Abstract
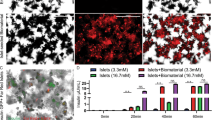
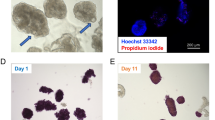
Insulin-like growth factor-II (IGF-II) has been shown to promote pancreatic β-cell survival. We evaluated the effect of co-encapsulating islets and bioengineered IGF-II-producing cells on islet cell survival. IGF-II or green fast protein (GFP) genes were transferred into TM4 cells, and purified using a neomycin resistance gene, leading to pure cell cultures (TM4-IGF-II or TM4-GFP) with a stable overexpression of the transferred gene. Islets were co-encapsulated with TM4-IGF-II or TM4-GFP, or encapsulated alone in alginate microcapsules. Rat and mouse islet cell survival was studied in vitro and in vivo, respectively. After 12 days in culture, islet viability (dual staining, acridine orange/propidium iodide) was 83% with TM4-IGF-II, compared with 51% (P<0.05) and 41% (P<0.001) with TM4-GFP and islets alone, respectively. The study of islet necrotic centers and the evaluation of islet function, using the MTS (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-5-(3-carboxymethoxyphenyl)-2-(4-sulfophenyl)-2H-tetrazolium, inner salt) assay, yielded similar results. From 125 days after transplantation, more diabetic mice maintained normoglycemia when they were transplanted with islets co-encapsulated with TM4-IGF-II (4/7). A significant difference for the maintenance of normoglycemia was observed between recipients of islets co-encapsulated with TM4-IGF-II versus islets alone (P=0.023), or with TM4-GFP (P=0.048). In conclusion, the co-encapsulation of islets with bioengineered IGF-II-producing cells promotes islet cell survival.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shapiro AM, Lakey JR, Ryan EA, Korbutt GS, Toth E, Warnock GL et al. Islet transplantation in seven patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus using a glucocorticoid-free immunosuppressive regimen. N Engl J Med 2000; 343: 230–238.
Ryan EA, Paty BW, Senior PA, Bigam D, Alfadhli E, Kneteman NM et al. Five-year follow-up after clinical islet transplantation. Diabetes 2005; 54: 2060–2069.
Shapiro AM, Ricordi C, Hering BJ, Auchincloss H, Lindblad R, Robertson RP et al. International trial of the Edmonton protocol for islet transplantation. N Engl J Med 2006; 355: 1318–1330.
Rosenberg L . In vivo cell transformation: neogenesis of beta cells from pancreatic ductal cells. Cell Transplant 1995; 4: 371–383.
Ilieva A, Yuan S, Wang RN, Agapitos D, Hill DJ, Rosenberg L . Pancreatic islet cell survival following islet isolation: the role of cellular interactions in the pancreas. J Endocrinol 1999; 161: 357–364.
Robitaille R, Dusseault J, Henley N, Rosenberg L, Halle JP . Insulin-like growth factor II allows prolonged blood glucose normalization with a reduced islet cell mass transplantation. Endocrinology 2003; 144: 3037–3045.
Hill DJ, Strutt B, Arany E, Zaina S, Coukell S, Graham CF . Increased and persistent circulating insulin-like growth factor II in neonatal transgenic mice suppresses developmental apoptosis in the pancreatic islets. Endocrinology 2000; 141: 1151–1157.
Street CN, Lakey JR, Rajotte RV, Shapiro AM, Kieffer TJ, Lyon JG et al. Enriched human pancreatic ductal cultures obtained from selective death of acinar cells express pancreatic and duodenal homeobox gene-1 age-dependently. Rev Diabet Stud 2004; 1: 66–79.
Stempien MM, Fong NM, Rall LB, Bell GI . Sequence of a placental cDNA encoding the mouse insulin-like growth factor II precursor. DNA 1986; 5: 357–361.
Clark SA, Chick WL . Islet cell culture in defined serum-free medium. Endocrinology 1990; 126: 1895–1903.
Tang F, Hughes JA . Synthesis of a single-tailed cationic lipid and investigation of its transfection. J Control Release 1999; 62: 345–358.
Prud′homme GJ, Glinka Y, Khan AS, Draghia-Akli R . Electroporation-enhanced nonviral gene transfer for the prevention or treatment of immunological, endocrine and neoplastic diseases. Curr Gene Ther 2006; 6: 243–273.
Cheng H, Wolfe SH, Valencia V, Qian K, Shen L, Phillips MI et al. Efficient and persistent transduction of exocrine and endocrine pancreas by adeno-associated virus type 8. J Biomed Sci 2007; 14: 585–594.
Wang Z, Zhu T, Rehman KK, Bertera S, Zhang J, Chen C et al. Widespread and stable pancreatic gene transfer by adeno-associated virus vectors via different routes. Diabetes 2006; 55: 875–884.
Park MK, Kim DK, Lee HJ . Adenoviral mediated hepatocyte growth factor gene attenuates hyperglycemia and beta cell destruction in overt diabetic mice. Exp Mol Med 2003; 35: 494–500.
Lopez-Talavera JC, Garcia-Ocana A, Sipula I, Takane KK, Cozar-Castellano I, Stewart AF . Hepatocyte growth factor gene therapy for pancreatic islets in diabetes: reducing the minimal islet transplant mass required in a glucocorticoid-free rat model of allogeneic portal vein islet transplantation. Endocrinology 2004; 145: 467–474.
