Abstract
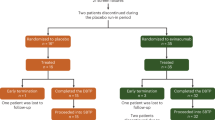
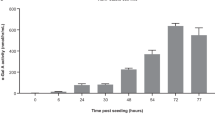
We describe the 2-year follow-up of an open-label trial (CT-AMT-011–01) of AAV1-LPLS447X gene therapy for lipoprotein lipase (LPL) deficiency (LPLD), an orphan disease associated with chylomicronemia, severe hypertriglyceridemia, metabolic complications and potentially life-threatening pancreatitis. The LPLS447X gene variant, in an adeno-associated viral vector of serotype 1 (alipogene tiparvovec), was administered to 14 adult LPLD patients with a prior history of pancreatitis. Primary objectives were to assess the long-term safety of alipogene tiparvovec and achieve a ⩾40% reduction in fasting median plasma triglyceride (TG) at 3–12 weeks compared with baseline. Cohorts 1 (n=2) and 2 (n=4) received 3 × 1011 gc kg−1, and cohort 3 (n=8) received 1 × 1012 gc kg−1. Cohorts 2 and 3 also received immunosuppressants from the time of alipogene tiparvovec administration and continued for 12 weeks. Alipogene tiparvovec was well tolerated, without emerging safety concerns for 2 years. Half of the patients demonstrated a ⩾40% reduction in fasting TG between 3 and 12 weeks. TG subsequently returned to baseline, although sustained LPLS447X expression and long-term changes in TG-rich lipoprotein characteristics were noted independently of the effect on fasting plasma TG.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brunzell JD, Deeb SS . Familial lipoprotein lipase deficiency, Apo C-II deficiency and hepatic lipase deficiency. In: Scriver CR, Beaudet AL, Sly WS, Valle D (eds). The Metabolic Basis of Inherited Disease 8th ed. McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, 2001, pp 2789–2816.
Black DM, Sprecher DL . Dietary treatment and growth of hyperchylomicronemic children severely restricted in dietary fat. Am J Dis Child 1993; 147: 60–62.
Chait A, Robertson HT, Brunzell JD . Chylomicronemia syndrome in diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 1981; 4: 343–348.
Chait A, Brunzell JD . Chylomicronemia syndrome. Adv Int Med 1992; 37: 249–273.
Santamarina-Fojo S . The familial chylomicronemia syndrome. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 1998; 27: 551–567.
Benlian P, De Gennes JL, Foubert L, Zhang H, Gagné SE, Hayden M . Premature atherosclerosis in patients with familial chylomicronaemia caused by mutations in the lipoprotein lipase gene. N Engl J Med 1996; 335: 848–854.
Fortson MR, Freedman SN, Webster PD . Clinical assessment of hyperlipidemic pancreatitis. Am J Gastroenterol 1995; 90: 2134–2139.
Goldberg IJ . Lipoprotein lipase and lipolysis: central roles in lipoprotein metabolism and atherogenesis. J Lipid Res 1996; 37: 693–707.
Mahley RW, Ji ZS . Remnant lipoprotein metabolism: key pathways involving cell-surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans and apolipoprotein E. J Lipid Res 1999; 40: 1–16.
Mead JR, Irvine SA, Ramji DP . Lipoprotein lipase: structure, function, regulation, and role in disease. J Mol Med 2002; 80: 753–769.
Mössner J, Bödeker H, Kimura W, Meyer F, Böhm S, Fischbach W . Isolated rat pancreatic acini as a model to study the potential role of lipase in the pathogenesis of acinar cell destruction. Int J Pancreatol 1992; 12: 285–296.
Kimura W, Meyer F, Hess D, Kirchner T, Fischbach W, Mössner J . Comparison of different treatment modalities in experimental pancreatitis in rats. Gastroenterology 1992; 103: 1916–1924.
Kimura W, Mössner J . Role of hypertriglyceridemia in the pathogenesis of experimental acute pancreatitis in rats. Int J Pancreatol 1996; 20: 177–184.
Saharia P, Margolis S, Zuidema GD, Cameron JL . Acute pancreatitis with hyperlipemia: studies with an isolated perfused canine pancreas. Surgery 1977; 82: 60–67.
Wang Y, Sternfeld L, Yang F, Rodriguez JA, Ross C, Hayden MR et al. Enhanced susceptibility to pancreatitis in severe hypertriglyceridaemic lipoprotein lipase-deficient mice and agonist-like function of pancreatic lipase in pancreatic cells. Gut 1992; 58: 422–430.
