Abstract
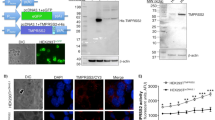
First-generation adenoviral (Ad) vectors are frequently used vectors for experimental and clinical gene transfer. Earlier it has been shown that parallel overexpression of the cell cycle regulator p21Waf1/Cip1 (p21) or antiapoptotic bcl-2 from a second vector reduces cytotoxicity and improves transgene expression. Here, we investigate whether the co-expression of p21 and α1-antitrypsin from a single vector improves vector safety and α1-antitrypsin expression. Cell lines (A549 and HeLa) and primary cells (small airway epithelial cells and hepatocytes) were infected with adenovirus vectors transducing α1-antitrypsin with (AdCMV.p21-RSV.hAAT) or without (AdRSV.hAAT) p21. α1-Antitrypsin expression and cytotoxicity were analyzed using western blot/ELISA and LDH/ALT/AST assays, respectively. Cell cycle profiles were determined by flow cytometry. Co-expression of p21 strongly increased the α1-antitrypsin expression in all cell types and at all doses tested. No changes in ALT/AST from hepatocytes and only minor increases in the LDH release in A549 and HeLa were observed with either vector. Cell cycle profiles were also not affected adversely. Incorporation of p21 in Ad vectors together with a gene of interest improves the vector performance; such vectors will allow the application of lower doses and thereby reduce immunological side effects.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang Y, Jooss KU, Su Q, Ertl HC, Wilson JM . Immune responses to viral antigens versus transgene product in the elimination of recombinant adenovirus-infected hepatocytes in vivo. Gene Therapy 1996; 3: 137–144.
Teodoro JG, Branton PE . Regulation of apoptosis by viral gene products. J Virol 1997; 71: 1739–1746.
Muruve DA . The innate immune response to adenovirus vectors. Hum Gene Ther 2004; 15: 1157–1166.
Bilbao G, Contreras JL, Zhan H-G, Pike MJ, Overturf K, Mikheeva G et al. Adenovirus-mediated gene expression in vivo is enhanced by the antiapoptotic bcl-2 gene. J Virol 1999; 73: 6992–7000.
Wolff G, Schumacher A, Nüssler AK, Ruppert V, Karawajew L, Wehnes E et al. Coexpression of p21(WAF1/CIP1) in adenovirus vector transfected human primary hepatocytes prevents apoptosis resulting in improved transgene expression. Gene Therapy 2003; 10: 668–677.
Yang ZY, Perkins ND, Ohno T, Nabel EG, Nabel GJ . The p21 cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor suppresses tumorigenicity in vivo. Nat Med 1995; 1: 1052–1056.
Medema RH, Klompmaker R, Smits VAJ, Rijksen G . p21waf1 can block cell cycle at two points in the cell cycle, but does not interfere with processive DNA-replication or stress-activated kinases. Oncogene 1998; 16: 431–441.
Niculescu 3rd AB, Chen X, Smeets M, Hengst L, Prives C, Reed SI . Effects of p21Cip1/Waf1 at both the G1/S and the G2/M cell cycle transitions: pRb is a critical determinant in blocking DNA replication and in preventing endoreduplication. Mol Cell Biol 1998; 18: 629–643.
Asada M, Yamada T, Ichijo H, Delia D, Miyazono K, Fukumuro K et al. Apoptosis inhibitory activity of cytoplasmic p21Cip1/Waf1 in monocytic differentiation. EMBO J 1999; 18: 1223–1234.
Suzuki A, Tsutomi Y, Yamamoto N, Shibutani T, Akahane K . Mitochondrial regulation of cell death: mitochondria are essential for procaspase 3-p21 complex formation to resist Fas-mediated cell death. Mol Cell Biol 1999; 19: 3842–3847.
