Abstract
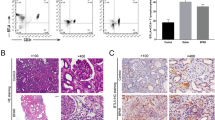
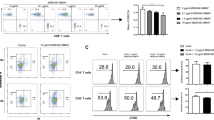
The humoral branch of the immune response has an important role in acute and chronic allograft dysfunction. The CD40/CD40L costimulatory pathway is crucial in B- and T- alloresponse. Our group has developed a new small interfering RNA (siRNA) molecule against CD40 that effectively inhibits its expression. The aim of the present study was to prevent rejection in an acute vascular rejection model of kidney transplant by intra-graft gene silencing with anti-CD40 siRNA (siCD40), associated or not with sub-therapeutic rapamycin. Four groups were designed: unspecific siRNA as control; sub-therapeutic rapamycin; siCD40; and combination therapy. Long-surviving rats were found only in both siCD40-treated groups. The CD40 mRNA was overexpressed in control grafts but treatment with siCD40 decreased its expression. Recipient spleen CD40+ B-lymphocytes were reduced in both siCD40-treated groups. Moreover, CD40 silencing reduced donor-specific antibodies, graft complement deposition and immune-inflammatory mediators. The characteristic histological features of humoral rejection were not found in siCD40-treated grafts, which showed a more cellular histological pattern. Therefore, the intra-renal effective blockade of the CD40/CD40L signal reduces the graft inflammation as well as the incidence of humoral vascular acute rejection, finally changing the type of rejection from humoral to cellular.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Turgeon NA, Kirk AD, Iwakoshi NN . Differential effects of donor-specific alloantibody. Transplant Rev (Orlando) 2009; 23: 25–33.
Gilligan BJ, Woo HM, Kosieradzki M, Torrealba JR, Southard JH, Mangino MJ . Prolonged hypothermia causes primary nonfunction in preserved canine renal allografts due to humoral rejection. Am J Transplant 2004; 4: 1266–1273.
Van Kooten C, Banchereau J . CD40-CD40 ligand. J Leukoc Biol 2000; 67: 2–17.
Shoker AS, Lun ZR, Choudry R, Saxena A . Analysis of the CD40/CD40L role in the sustenance of alloreactive antibody production. Transpl Immunol 2001; 8: 219–228.
Li XL, Menoret S, Le Mauff B, Angin M, Anegon I . Promises and obstacles for the blockade of CD40-CD40L interactions in allotransplantation. Transplantation 2008; 86: 10–15.
Rizvi M, Pathak D, Freedman JE, Chakrabarti S . CD40-CD40 ligand interactions in oxidative stress, inflammation and vascular disease. Trends Mol Med 2008; 14: 530–538.
Vowinkel T, Wood KC, Stokes KY, Russell J, Krieglstein CF, Granger DN . Differential expression and regulation of murine CD40 in regional vascular beds. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2006; 290: H631–H639.
van Kooten C, Woltman AM, Daha MR . Immunological function of tubular epithelial cells: the functional implications of CD40 expression. Exp Nephrol 2000; 8: 203–207.
Yellin MJ, D’Agati V, Parkinson G, Han AS, Szema A, Baum D et al. Immunohistologic analysis of renal CD40 and CD40L expression in lupus nephritis and other glomerulonephritides. Arthritis Rheum 1997; 40: 124–134.
Gaweco AS, Mitchell BL, Lucas BA, McClatchey KD, Van Thiel DH . CD40 expression on graft infiltrates and parenchymal CD154 (CD40L) induction in human chronic renal allograft rejection. Kidney Int 1999; 55: 1543–1552.
Mengel M, Mueller I, Behrend M, von Wasielewski R, Radermacher J, Schwarz A et al. Prognostic value of cytotoxic T-lymphocytes and CD40 in biopsies with early renal allograft rejection. Transpl Int 2004; 17: 293–300.
Pluvinet R, Olivar R, Krupinski J, Herrero-Fresneda I, Luque A, Torras J et al. CD40: an upstream master switch for endothelial cell activation uncovered by RNAi-coupled transcriptional profiling. Blood 2008; 112: 3624–3637.
