Abstract
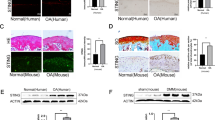
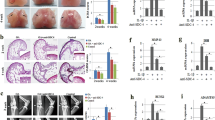
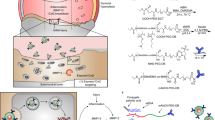
Hypoxia-inducible factor-2α (Hif-2α) is a potential therapeutic target for osteoarthritis (OA), but the application of this target in the delivery of therapeutic agents to chondrocytes remains a challenge. A chondrocyte-targeting vector was constructed in a previous study to enhance transfection efficiency and specificity of chondrocytes in vivo. This study used vectors to deliver small-interfering RNA (siRNA) and silenced Hif-2α expression to prevent cartilage degeneration in OA-affected mice. After siRNA transfection was conducted by cartilage-targeting nanoparticles, the protein levels of Hif-2α, matrix metalloproteinases (MMP-13, -9), a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs (ADAMTS-4, -5), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), type X collagen and nuclear factor (NF)-κB in interleukin-1-beta (IL-1β)-stimulated chondrocytes were determined. Chondrocyte-targeting ability was also determined by fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-labeled siRNA tracking under a confocal microscope. OA model was established by surgically destabilizing the knee joints of a mouse. Hif-2α siRNA was then delivered intra-articularly with nanoparticles in vivo. Cartilage degeneration and synovium inflammation in the knee joints were analyzed by histomorphometry. IL-1β levels in the synovial fluid were also measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. In vitro assay results showed that catabolic factors, including Hif-2α, MMP-13 and -9, ADAMTS-4, VEGF, collagen type X and NF-κB, were downregulated after Hif-2α-siRNA transfection by chondrocyte-targeting nanoparticles. In vivo assay results with FITC-labeled siRNA tracking also confirmed that nanoparticles promoted the local concentration and prolonged the retention time of siRNA in the cartilage. Histological analysis results confirmed that nanoparticle-mediated siRNA maintained cartilage integrity and alleviated synovium inflammation. IL-1β levels decreased after siRNA was silenced by nanoparticles. Thus, chondrocyte-targeting nanoparticles could deliver Hif-2α siRNA to cartilage and specifically inhibit the expression of catabolic proteins.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Newman AP . Articular cartilage repair. Am J Sports Med 1998; 26: 309–324.
Troeberg L, Nagase H . Proteases involved in cartilage matrix degradation in osteoarthritis. Biochim Biophys Acta 2012; 1824: 133–145.
Echtermeyer F, Bertrand J, Dreier R, Meinecke I, Neugebauer K, Fuerst M et al. Syndecan-4 regulates ADAMTS-5 activation and cartilage breakdown in osteoarthritis. Nat Med 2009; 15: 1072–1076.
Aigner T, McKenna L . Molecular pathology and pathobiology of osteoarthritic cartilage. Cell Mol Life Sci 2002; 59: 5–18.
Miyaki S, Nakasa T, Otsuki S, Grogan SP, Higashiyama R, Inoue A et al. MicroRNA-140 is expressed in differentiated human articular chondrocytes and modulates interleukin-1 responses. Athritis Rheum 2009; 60: 2723–2730.
Akhtar N, Rasheed Z, Ramamurthy S, Anbazhagan AN, Voss FR, Haqqi TM . MicroRNA-27b regulates the expression of matrix metalloproteinase 13 in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes. Athritis Rheum 2010; 62: 1361–1371.
Zwerina J, Redlich K, Polzer K, Joosten L, Krönke G, Distler J et al. TNF-induced structural joint damage is mediated by IL-1. PNAS 2007; 104: 11742–11747.
Baragi VM, Becher G, Bendele AM, Biesinger R, Bluhm H, Boer J et al. A new class of potent matrix metalloproteinase 13 inhibitors for potential treatment of osteoarthritis: Evidence of histologic and clinical efficacy without musculoskeletal toxicity in rat models. Arthritis Rheum 2009; 60: 2008–2018.
Chia SL, Sawaji Y, Burleigh A, McLean C, Inglis J, Saklatvala J et al. Fibroblast growth factor 2 is an intrinsic chondroprotective agent that suppresses ADAMTS-5 and delays cartilage degradation in murine osteoarthritis. Athritis Rheum 2009; 60: 2019–2027.
Flemming A . Target identification: HIF2alpha central player in osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2010; 9: 517.
Husa M, Liu-Bryan R, Terkeltaub R . Shifting HIFs in osteoarthritis. Nat Med 2010; 16: 641–644.
