Abstract
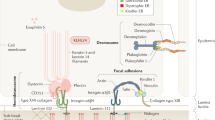
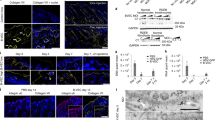
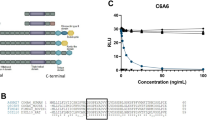
Recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (RDEB) is a severe genodermatosis caused by loss-of-function mutations in COL7A1 encoding type VII collagen, the component of anchoring fibrils. As exogenous type VII collagen may elicit a deleterious immune response in RDEB patients during upcoming clinical trials of gene therapies or protein replacement therapies, we developed enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and enzyme-linked immunosorbent spot (ELISPOT) assays to analyze B- and T-cell responses, to the full-length type VII collagen. The ELISA was highly sensitive and specific when tested against sera from 41 patients with epidermolysis bullosa acquisita (EBA), and the IFN-γ ELISPOT detected a cellular response that correlated with ongoing EBA manifestations. Both tests were next applied to assess the risk of an immune response to type VII collagen in seven RDEB patients with a range of type VII collagen expression profiles. Immune responses against type VII collagen were dependent on the expression of type VII collagen protein, and consequently on the nature and position of the respective COL7A1 mutations. These immunologic tests will be helpful for the selection of RDEB patients for future clinical trials aiming at restoring type VII collagen expression, and in monitoring their immune response to type VII collagen after treatment.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Uitto J, Pulkkinen L, Christiano AM . Molecular basis of the dystrophic and junctional forms of epidermolysis bullosa: mutations in the type VII collagen and kalinin (laminin 5) genes. J Invest Dermatol 1994; 103: 39S–46S.
Uitto J, Chung-Honet LC, Christiano AM . Molecular biology and pathology of type VII collagen. Exp Dermatol 1992; 1: 2–11.
Hovnanian A, Hilal L, Blanchet-Bardon C, de Prost Y, Christiano AM, Uitto J et al. Recurrent nonsense mutations within the type VII collagen gene in patients with severe recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Am J Hum Genet 1994; 55: 289–296.
Aumailley M, Has C, Tunggal L, Bruckner-Tuderman L . Molecular basis of inherited skin-blistering disorders, and therapeutic implications. Expert Rev Mol Med 2006; 8: 1–21.
Varki R, Sadowski S, Uitto J, Pfendner E . Epidermolysis bullosa. II. Type VII collagen mutations and phenotype-genotype correlations in the dystrophic subtypes. J Med Genet 2007; 44: 181–192.
Fine JD, Eady RA, Bauer EA, Bauer JW, Bruckner-Tuderman L, Heagerty A et al. The classification of inherited epidermolysis bullosa (EB): Report of the Third International Consensus Meeting on Diagnosis and Classification of EB. J Am Acad Dermatol 2008; 58: 931–950.
Dang N, Murrell DF . Mutation analysis and characterization of COL7A1 mutations in dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Exp Dermatol 2008; 17: 553–568.
Mavilio F, Pellegrini G, Ferrari S, Di Nunzio F, Di Iorio E, Recchia A et al. Correction of junctional epidermolysis bullosa by transplantation of genetically modified epidermal stem cells. Nat Med 2006; 12: 1397–1402.
Titeux M, Pendaries V, Zanta-Boussif A, Décha A, Pironon N, Tonasso L et al. SIN retroviral vectors expressing COL7A1 under human promoters for ex vivo gene therapy of recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Mol Ther 2010 (in press).
Chen H, Berard J, Luo H, Landers M, Vinet B, Bradley WE et al. Compromised allograft rejection response in transgenic mice expressing antisense sequences to retinoic acid receptor beta2. J Immunol 1997; 159: 623–634.
Tripathy SK, Black HB, Goldwasser E, Leiden JM . Immune responses to transgene-encoded proteins limit the stability of gene expression after injection of replication-defective adenovirus vectors. Nat Med 1996; 2: 545–550.
Aubert D, Menoret S, Chiari E, Pichard V, Durand S, Tesson L et al. Cytotoxic immune response blunts long-term transgene expression after efficient retroviral-mediated hepatic gene transfer in rat. Mol Ther 2002; 5: 388–396.
Chirino AJ, Ary ML, Marshall SA . Minimizing the immunogenicity of protein therapeutics. Drug Discov Today 2004; 9: 82–90.
Koren E, Zuckerman LA, Mire-Sluis AR . Immune responses to therapeutic proteins in humans—clinical significance, assessment and prediction. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 2002; 3: 349–360.
Chuah MK, Schiedner G, Thorrez L, Brown B, Johnston M, Gillijns V et al. Therapeutic factor VIII levels and negligible toxicity in mouse and dog models of hemophilia A following gene therapy with high-capacity adenoviral vectors. Blood 2003; 101: 1734–1743.