Tremblay K, Méthot J, Brisson D, Gaudet D . Etiology and risk of lactescent plasma and severe hypertriglyceridemia. J Clin Lipidol 2011; 5: 37–44.
Gaudet D, de Wal J, Tremblay K, Déry S, van Deventer S, Freidig A et al. Review of the clinical development of alipogene tiparvovec gene therapy for lipoprotein lipase deficiency. Atheroscler Suppl 2010; 11: 55–60.
Brisson D, Méthot J, Tremblay K, Tremblay M, Perron P, Gaudet D . Comparison of the efficacy of fibrates on hypertriglyceridemic phenotypes with different genetic and clinical characteristics. Pharmacogenet Genomics 2010; 20: 742–747.
Schnepp BC, Jensen RL, Clark KR, Johnson PR . Infectious molecular clones of Adeno-associated virus isolated directly from human tissues. J Virol 2009; 83: 1456–1464.
Daya S, Berns KI . Gene therapy using adeno-associated virus vectors. Clin Microbiol Rev 2008; 21: 583–593.
Rip J, Nierman MC, Sierts JA, Petersen W, Van den Oever K, Van Raalte D et al. Gene therapy for lipoprotein lipase deficiency: working toward clinical application. Hum Gene Ther 2005; 16: 1276–1286.
Ross CJ, Twisk J, Bakker AC, Miao F, Verbart D, Rip J et al. Correction of feline lipoprotein lipase deficiency with adeno-associated virus serotype 1-mediated gene transfer of the lipoprotein lipase S447X beneficial mutation. Hum Gene Ther 2006; 17: 487–499.
Ross CJ, Twisk J, Meulenberg JM, Liu G, van den Oever K, Moraal E et al. Long-term correction of murine lipoprotein lipase deficiency with AAV1-mediated gene transfer of the naturally occurring LPL(S447X) beneficial mutation. Hum Gene Ther 2004; 15: 906–919.
Rip J, Nierman MC, Ross CJ, Jukema JW, Hayden MR, Kastelein JJ et al. Lipoprotein lipase S447X: a naturally occurring gain-of-function mutation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2006; 26: 1236–1245.
Stroes ES, Nierman MC, Meulenberg JJ, Franssen R, Twisk J, Henny CP et al. Intramuscular administration of AAV1-lipoprotein lipase S447X lowers triglycerides in lipoprotein lipase-deficient patients. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2008; 28: 2303–2304.
Mingozzi F, Meulenberg JJ, Hui DJ, Basner-Tschakarjan E, Hasbrouck NC, Edmonson SA et al. AAV-1-mediated gene transfer to skeletal muscle in humans results in dose-dependent activation of capsid-specific T cells. Blood 2009; 114: 2077–2086.
Burnett JR, Hooper AJ . Alipogene tiparvovec, an adeno-associated virus encoding the Ser(447)X variant of the human lipoprotein lipase gene for the treatment of patients with lipoprotein lipase deficiency. Curr Opin Mol Ther 2009; 11: 681–691.
Clinical Trials.gov Safety and Efficacy in LPL-Deficient Subjects of AMT-011, an Adeno-Associated Viral Vector Expressing Human Lipoprotein Lipase [S447X]. Protocol summary. Last accessed on September 27 2010 at http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01109498?term=LPLD&rank=1.
Jiang H, Couto LB, Patarroyo-White S, Liu T, Nagy D, Vargas JA et al. Effects of transient immunosuppression on adenoassociated, virus-mediated, liver-directed gene transfer in rhesus macaques and implications for human gene therapy. Blood 2006; 108: 3321–3328.
Brantly ML, Chulay JD, Wang L, Mueller C, Humphries M, Spencer LT et al. Sustained transgene expression despite T lymphocyte responses in a clinical trial of rAAV1-AAT gene therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009; 106: 16363–16368.
Jiang H, Pierce GF, Ozelo MC, de Paula EV, Vargas JA, Smith P et al. Evidence of multiyear factor IX expression by AAV-mediated gene transfer to skeletal muscle in an individual with severe hemophilia B. Mol Ther 2006; 14: 452–455.
