Abstract
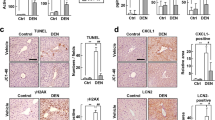
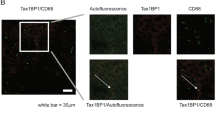
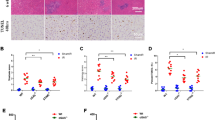
The wild-type baculovirus Autographa californica multiple nuclear polyhedrosis virus (AcMNPV) infects a range of mammalian cell types in vitro but does not replicate in these cells. The current study investigated the in vivo effect of AcMNPV in the mouse model of liver cirrhosis induced by the mutagen dimethylnitrosamine. Intraperitoneal injection of AcMNPV induced an immune response. The baculovirus was taken up by the liver and spleen where it suppressed liver injury and fibrosis through the induction of interferons. This study presents the first evidence of the feasibility of using baculovirus to treat liver cirrhosis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
World Health Organization. Hepatitis C: global prevalence. Wkly Epidemiol Rec 1997; 72: 341–344.
Fishman JA, Rubin RH, Koziel MJ, Periera BJ . Hepatitis C virus and organ transplantation. Transplantation 1996; 62: 147–154.
Heathcote EJ, Shiffman ML, Cooksley WG, Dusheiko GM, Lee SS, Balart L et al. Peginterferon alfa-2a in patients with chronic hepatitis C and cirrhosis. N Engl J Med 2000; 343: 1673–1680.
Zeuzem S, Feinman SV, Rasenack J, Heathcote EJ, Lai MY, Gane E et al. Peginterferon alfa-2a in patients with chronic hepatitis C. N Engl J Med 2000; 343: 1666–1672.
Bataller R, Brenner DA . Liver fibrosis. J Clin Invest 2005; 115: 209–218.
Abe T, Takahashi H, Hamazaki H, Miyano-Kurosaki N, Matsuura Y, Takaku H . Baculovirus induces an innate immune response and confers protection from lethal influenza virus infection in mice. J Immunol 2003; 171: 1133–1139.
Abe T, Hemmi H, Moriishi K, Tamura S, Takaku H, Akira S et al. Involvement of the Toll-like receptor 9 signaling pathway in the induction of innate immunity by baculovirus. J Virol 2005; 79: 2847–2858.
Gronowski AM, Hilbert DM, Sheehan KC, Garotta G, Schreiber RD . Baculovirus stimulates antiviral effect in mammalian cells. J Virol 1999; 73: 9944–9951.
Beck NB, Sidhu JS, Omiecinski CJ . Baculovirus vectors repress phenobarbital-mediated gene induction and stimulate cytokine expression in primary cultures of rat hepatocytes. Gene Therapy 2000; 7: 1274–1283.
Baroni GS, D’Ambrosio L, Curto P, Casini A, Mancini R, Jezequel AM et al. Interferon gamma decreases hepatic stellate cell activation and extracellular matrix deposition in rat liver fibrosis. Hepatology 1996; 23: 1189–1199.
Suzuki K, Aoki K, Ohnami S, Yoshida K, Kazui T, Kato N et al. Adenovirus-mediated gene transfer of interferon a improves dimethylnitrosamine-induced liver cirrhosis in rat model. Gene Therapy 2003; 10: 765–773.
Kitamura K, Nakamoto Y, Akiyama M, Fujii C, Kondo T, Kobayashi K et al. Pathogenic roles of tumor necrosis factor receptor p55-mediated signals in dimethylnitrosamine-induced murine liver fibrosis. Lab Invest 2002; 82: 571–583.
Jenkins SA, Grandison A, Baxter JN, Day DW, Taylor I, Shields R . A dimethylnitrosamine-induced model of cirrhosis and portal hypertension in the rat. J Hepatol 1985; 1: 489–499.
Jezequel AM, Ballardini G, Mancini R, Paolucci F, Bianchi FB, Orlandi F . Modulation of extracellular matrix components during dimethylnitrosamine-induced cirrhosis. J Hepatol 1990; 11: 206–214.
Tsukamoto H, Matsuoka M, French SW . Experimental models of hepatic fibrosis: a review. Semin Liver Dis 1990; 10: 56–65.
Ramadori G . The stellate cell of the liver. New insights into pathophysiology of an intriguing cell. Virchows Archiv B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol 1991; 61: 147–158.
Fernandez-Munoz D, Caramelo C, Santos JC . Systemic and splanchnic hemodynamic disturbances in conscious rats with experimental liver cirrhosis without ascites. Am J Physiol 1985; 249: G316–G320.
Baraona E, Liu W, Ma X-L, Svegliati Baroni G, Lieber CS . Acetaldehyde-collagen adducts in N-nitrosodimethylamine-induced liver cirrhosis. Life Sci 1993; 52: 1249–1255.