Remington J, Wang X, Hou Y, Zhou H, Burnett J, Muirhead T et al. Injection of recombinant human type VII collagen corrects the disease phenotype in a murine model of dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Mol Ther 2009; 17: 26–33.
Madoiwa S, Yamauchi T, Kobayashi E, Hakamata Y, Dokai M, Makino N et al. Induction of factor VIII-specific unresponsiveness by intrathymic factor VIII injection in murine hemophilia A. J Thromb Haemost 2009; 7: 811–824.
Barbosa MD, Celis E . Immunogenicity of protein therapeutics and the interplay between tolerance and antibody responses. Drug Discov Today 2007; 12: 674–681.
Czerkinsky CC, Nilsson LA, Nygren H, Ouchterlony O, Tarkowski A . A solid-phase enzyme-linked immunospot (ELISPOT) assay for enumeration of specific antibody-secreting cells. J Immunol Methods 1983; 65: 109–121.
van der Meide PH, Groenestein RJ, de Labie MC, Heeney J, Pala P, Slaoui M . Enumeration of lymphokine-secreting cells as a quantitative measure for cellular immune responses in rhesus macaques. J Med Primatol 1995; 24: 271–281.
Roenigk Jr HH, Ryan JG, Bergfeld WF . Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita. Report of three cases and review of all published cases. Arch Dermatol 1971; 103: 1–10.
Woodley DT, Burgeson RE, Lunstrum G, Bruckner-Tuderman L, Reese MJ, Briggaman RA . Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita antigen is the globular carboxyl terminus of type VII procollagen. J Clin Invest 1988; 81: 683–687.
Sitaru C, Mihai S, Zillikens D . The relevance of the IgG subclass of autoantibodies for blister induction in autoimmune bullous skin diseases. Arch Dermatol Res 2007; 299: 1–8.
Woodley DT, Remington J, Chen M . Autoimmunity to type VII collagen: epidermolysis bullosa acquisita. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 2007; 33: 78–84.
Chen M, Chan LS, Cai X, O'Toole EA, Sample JC, Woodley DT . Development of an ELISA for rapid detection of anti-type VII collagen autoantibodies in epidermolysis bullosa acquisita. J Invest Dermatol 1997; 108: 68–72.
Bruckner P, Prockop DJ . Proteolytic enzymes as probes for the triple-helical conformation of procollagen. Anal Biochem 1981; 110: 360–368.
Chen M, Costa FK, Lindvay CR, Han YP, Woodley DT . The recombinant expression of full-length type VII collagen and characterization of molecular mechanisms underlying dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 2118–2124.
Morris NP, Keene DR, Glanville RW, Bentz H, Burgeson RE . The tissue form of type VII collagen is an antiparallel dimer. J Biol Chem 1986; 261: 5638–5644.
Guo L, Hu-Li J, Paul WE . Probabilistic regulation in TH2 cells accounts for monoallelic expression of IL-4 and IL-13. Immunity 2005; 23: 89–99.
Titeux M, Pendaries V, Tonasso L, Decha A, Bodemer C, Hovnanian A . A frequent functional SNP in the MMP1 promoter is associated with higher disease severity in recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Hum Mutat 2008; 29: 267–276.
Hein LK, Bawden M, Muller VJ, Sillence D, Hopwood JJ, Brooks DA . alpha-L-iduronidase premature stop codons and potential read-through in mucopolysaccharidosis type I patients. J Mol Biol 2004; 338: 453–462.
Yunis EJ, Zuniga J, Romero V . Chimerism and tetragametic chimerism in humans: implications in autoimmunity, allorecognition and tolerance. Immunol Res 2007; 38: 213–236.
Williams CA, Wallace MR, Drury KC, Kipersztok S, Edwards RK, Williams RS et al. Blood lymphocyte chimerism associated with IVF and monochorionic dizygous twinning: case report. Hum Reprod 2004; 19: 2816–2821.
Rizzi M, Gerloni M, Srivastava AS, Wheeler MC, Schuler K, Carrier E et al. In utero DNA immunisation. Immunity over tolerance in fetal life. Vaccine 2005; 23: 4273–4282.
Watts AM, Stanley JR, Shearer MH, Hefty PS, Kennedy RC . Fetal immunization of baboons induces a fetal-specific antibody response. Nat Med 1999; 5: 427–430.
Lapiere JC, Woodley DT, Parente MG, Iwasaki T, Wynn KC, Christiano AM et al. Epitope mapping of type VII collagen. Identification of discrete peptide sequences recognized by sera from patients with acquired epidermolysis bullosa. J Clin Invest 1993; 92: 1831–1839.
Jones DA, Hunt III SW, Prisayanh PS, Briggaman RA, Gammon WR . Immunodominant autoepitopes of type VII collagen are short, paired peptide sequences within the fibronectin type III homology region of the noncollagenous (NC1) domain. J Invest Dermatol 1995; 104: 231–235.