Flotte TR, Trapnell BC, Humphries M, Carey B, Calcedo R, Rouhani F et al. Phase 2 clinical trial of a recombinant adeno-associated virus vector expressing alpha 1 antitrypsin: interim results. Hum Gene Ther 2011; 22: 1239–1247.
Carpentier A, Frisch F, Labbe SM, Methot J, Gagné C, Déry S et al. Gene therapy with alipogene tiparvovec results in enhanced post-prandial clearance of chylomicrons in LPLD patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2012; 97: 1635–1644.
Gaudet D, Methot J, Gagné C, Déry S, Tremblay K, De Wal J et al. Modifications in triglyceride-rich lipoprotein metabolism induced by alipogene tiparvovec (aav1-lpls447x gene therapy) correlate with clinical benefit in patients with lipoprotein lipase deficiency (lpld). Proc Am Heart Assoc 2010, Circulation suppl, Abstract 21355.
The Society for Surgery of the Alimentary Tract Guideline On The Treatment Of Acute Pancreatitis 2004, ( http://www.ssat.com/cgi-bin/acupanc6.cgi ) (last accessed 12 July 2011).
Iverius PH, Brunzell JD . Human adipose tissue lipoprotein lipase: changes with feeding and relation to postheparin plasma enzyme. Am J Physiol 1985; 249: E107–E114.
Aronica E, van Kempen AA, van der Heide M, Poll-The BT, van Slooten HJ, Troost D et al. Congenital disorder of glycosylation type Ia: a clinicopathological report of a newborn infant with cerebellar pathology. Acta Neuropathol 2005; 109: 433–442.
Miller FW, Love LA, Barbieri SA, Balow JE, Plotz PH . Lymphocyte activation markers in idiopathic myositis: changes with disease activity and differences among clinical and autoantibody subgroups. Clin Exp Immunol 1990; 81: 373–379.
Troost D, Das PK, van den Oord JJ, Louwerse ES . Immunohistological alterations in muscle of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: mononuclear cell phenotypes and expression of MHC products. Clin Neuropathol 1992; 11: 115–120.
Acknowledgements
We thank all participants in the clinical study; staff from the Academic Medical Center (AMC), Amsterdam, the Children's Hospital of Philadelphia; IATEC, TCTC, ECOGENE-21 Clinical Research Center, the Chicoutimi Hospital and Amsterdam Molecular Therapeutics B.V. Medical writing support was provided by Pam Pickering, Conscience Creative LLP, Leatherhead, Surrey, UK. This study was supported by Amsterdam Molecular Therapeutics, The Netherlands. KT is a Université de Montréal post-doctoral and CCRP fellow, and receives support from the Canadian Heart and Stroke Foundation. JM was a Université de Montréal post-doctoral fellow, and received support from the Canadian Institutes for Health Research (CIHR) during the study, and DG was the holder of the Canada Research Chair in preventive genetics and community genomics (www.chairs.gc.ca), which is also supported by a CIHR team grant (no. CTP-82941; http://clinicaltrials.gov/ number: NCT01109498).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The funding body (AMT) was involved in all aspects of the study (study design, data collection and analysis, and data interpretation in collaboration with the CRO and principal investigator. Five authors (J.dW., J.T., S.vD., N.vdB. and V.S-F) are employees of AMT. The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest. The principal investigator of the study (DG) has no financial interest in AMT and made all final editorial decisions regarding the manuscript.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Gene Therapy website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gaudet, D., Méthot, J., Déry, S. et al. Efficacy and long-term safety of alipogene tiparvovec (AAV1-LPLS447X) gene therapy for lipoprotein lipase deficiency: an open-label trial. Gene Ther 20, 361–369 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2012.43
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2012.43
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
tRNA therapeutics for genetic diseases
Nature Reviews Drug Discovery (2024)
-
Prednisolone and rapamycin reduce the plasma cell gene signature and may improve AAV gene therapy in cynomolgus macaques
Gene Therapy (2024)
-
Selection of appropriate non-clinical animal models to ensure translatability of novel AAV-gene therapies to the clinic
Gene Therapy (2024)
-
Lipoamide dehydrogenase (LADH) deficiency: medical perspectives of the structural and functional characterization of LADH and its pathogenic variants
Biologia Futura (2023)
-
Causes, clinical findings and therapeutic options in chylomicronemia syndrome, a special form of hypertriglyceridemia
Lipids in Health and Disease (2022)