Larsen CP, Elwood ET, Alexander DZ, Ritchie SC, Hendrix R, Tucker-Burden C et al. Long-term acceptance of skin and cardiac allografts after blocking CD40 and CD28 pathways. Nature 1996; 381: 434–438.
Kirk AD, Harlan DM, Armstrong NN, Davis TA, Dong Y, Gray GS et al. CTLA4-Ig and anti-CD40 ligand prevent renal allograft rejection in primates. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997; 94: 8789–8794.
Kirk AD, Burkly LC, Batty DS, Baumgartner RE, Berning JD, Buchanan K et al. Treatment with humanized monoclonal antibody against CD154 prevents acute renal allograft rejection in nonhuman primates. Nat Med 1999; 5: 686–693.
Ossevoort MA, Ringers J, Kuhn EM, Boon L, Lorre K, van den Hout Y et al. Prevention of renal allograft rejection in primates by blocking the B7/CD28 pathway. Transplantation 1999; 68: 1010–1018.
Suntharalingam G, Perry MR, Ward S, Brett SJ, Castello-Cortes A, Brunner MD et al. Cytokine storm in a phase 1 trial of the anti-CD28 monoclonal antibody TGN1412. N Engl J Med 2006; 355: 1018–1028.
Kawai T, Andrews D, Colvin RB, Sachs DH, Cosimi AB . Thromboembolic complications after treatment with monoclonal antibody against CD40 ligand. Nat Med 2000; 6: 114.
Pluvinet R, Petriz J, Torras J, Herrero-Fresneda I, Cruzado JM, Grinyo JM et al. RNAi-mediated silencing of CD40 prevents leukocyte adhesion on CD154-activated endothelial cells. Blood 2004; 104: 3642–3646.
Herrero-Fresneda I, Franquesa M, Torras J, Vidal A, Aran J, Pluvinet R et al. Role of cold ischemia in acute rejection: characterization of a humoral-like acute rejection in experimental renal transplantation. Transplant Proc 2005; 37: 3712–3715.
Herrero-Fresneda I, Torras J, Vidal A, Lloberas N, Cruzado JM, Grinyo JM . Reduction of postischemic immune inflammatory response: an effective strategy for attenuating chronic allograft nephropathy. Transplantation 2005; 79: 165–173.
Sacks SH, Zhou W . Locally produced complement and its role in renal allograft rejection. Am J Transplant 2003; 3: 927–932.
Pratt JR, Basheer SA, Sacks SH . Local synthesis of complement component C3 regulates acute renal transplant rejection. Nat Med 2002; 8: 582–587.
Sacks S, Zhou W . New boundaries for complement in renal disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 2008; 19: 1865–1869.
Linfert D, Chowdhry T, Rabb H . Lymphocytes and ischemia-reperfusion injury. Transplant Rev (Orlando) 2009; 23: 1–10.
Jang HR, Ko GJ, Wasowska BA, Rabb H . The interaction between ischemia-reperfusion and immune responses in the kidney. J Mol Med 2009; 87: 859–864.
Burne-Taney MJ, Ascon DB, Daniels F, Racusen L, Baldwin W, Rabb H . B cell deficiency confers protection from renal ischemia reperfusion injury. J Immunol 2003; 171: 3210–3215.
Xu H, Yan J, Huang Y, Chilton PM, Ding C, Schanie CL et al. Costimulatory blockade of CD154-CD40 in combination with T-cell lymphodepletion results in prevention of allogeneic sensitization. Blood 2008; 111: 3266–3275.
Andreakos E, Foxwell B, Feldmann M . Is targeting Toll-like receptors and their signaling pathway a useful therapeutic approach to modulating cytokine-driven inflammation? Immunol Rev 2004; 202: 250–265.
Andrade CF, Waddell TK, Keshavjee S, Liu M . Innate immunity and organ transplantation: the potential role of toll-like receptors. Am J Transplant 2005; 5: 969–975.
Land WG . The role of postischemic reperfusion injury and other nonantigen-dependent inflammatory pathways in transplantation. Transplantation 2005; 79: 505–514.
Weiler M, Kachko L, Chaimovitz C, Van Kooten C, Douvdevani A . CD40 ligation enhances IL-15 production by tubular epithelial cells. J Am Soc Nephrol 2001; 12: 80–87.