Woodley DT, O'Keefe EJ, McDonald JA, Reese MJ, Briggaman RA, Gammon WR . Specific affinity between fibronectin and the epidermolysis bullosa acquisita antigen. J Clin Invest 1987; 79: 1826–1830.
Chen M, Doostan A, Bandyopadhyay P, Remington J, Wang X, Hou Y et al. The cartilage matrix protein subdomain of type VII collagen is pathogenic for epidermolysis bullosa acquisita. Am J Pathol 2007; 170: 2009–2018.
Rocino A, Santagostino E, Mancuso ME, Mannucci PM . Immune tolerance induction with recombinant factor VIII in hemophilia A patients with high responding inhibitors. Haematologica 2006; 91: 558–561.
Mingozzi F, Hasbrouck NC, Basner-Tschakarjan E, Edmonson SA, Hui DJ, Sabatino DE et al. Modulation of tolerance to the transgene product in a nonhuman primate model of AAV-mediated gene transfer to liver. Blood 2007; 110: 2334–2341.
Joffre O, Santolaria T, Calise D, Al Saati T, Hudrisier D, Romagnoli P et al. Prevention of acute and chronic allograft rejection with CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory T lymphocytes. Nat Med 2008; 14: 88–92.
Faria AM, Weiner HL . Oral tolerance: therapeutic implications for autoimmune diseases. Clin Dev Immunol 2006; 13: 143–157.
Dobrzynski E, Fitzgerald JC, Cao O, Mingozzi F, Wang L, Herzog RW . Prevention of cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses to factor IX-expressing hepatocytes by gene transfer-induced regulatory T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 4592–4597.
Cao O, Furlan-Freguia C, Arruda VR, Herzog RW . Emerging role of regulatory T cells in gene transfer. Curr Gene Ther 2007; 7: 381–390.
Cao O, Dobrzynski E, Wang L, Nayak S, Mingle B, Terhorst C et al. Induction and role of regulatory CD4+CD25+ T cells in tolerance to the transgene product following hepatic in vivo gene transfer. Blood 2007; 110: 1132–1140.
Ortiz-Urda S, Lin Q, Green CL, Keene DR, Marinkovich MP, Khavari PA . Injection of genetically engineered fibroblasts corrects regenerated human epidermolysis bullosa skin tissue. J Clin Invest 2003; 111: 251–255.
Wong T, Gammon L, Liu L, Mellerio JE, Dopping-Hepenstal PJ, Pacy J et al. Potential of fibroblast cell therapy for recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. J Invest Dermatol 2008; 128: 2179–2189.
Woodley DT, Krueger GG, Jorgensen CM, Fairley JA, Atha T, Huang Y et al. Normal and gene-corrected dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa fibroblasts alone can produce type VII collagen at the basement membrane zone. J Invest Dermatol 2003; 121: 1021–1028.
Mecklenbeck S, Compton SH, Mejía JE, Cervini R, Hovnanian A, Bruckner-Tuderman L et al. A microinjected COL7A1-PAC vector restores synthesis of intact procollagen VII in a dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa keratinocyte cell line. Human Gene Therapy 2002; 13: 1655–1662.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Mei Chen for the gift of the polyclonal anti-NC1 antibody, and Professor Yann Barrandon for sharing the immortalized RDEB keratinocyte cell line and for the protein extract of patient 10 cells. We are grateful to Drs Joost van Meerwijk and Paola Romagnoli for fruitful discussion, and Drs Gilbert Fournié and Abdelhadi Saoudi for their critical reading of the manuscript. This work was supported by the Epidermolyse Bulleuse Association d'Entraide (EBAE), the Association Française contre les Myopathies (AFM), the Geneskin European coordination action project, the Therapeuskin European specific targeted research project, the Midi-Pyrénées Region, the French Ministry of Health through the reference centers for genetic skin diseases, and the Agence Nationale pour la Recherche (ANR, DEBCURE, No. ANR-07-BLAN-0105).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Gene Therapy website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pendaries, V., Gasc, G., Titeux, M. et al. Immune reactivity to type VII collagen: implications for gene therapy of recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. Gene Ther 17, 930–937 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2010.36
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2010.36
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Direct reprogramming of mouse fibroblasts into neural cells via Porphyra yezoensis polysaccharide based high efficient gene co-delivery
Journal of Nanobiotechnology (2017)
-
Epidermolysis Bullosa Acquisita Develops in Dominant Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa
Journal of Investigative Dermatology (2016)
-
Analysis of the functional consequences of targeted exon deletion in COL7A1 reveals prospects for dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa therapy
Molecular Therapy (2016)
-
De Novo Anti-Type VII Collagen Antibodies in Patients with Recessive Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa
Journal of Investigative Dermatology (2014)
-
Systemic Protein Therapy for Recessive Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa: How Far Are We from Clinical Translation?
Journal of Investigative Dermatology (2013)