Abstract
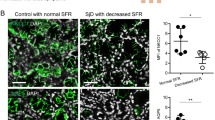
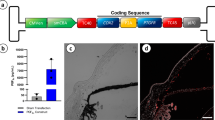
Anaemia is a common complication of chronic kidney disease, for which there is presently no adequate treatment. The delivery of human erythropoietin (hEPO) cDNA to salivary glands reportedly increases red blood cell counts, haematocrit (HCT) and haemoglobin concentration, representing a potential new method of renal anaemia treatment. However, no studies have examined the effects of this method in an animal model of renal anaemia. Here we established a miniature pig animal model of renal anaemia through continuous feeding with adenine. In these animals, we delivered the AAV2hEPO gene to the parotid glands through Stensen’s duct. As a control, we transferred AAVLacZ. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was used to detect hEPO in serum and saliva. Red blood counts and serum biochemistry were used to evaluate how hEPO gene administration affected renal anaemia. Compared with the control group, we found increased hEPO concentrations in parotid saliva and serum, respectively, at 2 and 6 weeks after AAV2hEPO administration to the anaemic animals. HCT and haemoglobin were also increased after AAV2hEPO was delivered; most serum indicators of renal damage were not changed over the time span of the experiment, suggesting the adenine-induced kidney damage had not been completely reversed. However, blood urea nitrogen and B2 microglobulin levels showed small but significant improvement. Overall, our present findings suggest that adeno-associated virus 2 (AAV2)-mediated gene transduction of hEPO via the parotid gland is a promising potential alternative therapy for renal anaemia.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jeong TH, Son YJ, Ryu HB, Koo BK, Jeong SM, Hoang P et al. Soluble expression and partial purification of recombinant human erythropoietin from E. coli. Protein Expr Purif 2014; 95: 211–218.
Jelkmann w . Molecular biology or erythropoietin. Intern Med 2004; 43: 649–659.
Miyaka T, Kung CK, Goldwasser E . Purification of human erythropoietin. J Biol Chem 1977; 252: 5558–5564.
Fried W . Erythropoietin and erythropoiesis. Exp Hemat 2009; 37: 1007–1015.
Isenman L, Liebow C, Rothman S . The endocrine secretion of mammalian digestive enzymes by exocrine glands. Am J Physiol 1999; 276: E223–E232.
Baum BJ, Voutetakis A, Wang J . Salivary glands: novel target sites for gene therapeutics. Trends Mol Med 2004; 10: 585–590.
Voutetakis A, Bossis I, Kok MR, Zhang W, Wang J, Cotrim AP et al. Salivary glands as a potential gene transfer target for gene therapeutics of some monogenetic endocrine disorders. Soc Endocrinol 2005; 185: 363–372.
Hai B, Yan X, Voutetakis A, Zheng C, Cotrim AP, Shan Z et al. Long-term transduction of miniature pig parotid glands using serotype 2 adeno-associated viral vectors. J Gene Med 2009; 11: 506–514.
Voutetakis A, Zheng C, Metzger M, Cotrim AP, Donahre RE, Dunbar CE et al. Sorting of transgenic secretory proteins in Rhesus macaque parotid glands after adenovirus-mediated gene transfer. Human Gene Ther 2008; 19: 1401–1405.
Li J, Wang SL, Zhu X, Sun K, Liu X, Zhang M . Organizational structure of small pig's parotid gland anatomy, imaging and observation. Chin J Dental Med 2000; 35: 121–122.
Yuan J, Wei-Wang GU . Application of miniature pig as animal model of human disease in biomedical research. Progr Vet Med 2011; 2: 108–111.
Ribeiro S, Garrido P, Fernandes J, Vala H, Rocha-Pereira P, Costa E et al. Renal risk-benefit determinants of recombinant human erythropoietin therapy in the remnant kidney rat model-hypertension, anaemia, inflammation and drug dose. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 2016; 43: 343–354.
Ali BH, Al Za'abi M, Ramkumar A, Yasin J, Nemmar A . Anemia in adenine-induced chronic renal failure and the influence of treatment with gum acacia thereon. Physiol Res 2014; 63: 351–358.
Li J, Shan Z, Ou G, Liu X, Zhang C, Baum BJ et al. Structural and functional characteristics of irradiation damage to parotid glands in the miniature pig. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2005; 62: 1510–1516.
Shan Z, Li J, Zheng C, Liu X, Fan Z, Zhang C et al. Increased fluid secretion after adenoviral-mediated transfer of the human aquaporin-1 cDNA to irradiated miniature pig parotid glands. Mol Ther 2005; 11: 444–451.
Guo L, Gao R, Xu J, Jin L, Cotrim AP, Yan X et al. AdLTR2EF1α-FGF2-mediated prevention of fractionatedirradiation-induced salivary hypofunction in swine. Gene Ther 2014; 21: 866–873.
Gao R, Yan X, Zheng C, Goldsmith CM, Afione S, Hai B et al. AAV2-mediated transfer of the human aquaporin-1 cDNArestores fluid secretion from irradiated miniature pigparotid glands. Gene Ther 2011; 18: 38–42.
