Abstract
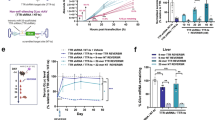
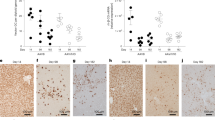
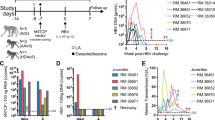
Chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection is closely related to the development of severe liver complications, including hepatocellular carcinoma. In previous studies, we reported that in vivo long-term HBV suppression in transgenic mice can be achieved without apparent toxicity by short hairpin RNA sequentially delivered using adeno-associated viral (AAV) vectors of different serotypes. Our goal herein was to address the clinical utility of this delivery system and, in particular, to determine whether RNA interference (RNAi) and its ability to induce long-term HBV suppression will modulate the development of HBV-associated liver pathology. As a model system, we used a unique HBV transgenic mouse model, containing a 1.3 times over length of the HBV genome, on the ICR mouse background. These transgenic mice produce high serum HBV titers comparable with human chronic HBV patients, and, importantly, manifest characteristic HBV-associated pathology, including progressive hepatocellular injury and the development of hepatocellular adenoma. Using this system, we injected animals with AAV vectors expressing either HBV-specific or a control luciferase-specific short hairpin RNA and followed animals for a total of 18 months. We report herein that AAV-mediated RNAi therapy profoundly inhibits HBV replication and gene expression, with a significant reduction in hepatic regeneration, liver enzymes and, importantly, the appearance of liver adenomas. Indeed, the therapeutic effect of RNAi correlated with the reduction in HBV titers. Our data demonstrate that appropriately designed RNAi therapy has the potential to prevent formation of HBV-associated hepatocellular adenoma.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ganem D, Prince AM . Hepatitis B virus infection—natural history and clinical consequences. N Engl J Med 2004; 350: 1118–1129.
Bosch FX, Ribes J, Cleries R, Diaz M . Epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Liver Dis 2005; 9: 191–211, v.
Chen CJ, Yang HI, Su J, Jen CL, You SL, Lu SN et al. Risk of hepatocellular carcinoma across a biological gradient of serum hepatitis B virus DNA level. JAMA 2006; 295: 65–73.
Iloeje UH, Yang HI, Su J, Jen CL, You SL, Chen CJ . Predicting cirrhosis risk based on the level of circulating hepatitis B viral load. Gastroenterology 2006; 130: 678–686.
Liaw YF, Sung JJ, Chow WC, Farrell G, Lee CZ, Yuen H et al. Lamivudine for patients with chronic hepatitis B and advanced liver disease. N Engl J Med 2004; 351: 1521–1531.
Hadziyannis SJ, Tassopoulos NC, Heathcote EJ, Chang TT, Kitis G, Rizzetto M et al. Long-term therapy with adefovir dipivoxil for HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B for up to 5 years. Gastroenterology 2006; 131: 1743–1751.
Mailliard ME, Gollan JL . Emerging therapeutics for chronic hepatitis B. Annu Rev Med 2006; 57: 155–166.
Konishi M, Wu CH, Wu GY . Inhibition of HBV replication by siRNA in a stable HBV-producing cell line. Hepatology 2003; 38: 842–850.
Wu HL, Huang LR, Huang CC, Lai HL, Liu CJ, Huang YT et al. RNA interference-mediated control of hepatitis B virus and emergence of resistant mutant. Gastroenterology 2005; 128: 708–716.
McCaffrey AP, Nakai H, Pandey K, Huang Z, Salazar FH, Xu H et al. Inhibition of hepatitis B virus in mice by RNA interference. Nat Biotechnol 2003; 21: 639–644.
Morrissey DV, Lockridge JA, Shaw L, Blanchard K, Jensen K, Breen W et al. Potent and persistent in vivo anti-HBV activity of chemically modified siRNAs. Nat Biotechnol 2005; 23: 1002–1007.
Uprichard SL, Boyd B, Althage A, Chisari FV . Clearance of hepatitis B virus from the liver of transgenic mice by short hairpin RNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 773–778.
Chen CC, Ko TM, Ma HI, Wu HL, Xiao X, Li J et al. Long-term inhibition of hepatitis B virus in transgenic mice by double-stranded adeno-associated virus 8-delivered short hairpin RNA. Gene Therapy 2007; 14: 11–19.
Chen CC, Sun CP, Ma HI, Fang CC, Wu PY, Xiao X et al. Comparative study of anti-hepatitis B virus RNA interference by double-stranded adeno-associated virus serotypes 7, 8, and 9. Mol Ther 2009; 17: 352–359.
Guidotti LG, Matzke B, Schaller H, Chisari FV . High-level hepatitis B virus replication in transgenic mice. J Virol 1995; 69: 6158–6169.
Meuleman P, Libbrecht L, Wieland S, De Vos R, Habib N, Kramvis A et al. Immune suppression uncovers endogenous cytopathic effects of the hepatitis B virus. J Virol 2006; 80: 2797–2807.
Nakamoto Y, Guidotti LG, Kuhlen CV, Fowler P, Chisari FV . Immune pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Exp Med 1998; 188: 341–350.
Shimizu Y, Guidotti LG, Fowler P, Chisari FV . Dendritic cell immunization breaks cytotoxic T lymphocyte tolerance in hepatitis B virus transgenic mice. J Immunol 1998; 161: 4520–4529.
Farza H, Hadchouel M, Scotto J, Tiollais P, Babinet C, Pourcel C . Replication and gene expression of hepatitis B virus in a transgenic mouse that contains the complete viral genome. J Virol 1988; 62: 4144–4152.
