy of erectile dysfunction treatments. Int J Impot Res 23, 9–16 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijir.2010.30
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijir.2010.30