Ryu JH, Shin Y, Huh YH, Yang S, Chun CH, Chun JS . Hypoxia-inducible factor-2α regulates Fas-mediated chondrocyte apoptosis during osteoarthritic cartilage destruction. Cell Death Differ 2012; 19: 440–450.
Murphy CL . HIF-2alpha—a mediator of osteoarthritis? Cell Res 2010; 20: 977–979.
Saito T, Fukai A, Mabuchi A, Ikeda T, Yano F, Ohba S et al. Transcriptional regulation of endochondral ossification by HIF-2alpha during skeletal growth and osteoarthritis development. Nat Med 2010; 16: 678–686.
Yang S, Kim J, Ryu JH, Oh H, Chun CH, Kim BJ, Min BH et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor-2alpha is a catabolic regulator of osteoarthritic cartilage destruction. Nat Med 2010; 16: 687–693.
Evans CH, Gouze JN, Gouze E, Robbins PD, Ghivizzani SC . Osteoarthritis gene therapy. Gene Ther 2004; 11: 379–389.
Martinek V, Ueblacker P, Imhoff AB . Current concepts of gene therapy and cartilage repair. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2003; 85: 782–788.
Chen LX, Lin L, Wang HJ, Wei XL, Fu X, Zhang JY et al. Suppression of early experimental osteoarthritis by in vivo delivery of the adenoviral vector-mediated NF-kappaBp65-specific siRNA. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2008; 16: 174–184.
Wang CR, Shiau AL, Chen SY, Cheng ZS, Li YT, Lee CH et al. Intra-articular lentivirus-mediated delivery of galectin-3 shRNA and galectin-1 gene ameliorates collagen-induced arthritis. Gene Ther 2010; 17: 1225–1233.
Howard KA, Paludan SR, Behlke MA, Besenbacher F, Deleuran B, Kjems J . Chitosan/siRNA nanoparticle-mediated TNF-alpha knockdown in peritoneal macrophages for anti-inflammatory treatment in a murine arthritis model. Mol Ther 2009; 17: 162–168.
Glover DJ, Lipps HJ, Jans DA . Towards safe, non-viral therapeutic gene expression in humans. Nat Rev Genet 2005; 6: 299–310.
Jabr-Milane L, van Vlerken L, Devalapally H, Shenoy D, Komareddy S, Bhavsar M et al. Multi-functional nanocarriers for targeted delivery of drugs and genes. J Control Release 2008; 130: 121–128.
Niidome T, Huang L . Gene therapy progress and prospects: nonviral vectors. Gene Ther 2002; 9: 1647–1652.
Lv H, Zhang S, Wang B, Cui S, Yan J . Toxicity of cationic lipids and cationic polymers in gene delivery. J Control Release 2006; 114: 100–109.
Pi Y, Zhang X, Shi J, Zhu J, Chen W, Zhang C et al. Targeted delivery of non-viral vectors to cartilage in vivo using a chondrocyte-homing peptide identified by phage display. Biomaterials 2011; 32: 6324–6332.
Henson FM, Vincent TA . Alterations in the vimentin cytoskeleton in response to single impact load in an in vitro model of cartilage damage in the rat. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 2008; 9: 94.
Laverty S, Girard CA, Williams JM, Hunziker EB, Pritzker KP . The OARSI histopathology initiative - recommendations for histological assessments of osteoarthritis in the rabbit. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2010; 18 (Suppl 3): S53–S65.
Pawlus MR, Hu CJ . Enhanceosomes as integrators of hypoxia inducible factor (HIF) and other transcription factors in the hypoxic transcriptional response. Cell Signal 2013; 25: 1895–1903.
Boissier MC, Bessis N . Risks and benefits of articular gene therapy. Joint Bone Spine 2003; 70: 486–488.
Cottard V, Mulleman D, Bouille P, Mezzina M, Boissier MC, Bessis N . Adeno-associated virus-mediated delivery of IL-4 prevents collagen-induced arthritis. Gene Ther 2000; 7: 1930–1939.
Bessis N, GarciaCozar FJ, Boissier MC . Immune responses to gene therapy vectors: influence on vector function and effector mechanisms. Gene Ther 2004; 11 (Suppl 1): S10–S17.
Mukherjee J . Nanosize drug delivery system. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 2014; 14: 1221.
Amar-Lewis E, Azagury A, Chintakunta R, Goldbart R, Traitel T, Prestwood J et al. Quaternized starch-based carrier for siRNA delivery: from cellular uptake to gene silencing. J Control Release. 2014; 185: 11.