Araki K, Miyazaki J, Hino O, Tomita N, Chisaka O, Matsubara K et al. Expression and replication of hepatitis B virus genome in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1989; 86: 207–211.
Araki K, Nishimura S, Ochiya T, Okubo K, Miyazaki J, Matsubara K et al. Production and effect of infectious Dane particles in transgenic mice. Jpn J Cancer Res 1991; 82: 235–239.
Zheng Y, Chen WL, Louie SG, Yen TS, Ou JH . Hepatitis B virus promotes hepatocarcinogenesis in transgenic mice. Hepatology 2007; 45: 16–21.
Guidotti LG, Rochford R, Chung J, Shapiro M, Purcell R, Chisari FV . Viral clearance without destruction of infected cells during acute HBV infection. Science 1999; 284: 825–829.
Thimme R, Wieland S, Steiger C, Ghrayeb J, Reimann KA, Purcell RH et al. CD8(+) T cells mediate viral clearance and disease pathogenesis during acute hepatitis B virus infection. J Virol 2003; 77: 68–76.
Chisari FV, Ferrari C . Hepatitis B virus immunopathogenesis. Annu Rev Immunol 1995; 13: 29–60.
Sugiyama M, Tanaka Y, Kurbanov F, Maruyama I, Shimada T, Takahashi S et al. Direct cytopathic effects of particular hepatitis B virus genotypes in severe combined immunodeficiency transgenic with urokinase-type plasminogen activator mouse with human hepatocytes. Gastroenterology 2009; 136: 652–662, e653.
Xu Z, Yen TS, Wu L, Madden CR, Tan W, Slagle BL et al. Enhancement of hepatitis B virus replication by its X protein in transgenic mice. J Virol 2002; 76: 2579–2584.
Koo JS, Seong JK, Park C, Yu DY, Oh BK, Oh SH et al. Large liver cell dysplasia in hepatitis B virus x transgenic mouse liver and human chronic hepatitis B virus-infected liver. Intervirology 2005; 48: 16–22.
Keng VW, Villanueva A, Chiang DY, Dupuy AJ, Ryan BJ, Matise I et al. A conditional transposon-based insertional mutagenesis screen for genes associated with mouse hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Biotechnol 2009; 27: 264–274.
Chen CJ, Iloeje UH, Yang HI . Long-term outcomes in hepatitis B: the REVEAL-HBV study. Clin Liver Dis 2007; 11: 797–816, viii.
DeLoia JA, Burk RD, Gearhart JD . Developmental regulation of hepatitis B surface antigen expression in two lines of hepatitis B virus transgenic mice. J Virol 1989; 63: 4069–4073.
Wang SH, Yeh SH, Lin WH, Wang HY, Chen DS, Chen PJ . Identification of androgen response elements in the enhancer I of hepatitis B virus: a mechanism for sex disparity in chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 2009; 50: 1392–1402.
Lin SM, Yu ML, Lee CM, Chien RN, Sheen IS, Chu CM et al. Interferon therapy in HBeAg positive chronic hepatitis reduces progression to cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol 2007; 46: 45–52.
Yuen MF, Seto WK, Chow DH, Tsui K, Wong DK, Ngai VW et al. Long-term lamivudine therapy reduces the risk of long-term complications of chronic hepatitis B infection even in patients without advanced disease. Antivir Ther 2007; 12: 1295–1303.
Chisari FV, Klopchin K, Moriyama T, Pasquinelli C, Dunsford HA, Sell S et al. Molecular pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma in hepatitis B virus transgenic mice. Cell 1989; 59: 1145–1156.
Dunsford HA, Sell S, Chisari FV . Hepatocarcinogenesis due to chronic liver cell injury in hepatitis B virus transgenic mice. Cancer Res 1990; 50: 3400–3407.
Kim CM, Koike K, Saito I, Miyamura T, Jay G . HBx gene of hepatitis B virus induces liver cancer in transgenic mice. Nature 1991; 351: 317–320.
Yu DY, Moon HB, Son JK, Jeong S, Yu SL, Yoon H et al. Incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in transgenic mice expressing the hepatitis B virus X-protein. J Hepatol 1999; 31: 123–132.
Lee TH, Finegold MJ, Shen RF, DeMayo JL, Woo SL, Butel JS . Hepatitis B virus transactivator X protein is not tumorigenic in transgenic mice. J Virol 1990; 64: 5939–5947.
Chou YC, Jeng KS, Chen ML, Liu HH, Liu TL, Chen YL et al. Evaluation of transcriptional efficiency of hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA by reverse transcription-PCR combined with the restriction enzyme digestion method. J Virol 2005; 79: 1813–1823.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Patrick SC Leung (University of California at Davis) for the critical readings of this manuscript, Dr An-Li Huang (Institute of Biomedical Sciences, Academia Sinica) for technical help with the electron microscopy and Dr Jim-Yih Chen (Institute of Biomedical Sciences, Academia Sinica) for statistical analysis. Dr Mi-Hua Tao was a sabbatical guest at the University of California School of Medicine at Davis in 2008–2009. This work was supported by Academia Sinica Summit Program and National Research Program for Genomic Medicine grant 98-3112-B-001-030 from the National Science Council, Taiwan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, CC., Chang, CM., Sun, CP. et al. Use of RNA interference to modulate liver adenoma development in a murine model transgenic for hepatitis B virus. Gene Ther 19, 25–33 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2011.60
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2011.60