Kirkiles-Smith NC, Mahboubi K, Plescia J, McNiff JM, Karras J, Schechner JS et al. IL-11 protects human microvascular endothelium from alloinjury in vivo by induction of survivin expression. J Immunol 2004; 172: 1391–1396.
Lai PC, Smith J, Bhangal G, Chaudhry KA, Chaudhry AN, Keith Jr JC et al. Interleukin-11 reduces renal injury and glomerular NF-kappa B activity in murine experimental glomerulonephritis. Nephron Exp Nephrol 2005; 101: e146–e154.
Curti A, Ratta M, Corinti S, Girolomoni G, Ricci F, Tazzari P et al. Interleukin-11 induces Th2 polarization of human CD4(+) T cells. Blood 2001; 97: 2758–2763.
Malyszko J, Malyszko JS, Pawlak K, Wolczynski S, Mysliwiec M . Apelin, a novel adipocytokine, in relation to endothelial function and inflammation in kidney allograft recipients. Transplant Proc 2008; 40: 3466–3469.
Kleinz MJ, Baxter GF . Apelin reduces myocardial reperfusion injury independently of PI3K/Akt and P70S6 kinase. Regul Pept 2008; 146: 271–277.
Masri B, Morin N, Cornu M, Knibiehler B, Audigier Y . Apelin (65-77) activates p70 S6 kinase and is mitogenic for umbilical endothelial cells. FASEB J 2004; 18: 1909–1911.
Han S, Wang G, Qi X, Englander EW, Greeley Jr GH . Involvement of a Stat3 binding site in inflammation-induced enteric apelin expression. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2008; 295: G1068–G1078.
Tiani C, Garcia-Pras E, Mejias M, de Gottardi A, Berzigotti A, Bosch J et al. Apelin signaling modulates splanchnic angiogenesis and portosystemic collateral vessel formation in rats with portal hypertension. J Hepatol 2009; 50: 296–305.
Kim SH, Zukowski K, Novak RF . Rapamycin effects on mTOR signaling in benign, premalignant and malignant human breast epithelial cells. Anticancer Res 2009; 29: 1143–1150.
Racusen LC, Solez K, Colvin RB, Bonsib SM, Castro MC, Cavallo T et al. The Banff 97 working classification of renal allograft pathology. Kidney Int 1999; 55: 713–723.
Herrero-Fresneda I, Torras J, Cruzado JM, Condom E, Vidal A, Riera M et al. Do alloreactivity and prolonged cold ischemia cause different elementary lesions in chronic allograft nephropathy? Am J Pathol 2003; 162: 127–137.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grants from Instituto de Salud Carlos III/FIS (PI03/0082, PI03/0516, PI06/0230, PS09/00107) and Fundación SENEFRO 2007. Immaculada Herrero-Fresneda and Josep M. Aran are researchers from ‘Programa Estabilización Investigadores’ financed by ISCIII and Dpt. Salut Generalitat Catalunya. Elia Ripoll is the recipient of a fellowship from IDIBELL. We thank Núria Bolaños and Esther Herrero and Serveis Científico-Tècnics (UB, Bellvitge) for technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Gene Therapy website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ripoll, E., Pluvinet, R., Torras, J. et al. In vivo therapeutic efficacy of intra-renal CD40 silencing in a model of humoral acute rejection. Gene Ther 18, 945–952 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2011.39
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2011.39
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The double edge of anti-CD40 siRNA therapy: It increases renal microcapillar density but favours the generation of an inflammatory milieu in the kidneys of ApoE−/− mice
Journal of Inflammation (2019)
-
CD154-CD40 T-cell co-stimulation pathway is a key mechanism in kidney ischemia-reperfusion injury
Kidney International (2015)
-
CD40 Generation 2.5 Antisense Oligonucleotide Treatment Attenuates Doxorubicin-induced Nephropathy and Kidney Inflammation
Molecular Therapy - Nucleic Acids (2015)
-
siRNA Technology in Kidney Transplantation: Current Status and Future Potential
BioDrugs (2014)
-
Progress Toward In Vivo Use of siRNAs-II
Molecular Therapy (2012)