Abstract
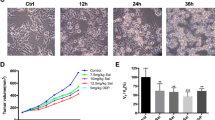
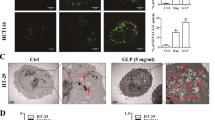
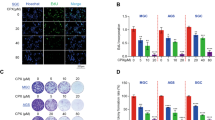
Salmonella have been demonstrated to inhibit tumor growth. However, the mechanism of Salmonella-induced tumor cell death is less defined. Autophagy is a cellular process that mediates the degradation of long-lived proteins and unwanted organelles in the cytosol. Tumor cells frequently display lower levels of basal autophagic activity than their normal counterparts and fail to increase autophagic activity in response to stresses. Autophagy is involved in the cell defense elimination of bacteria. The signaling pathways leading to activation of Salmonella-induced autophagy in tumor cells remain to be elucidated. We used autophagy inhibitor (3-Methyladenine) and apoptosis inhibitor (Z-VAD-FMK) to demonstrate that Salmonella may induce cell death via apoptosis and autophagic pathway. Meanwhile, we suggested that Salmonella induce autophagy in a dose- and time-dependent manner. The autophagic markers were increased after tumor cell infected with Salmonella. In addition, the protein express levels of phosph-protein kinase B (P-AKT), phosph-mammalian targets of rapamycin (P-mTOR), phosph-p70 ribosomal s6 kinase (P-p70s6K) in tumor cells were decreased by western analysis after Salmonella infection. In conclusion, our results point out that Salmonella induce the autophagic signaling pathway via downregulation of AKT/mTOR pathway. Herein, our findings that Salmonella in controlling tumor growth may induce autophagic signal pathway.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee CH, Wu CL, Tai YS, Shiau AL . Systemic administration of attenuated Salmonella choleraesuis in combination with cisplatin for cancer therapy. Mol Ther 2005; 11: 707–716.
Ganai S, Arenas RB, Sauer JP, Bentley B, Forbes NS . In tumors Salmonella migrate away from vasculature toward the transition zone and induce apoptosis. Cancer Gene Ther 2011; 18: 457–466.
Lee CH . Engineering bacteria toward tumor targeting for cancer treatment: current state and perspectives. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 2012; 93: 517–523.
Chen LM, Kaniga K, Galán JE . Salmonella spp. are cytotoxic for cultured macrophages. Mol Microbiol 1996; 21: 1101–1115.
Boise LH, Collins CM . Salmonella-induced cell death: apoptosis, necrosis or programmed cell death? Trends Microbiol 2001; 9: 64–67.
Hernandez LD, Pypaert M, Flavell RA, Galán JE . A Salmonella protein causes macrophage cell death by inducing autophagy. J Cell Biol 2003; 163: 1123–1131.
Kirkegaard K, Taylor MP, Jackson WT . Cellular autophagy: surrender, avoidance and subversion by microorganisms. Nat Rev Microbiol 2004; 2: 301–314.
Klionsky DJ, Emr SD . Autophagy as a regulated pathway of cellular degradation. Science 2000; 290: 1717–1721.
Pattingre S, Levine B . Bcl-2 inhibition of autophagy: a new route to cancer? Cancer Res 2006; 66: 2885–2888.
Kabeya Y, Mizushima U, Ueno T, Yamamoto A, Kirisako T, Noda T et al. LC3, a mammalian homologue of yeast Apg8p, is localized in autophagosome membranes after processing. EMBO J 2000; 19: 5720–5728.
Yo YT, Shieh GS, Hsu KF, Wu CL, Shiau AL . Licorice and licochalcone-A induce autophagy in LNCaP prostate cancer cells by suppression of Bcl-2 expression and the mTOR pathway. J Agri Food Chem 2009; 57: 8266–8273.
Lee YR, Hu HY, Kuo SH, Lei HY, Lin YS, Yeh TM et al. Dengue virus infection induces autophagy: an in vivo study. J Biomed Sci 2013; 20: 65.
Zhao M, Yang M, Li XM, Jiang P, Baranov E, Li S et al. Tumor-targeting bacterial therapy with amino acid auxotrophs of GFP-expressing Salmonella typhimurium. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 755–760.
Hoffman RM . Bugging tumors. Cancer Discov 2012; 2: 588–590.
Liu F, Zhang L, Hoffman RM, Zhao M . Vessel destruction by tumor-targeting Salmonella typhimurium A1-R is enhanced by high tumor vascularity. Cell Cycle 2010; 9: 4518–4524.
Nagakura C, Hayashi K, Zhao M, Yamauchi K, Yamamoto N, Tsuchiya H et al. Efficacy of a genetically-modified Salmonella typhimurium in an orthotopic human pancreatic cancer in nude mice. Anticancer Res 2009; 29: 1873–1878.
Yam C, Zhao M, Hayashi K, Ma H, Kishimoto H, McElroy M et al. Monotherapy with a tumor-targeting mutant of S. typhimurium inhibits liver metastasis in a mouse model of pancreatic cancer. J Surg Res 2010; 164: 248–255.