Fixler D, Zalevsky Z . In vivo tumor detection using polarization and wavelength reflection characteristics of gold nanorods. Nano Lett 2013; 13: 4.
Mizrahy S, Goldsmith M, Leviatan-Ben-Arye S, Kisin-Finfer E, Redy O, Srinivasan S et al. Tumor targeting profiling of hyaluronan-coated lipid based-nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2014; 6: 3742–3752.
Petros RA, DeSimone JM . Strategies in the design of nanoparticles for therapeutic applications. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2010; 9: 615–627.
Phillips MA, Gran ML, Peppas NA . Targeted nanodelivery of drugs and diagnostics. Nano Today 2010; 5: 143–159.
Veenbergen S, Bennink MB, Affandi AJ, Bessis N, Biton J, Arntz OJ et al. A pivotal role for antigen-presenting cells overexpressing SOCS3 in controlling invariant NKT cell responses during collagen-induced arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 2011; 70: 2167–2175.
Saidenberg-Kermanac'h N, Bessis N, Deleuze V, Bloquel C, Bureau M, Scherman D et al. Efficacy of interleukin-10 gene electrotransfer into skeletal muscle in mice with collagen-induced arthritis. J Gene Med 2003; 5: 164–171.
Loboda A, Jozkowicz A, Dulak J . HIF-1 versus HIF-2 - Is one more important than the other? Vasc Pharmacol 2012; 56: 245–251.
Pawlus MR, Wang L, Ware K, Hu CJ . Upstream stimulatory factor 2 and hypoxia-inducible factor 2α (HIF2α) cooperatively activate HIF2 target genes during hypoxia. Mol Cell Biol 2012; 32: 4595–4610.
Pawlus MR, Wang L, Murakami A, Dai G, Hu CJ . STAT3 or USF2 contributes to HIF target gene specificity. PLOS One 2013; 8: e72358.
Sena JA, Wang L, Hu CJ . BRG1 and BRM chromatin-remodeling complexes regulate the hypoxia response by acting as coactivators for a subset of hypoxia-inducible transcription factor target genes. Mol Cell Biol 2013; 33: 3849–3863.
Shay JE, Celeste Simon M . Hypoxia-inducible factors: Crosstalk between inflammation and metabolism. Semin Cell Dev Biol 2012; 23: 389–394.
Zhao X, Yue Y, Cheng W, Li J, Hu Y, qin L et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor: a potential therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Drug Targets 2013; 14: 7.
Lee H, Lytton-Jean AK, Chen Y, Love KT, Park AI, Karagiannis ED et al. Molecularly self-assembled nucleic acid nanoparticles for targeted in vivo siRNA delivery. Nat Nanotechnol 2012; 7: 389–393.
Alexis F, Zeng J, Shu W . PEI nanoparticles for targeted gene delivery. In: Friedmann T, Rossi J eds. Gene transfer: delivery and expression of DNA and RNA a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: New York pp 473–477 2007.
Harrison PE, Ashton IK, Johnson WE, Turner SL, Richardson JB, Ashton BA . The in vitro growth of human chondrocytes. Cell Tissue Bank 2000; 1: 255–260.
Caramés B, Taniguchi N, Otsuki S, Blanco FJ, Lotz M . Autophagy is a protective mechanism in normal cartilage, and its aging-related loss is linked with cell death and osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2010; 62: 791–801.
Kozawa E, Nishida Y, Cheng XW, Urakawa H, Arai E, Futamura N et al. Osteoarthritic change is delayed in a Ctsk-knockout mouse model of osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2012; 64: 454–464.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 81071474/H0605 and 81301539/H0605). This study was performed in the Institute of Sports Medicine, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on Gene Therapy website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pi, Y., Zhang, X., Shao, Z. et al. Intra-articular delivery of anti-Hif-2α siRNA by chondrocyte-homing nanoparticles to prevent cartilage degeneration in arthritic mice. Gene Ther 22, 439–448 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2015.16
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2015.16
This article is cited by
-
A pH-responsive metal-organic framework for the co-delivery of HIF-2α siRNA and curcumin for enhanced therapy of osteoarthritis
Journal of Nanobiotechnology (2023)
-
Focusing on the hypoxia-inducible factor pathway: role, regulation, and therapy for osteoarthritis
European Journal of Medical Research (2022)
-
Nanotechnology applications in rheumatology
Rheumatology International (2022)
-
High expression of NDRG3 in osteoarthritis patients
Arthroplasty (2021)
-
Disease-modifying therapeutic strategies in osteoarthritis: current status and future directions
Experimental & Molecular Medicine (2021)