Rao P, Cozar-Castellano I, Roccisana J, Vasavada RC, Garcia-Ocana A . Hepatocyte growth factor gene therapy for islet transplantation. Expert Opin Biol Ther 2004; 4: 507–518.
She F, Sun W, Mao JM, Wang X . Calcitonin gene-related peptide gene therapy suppresses reactive oxygen species in the pancreas and prevents mice from autoimmune diabetes. Sheng Li Xue Bao 2003; 55: 625–632.
Miao G, Mace J, Kirby M, Hopper A, Peverini R, Chinnock R et al. In vitro and in vivo improvement of islet survival following treatment with nerve growth factor. Transplantation 2006; 81: 519–524.
Narang AS, Sabek O, Gaber AO, Mahato RI . Co-expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist improves human islet survival and function. Pharm Res 2006; 23: 1970–1982.
Chong MM, Chen Y, Darwiche R, Dudek NL, Irawaty W, Santamaria P et al. Suppressor of cytokine signaling-1 overexpression protects pancreatic beta cells from CD8+ T cell-mediated autoimmune destruction. J Immunol 2004; 172: 5714–5721.
Benhamou PY, Mullen Y, Shaked A, Bahmiller D, Csete ME . Decreased alloreactivity to human islets secreting recombinant viral interleukin 10. Transplantation 1996; 62: 1306–1312.
Grey ST, Longo C, Shukri T, Patel VI, Csizmadia E, Daniel S et al. Genetic engineering of a suboptimal islet graft with A20 preserves beta cell mass and function. J Immunol 2003; 170: 6250–6256.
Sung HH, Juang JH, Lin YC, Kuo CH, Hung JT, Chen A et al. Transgenic expression of decoy receptor 3 protects islets from spontaneous and chemical-induced autoimmune destruction in nonobese diabetic mice. J Exp Med 2004; 199: 1143–1151.
Suarez-Pinzon WL, Marcoux Y, Ghahary A, Rabinovitch A . Gene transfection and expression of transforming growth factor-beta1 in nonobese diabetic mouse islets protects beta-cells in syngeneic islet grafts from autoimmune destruction. Cell Transplant 2002; 11: 519–528.
Tellez N, Montolio M, Biarnes M, Castano E, Soler J, Montanya E . Adenoviral overexpression of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist protein increases beta-cell replication in rat pancreatic islets. Gene Therapy 2005; 12: 120–128.
Tian C, Ansari MJ, Paez-Cortez J, Bagley J, Godwin J, Donnarumma M et al. Induction of robust diabetes resistance and prevention of recurrent type 1 diabetes following islet transplantation by gene therapy. J Immunol 2007; 179: 6762–6769.
Sanlioglu AD, Griffith TS, Omer A, Dirice E, Sari R, Altunbas HA et al. Molecular mechanisms of death ligand-mediated immune modulation: a gene therapy model to prolong islet survival in type 1 diabetes. J Cell Biochem 2008; 104: 710–720.
Langlois G, Dusseault J, Bilodeau S, Tam SK, Magassouba D, Halle JP . Direct effect of alginate purification on the survival of islets immobilized in alginate-based microcapsules. Acta Biomater 2009; 5: 3433–3440.
De Vos P, de Han BJ, Faas MM . Development of a bioartificial hypervascularized removable implantation site for encapsulated islets. In: Hallé JP de Vos P, Rosenberg L (eds). The Bioartificial Pancreas and other Biohybrid Therapies. Transworld Research Network: Kerala, India, 2009, pp 373–382.
Lewis AS, Fisher RJ, Weir GC, Colton CK . Improving oxygen supply to encapsulated cells and islets. In: Hallé JP de Vos P, Rosenberg L (eds). The Bioartificial Pancreas and other Biohybrid Therapies. Transworld Research Network: Kerala, India, 2009, pp 205–242.
Gotoh M, Maki T, Kiyoizumi T, Satomi S, Monaco AP . An improved method for isolation of mouse pancreatic islets. Transplantation 1985; 40: 437–438.
Hallé JP, Leblond FA, Pariseau JF, Jutras P, Brabant MJ, Lepage Y . Studies on 300 μm microcapsules II - Parameters governing the production of alginate beads by high voltage electrostatic pulses. Cell Transplant 1994; 3: 365–372.
Bank HL . Assessment of islet cell viability using fluorescent dyes. Diabetologia 1987; 30: 812–816.
Cory AH, Owen TC, Barltrop JA, Cory JG . Use of an aqueous soluble tetrazolium/formazan assay for cell growth assays in culture. Cancer Commun 1991; 3: 207–212.
Acknowledgements
We thank Stéphanie Bilodeau for revising the manuscript. This work was supported by the Canadian Diabetes Association, Diabète Québec and l’Association des Diabétiques de Lanaudière. JD has received a student scholarship from the Fonds de recherche en santé du Québec. RL is financially supported by the CIHR-JDRF Regenerative Medicine program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jourdan, G., Dusseault, J., Benhamou, P. et al. Co-encapsulation of bioengineered IGF-II-producing cells and pancreatic islets: effect on beta-cell survival. Gene Ther 18, 539–545 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2010.166
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2010.166
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
A gelatin hydrogel nonwoven fabric improves outcomes of subcutaneous islet transplantation
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Pancreatic Islet Transplantation Technologies: State of the Art of Micro- and Macro-Encapsulation
Current Transplantation Reports (2017)
-
Alginate Hydrogel as a Potential Alternative to Hyaluronic Acid as Submucosal Injection Material
Digestive Diseases and Sciences (2013)