Bohl D, Bosch A, Cardona A, Salvetti A, Heard JM . Improvement of erythropoiesis in beta-thalassemic mice by continuous erythropoietin delivery from muscle. Blood 2000; 95: 2793–2798.
Piras BA, Tian Y, Xu Y, Thomas NA, O'Connor DM, French BA . Systemic injection of AAV9 carrying promoter targets gene expression to a myofibroblast-like lineage in mouse hearts after reperfused myocardial infarction. Gene Ther 2016; 23: 469–478.
Johnston J, Tazelaar J, Rivera VM, Clackson T, Gao GP, Wilson JM et al. Regulated expression of erythropoietin from an AAV vector safely improves the anemia of beta-thalassemia in a mouse model. Mol Ther 2003; 7: 493–497.
Voutetakis A, Wang J, Baum BJ . Utilizing endocrine secretory pathways in salivary glands for systemic gene therapeutics. J Cell Physiol 2004; 199: 1–7.
Voutetakis A, Kok MR, Zheng C, Bossis I, Wang J, Cotrim AP et al. Re-engineered salivary glands are stable endogenous bioreactors for systemic gene therapeutics. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 3053–3058.
Perez P, Rowzee AM, Zheng C, Adriaansen J, Baum BJ . Salivary epithelial cells: an unassuming target site for gene therapeutics. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2010; 42: 773–777.
Proctor GB, Carpenter GH . Salivary secretion: mechanism and nerul regulation. Monogr Oral Sci 2014; 24: 14–29.
Dannies P . Mechanisms for storage of prolactin and growth hormone in secretory granules. Mol Genet Metab 2002; 76: 6–13.
Bazan JF . A novel family of growth factor receptors: a common binding domain in the growth hormone, prolactin, erythropoietin and IL-6 receptors, and the p75 IL-2 receptor beta-chain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1989; 164: 788–795.
Voutetakis A, Zheng C, Mineshiba F, Cotrim AP, Goldsmith CM, Schmidt M et al. Adeno-associated virus serotype 2-mediated gene transfer to the parotid glands of nonhuman primates. Hum Gene Ther 2007; 18: 142–150.
Zheng C, Voutetakis A, Goldstein B, Afione S, Rivera VM, Clackson T et al. Assessment of the safety and biodistribution of a regulated AAV2 gene transfer vector after delivery to murine submandibular glands. Toxicol Sci 2011; 123: 247–255.
Yan X, Voutetakis A, Zheng C, Hai B, Zhang C, Baum BJ et al. Sorting of transgenic secretory proteins in miniature pig parotid glands following adenoviral-mediated gene transfer. J Gene Med 2007; 9: 779–787.
Voutetakis A, Bossis I, Kok MR, Zhang W, Wang J, Cotrim AP et al. Salivary glands as a potential gene transfer target for gene therapeutics of some monogenetic endocrine disorders. J Endocrinol 2005; 185: 363–372.
Voutetakis A, Zheng C, Metzger M, Afione S, Cotrim AP, Eckhaus MA et al. Sorting of transgenic secretory proteins in rhesus macaque parotid glands following adenoviral mediated gene transfer. Hum Gene Ther 2008; 19: 1401–1406.
Fölsch H, Ohno H, Bonifacino JS, Mellman I . A novel clathrin adaptor complex mediates basolateral targeting in polarized epithelial cells. Cell 1999; 99: 189–198.
Cosen-Binker LI, Lam PP, Binker MG, Gaisano HY . Alcohol/cholecystokinin-evoked pancreatic acinar basolateral exocytosis is mediated by protein kinase C alpha phosphorylation of Munc18c. J Biol Chem 2007; 282: 13047–13058.
Locatelli F, Pozzoni P, Vecchio LD . Recombinant human epoetin beta in the treatment of renal anemia. Ther Clin Risk Manag 2007; 3: 433–439.
Garrido P, Ribeiro S, Fernandes J, Vala H, Rocha-Pereira P, Bronze-da -Rocha E . Resistance to recombinant human erythropoietin therapy in a rat model of chronic kidney disease associated anemia. Int J Mol Sci 2016; 17: 28.
Boye SE, Alesander JJ, Witherspoon CD, Boye SL, Peterson JJ, Clark ME . Highly efficient delivery of adeno-associated viral vectors to the primate retina. Hum Gene Ther 2016; 27: 580–597.
Kaludov N, Handelman B, Chiorini JA . Scalable purification of adeno-associated virus serotypes 2, 4, or 5 using ion exchange chromatography. Hum Gene Ther 2002; 13: 1235–1243.
Li J, Zheng C, Zhang X, Liu X, Zhang C, Goldsmith CM et al. Developing a convenient large animal model for gene transfer to salivary glands in vivo. J Gene Med 2004; 6: 55–63.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant Number 2016YFC1102604), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81070843 to ZCS), Beijing Natural Science Foundation (7172090) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81600884 to ZHG).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, C., Fan, Z., Gao, Z. et al. Delivery of human erythropoietin gene with an adeno-associated virus vector through parotid glands to treat renal anaemia in a swine model. Gene Ther 24, 692–698 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2017.70
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2017.70