Zhao M, Yang M, Ma H, Li X, Tan X, Li S et al. Targeted therapy with a Salmonella typhimurium leucine-arginine auxotroph cures orthotopic human breast tumors in nude mice. Cancer Res 2006; 66: 7647–7652.
Birmingham CL, Brumell JH . Autophagy recognizes intracellular Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium in damaged vacuoles. Autophagy 2006; 2: 156–158.
von Muhlinen N, Akutsu M, Ravenhill BJ, Foeglein Á, Bloor S, Rutherford TJ et al. An essential role for the ATG8 ortholog LC3C in antibacterial autophagy. Autophagy 2013; 9: 784–786.
Tattoli I, Sorbara MT, Philpott DJ, Girardin SE . Bacterial autophagy: the trigger, the target and the timing. Autophagy 2012; 8: 1848–1850.
Hsu KF, Wu CL, Huang SC, Wu CM, Hsiao JR, Yo YT et al. Cathepsin L mediates resveratrol-induced autophagy and apoptotic cell death in cervical cancer cells. Autophagy 2009; 5: 451–460.
Eisenberg-Lerner A, Bialik S, Simon HU, Kimchi A . Life and death partners: apoptosis, autophagy and the cross-talk between them. Cell Death Differ 2009; 16: 966–975.
Sun PH, Zhu LM, Qiao MM, Zhang YP, Jiang SH, Wu YL et al. The XAF1 tumor suppressor induces autophagic cell death via upregulation of Beclin-1 and inhibition of Akt pathway. Cancer Lett 2011; 310: 170–180.
Basciani S, Vona R, Matarrese P, Ascione B, Mariani S, Cauda R et al. Imatinib interferes with survival of multi drug resistant Kaposi's sarcoma cells. FEBS Lett 2007; 581: 5897–5903.
Lee CH, Hsieh JL, Wu CL, Hsu PY, Shiau AL . T cell augments the antitumor activity of tumor-targeting Salmonella.. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 2011; 90: 1381–1388.
Lee CH, Hsieh JL, Wu CL, Hsu HC, Shiau AL . B cells are required for tumor-targeting Salmonella in host. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 2011; 92: 1251–1260.
Chang WW, Kuan YD, Chen MC, Lin ST, Lee CH . Tracking of mouse breast cancer stem-like cells with Salmonella. Exp Biol Med 2012; 237: 1189–1196.
Chen MC, Chang WW, Kuan YD, Lin ST, Hsu HC, Lee CH . Resveratrol inhibits LPS-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in mouse melanoma model. Innate Immun 2012; 18: 685–693.
Lee CH, Wu CL, Chen SH, Shiau AL . Humoral immune responses inhibit the antitumor activities mediated by Salmonella enterica serovar Choleraesuis. J Immunother 2009; 32: 376–388.
Lee CH, Wu CL, Shiau AL . Endostatin gene therapy delivered by Salmonella choleraesuis in murine tumor models. J Gene Med 2004; 6: 1382–1393.
Shiau AL, Shen YT, Hsieh JL, Wu CL, Lee CH . Scutellaria barbata inhibits angiogenesis through downregulation of HIF-1 α in lung tumor. Environ Toxicol 2012, e-pub ahead of print 13 February 2012 doi:10.1002/tox.21763.
Hsu SC, Lin JH, Weng SW, Chueh FS, Yu CC, Lu KW et al. Crude extract of Rheum palmatum inhibits migration and invasion of U-2 OS human osteosarcoma cells by suppression of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9. Biomedicine 2013; 3: 120–129.
Chang WW, Lai CH, Chen MC, Liu CF, Kuan YD, Lin ST et al. 2013. Salmonella enhance chemosensitivity in tumor through connexin 43 upregulation. Int J Cancer 2013; 133: 1926–1935.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Science Council from Taiwan (NSC101-2320-B039-012-MY3) and China Medical University (CMU102-S-29). We are grateful for the technical assistance of Electron Microscope Laboratory of Tzong Jwo Tang, School of Medicine, Fu Jen Catholic University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on Gene Therapy website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, CH., Lin, ST., Liu, JJ. et al. Salmonella induce autophagy in melanoma by the downregulation of AKT/mTOR pathway. Gene Ther 21, 309–316 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2013.86
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2013.86
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Selective autophagy in cancer: mechanisms, therapeutic implications, and future perspectives
Molecular Cancer (2024)
-
Intratumoural microbiota: from theory to clinical application
Cell Communication and Signaling (2023)
-
Current advances in microbial-based cancer therapies
Medical Oncology (2023)
-
A Systemic Review on Fitness and Survival of Salmonella in Dynamic Environment and Conceivable Ways of Its Mitigation
Indian Journal of Microbiology (2023)
-
Engineered Salmonella inhibits GPX4 expression and induces ferroptosis to suppress glioma growth in vitro and in vivo
Journal of Neuro-Oncology (2023)