Huang S, Shu L, Dilling MB, Easton J, Harwood FC, Ichijo H et al. Sustained activation of the JNK cascade and rapamycin-induced apoptosis are suppressed by p53/p21Cip1. Mol Cell 2003; 11: 1491–1501.
Shim J, Lee H, Park J, Kim H, Choi EJ . A non-enzymatic p21 protein inhibitor of stress-activated protein kinases. Nature 1996; 381: 804–806.
Gregory DJ, Garcia-Wilson E, Poole JC, Snowden AW, Roninson IB, Perkins ND . Induction of transcription through the p300 CRD1 motif by p21WAF1/CIP1 is core promoter specific and cyclin dependent kinase independent. Cell Cycle 2002; 1: 343–350.
Delavaine L, La Thangue NB . Control of E2F activity by p21Waf1/Cip1. Oncogene 1999; 18: 5381–5392.
Kitaura H, Shinshi M, Uchikoshi Y, Ono T, Iguchi-Ariga SMM, Ariga H . Reciprocal regulation via protein-protein interaction between c-Myc and p21cip1/waf1/sdi1 in DNA replication and transcription. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 10477–10483.
Coqueret O, Gascan H . Functional interaction of STAT3 transcription factor with the cell cycle inhibitor p21WAF1/CIP1/SDI1. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 18794–18800.
Snowden AW, Anderson LA, Webster GA, Perkins ND . A novel transcriptional repression domain mediates p21(WAF1/CIP1) induction of p300 transactivation. Mol Cell Biol 2000; 20: 2676–2686.
Poole JC, Thain A, Perkins ND, Roninson IB . Induction of transcription by p21Waf1/Cip1/Sdi1: role of NFkappaB and effect of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Cell Cycle 2004; 3: 931–940.
Steinwaerder DS, Lieber A . Insulation from viral transcriptional regulatory elements improves inducible transgene expression from adenovirus vectors in vitro and in vivo. Gene Therapy 2000; 7: 556–567.
Nakai M, Komiya K, Murata M, Kimura T, Kanaoka M, Kanegae Y et al. Expression of pIX gene induced by transgene promoter: possible cause of host immune response in first-generation adenoviral vectors. Hum Gene Ther 2007; 18: 925–936.
Garcia-Wilson E, Perkins ND . p21WAF1/CIP1 regulates the p300 sumoylation motif CRD1 through a C-terminal domain independently of cyclin/CDK binding. Cell Cycle 2005; 4: 1113–1119.
Shikama N, Lyon J, La Thangue NB . The p300/CBP family: integrating signals with transcription factors and chromatin. Trends Cell Biol 1997; 7: 230–236.
Bowers WJ, Baglia LA, Ruddel A . Regulation of avian leukosis virus long terminal repeat-enhanced transcription by C/EBP-Rel interactions. J Virol 1996; 70: 3051–3059.
Mobley CM, Sealy L . Role of the transcription start site core region and transcription factor YY1 in Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat promoter activity. J Virol 1998; 72: 6592–6601.
Funk JO, Waga S, Harry JB, Espling E, Stillman B, Galloway DA . Inhibition of CDK activity and PCNA-dependent DNA replication by p21 is blocked by interaction with the HPV-16 E7 oncoprotein. Genes Dev 1997; 11: 2090–2100.
Jones DL, Alani RM, Münger K . The human papillomavirus E7 oncoprotein can uncouple cellular differentiation and proliferation in human keratinocytes by abrogating p21Cip1-mediated inhibition of cdk2. Genes Dev 1997; 11: 2101–2111.
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the technical assistance of Margitta Schüman. This work was funded by a Grant (10134771) from the ProFIT program of the Investitionsbank Berlin.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Gene Therapy website (http://www.nature.com/gt)
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schumacher, A., Horvat, S., Woischwill, C. et al. Co-expression of p21Waf1/Cip1 in adenovirus vectors improves expression of a second transgene. Gene Ther 16, 574–578 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2009.2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2009.2