Mancini R, Jezequel AM, Benedetti A, Paolucci F, Trozzi L, Orandi F . Quantitative analysis of proliferating sinusoidal cells in dimethylnitrosamine-induced cirrhosis. An immunohistochemical study. J Hepatol 1992; 15: 361–366.
Ala-Kokko L, Pihlajaniemi T, Myers CJ, Kivirikko KI, Savo-lainen ER . Gene expression of type I, III and IV collagens in hepatic fibrosis induced by dimethylnitrosamine in the rat. Biochem J 1987; 244: 75–79.
Hofmann C, Strauss M . Baculovirus-mediated gene transfer in the presence of human serum or blood facilitated by inhibition of the complement system. Gene Therapy 1998; 5: 531–536.
Hüser A, Rudolph M, Hofmann C . Incorporation of decay-accelerating factor into the baculovirus envelope generates complement-resistant gene transfer vectors. Nat Biotechnol 2001; 19: 451–455.
Jézéquel AM, Mancini R, Rinaldesi ML, Macarri G, Venturini C, Orlandi F . A morphological study of the early stages of hepatic fibrosis induced by low doses of dimethylnitrosamine in the rat. J Hepatol 1987; 5: 174–181.
Fujimoto J, Kaneda Y . Reversing liver cirrhosis: impact of gene therapy for liver cirrhosis. Gene Therapy 1999; 6: 305–306.
Lee HS, Huang GT, Miau LH, Chiou LL, Chen CH, Sheu JC . Expression of matrix metalloproteinases in spontaneous regression of liver fibrosis. Hepatogastroenterology 2001; 48: 1114–1117.
Watanabe T, Niioka M, Hozawa S, Kameyama K, Hayashi T, Arai M et al. Gene expression of interstitial collagenase in both progressive and recovery phase of rat liver fibrosis induced by carbon tetrachloride. J Hepatol 2000; 33: 224–235.
Overall CM, Wrana JL, Sodek J . Transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulation of 72-kDa gelatinase/type IV collagenase by transforming growth factor-beta 1 in human fibroblasts. Comparisons with collagenase and tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase gene expression. J Biol Chem 1991; 266: 14064–14071.
Poncelet AC, Schnaper HW . Regulation of human mesangial cell collagen expression by transforming growth factor-beta 1. Am J Physiol 1998; 275: F458–F466.
Ikeda K, Wakahara T, Wang YQ, Kadoya H, Kawada N, Kaneda K . In vitro migratory potential of rat quiescent hepatic stellate cells and its augmentation by cell activation. Hepatology 1999; 29: 1760–1767.
Iredale JP, Benyon RC, Arthur MJ, Ferris WF, Alcolado R, Winwood PJ et al. Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 messenger RNA expression is enhanced relative to interstitial collagenase messenger RNA in experimental liver injury and fibrosis. Hepatology 1996; 24: 176–184.
Powrie F, Coffman RL . Cytokine regulation of T-cell function: potential for therapeutic intervention. Immunol Today 1993; 14: 270–274.
Czaja MJ, Weiner FR, Eghbali M, Giambrone MA, Zern MA . Differential effects of gamma-interferon on collagen and fibronectin gene expression. J Biol Chem 1987; 262: 13348–13351.
Goldring MB, Sandell LJ, Stephenson ML, Krane SM . Immune interferon suppresses levels of procollagen mRNA and type III collagen synthesis in cultured human articular and costal chondrocytes. J Biol Chem 1986; 261: 9049–9055.
Smith DD, Gowen M, Mundy GR . Effects of interferon-gamma and other cytokines on collagen synthesis in fetal rat bones cultures. Endocrinology 1987; 120: 2494–2499.
Jimenez SA, Freundlich B, Rosenbloom J . Selective inhibition of human diploid fibroblast collagen synthesis by interferons. J Clin Invest 1984; 74: 1112–1116.
Granstein RD, Murphy GF, Margolis RJ, Byrne MH, Amento EP . Gamma interferon inhibits collagen synthesis in vivo in the mouse. J Clin Invest 1987; 79: 1254–1258.
Granstein RD, Deak MR, Jacques SL, Margolis RJ, Flotte TJ, Whitaker D et al. The systemic administration of gamma interferon inhibits collagen synthesis and acute inflammation in a murine skin wounding model. J Invest Dermatol 1989; 93: 18–27.
Hyde DM, Henderson TS, Giri SN, Tyler NK, Stovall MY . Effect of murine gamma interferon on the cellular response to bleomycine in mice. Exp Lung Res 1988; 14: 687–704.
Brinkmann V, Foroutan H, Sachs M, Weidner KM, Birchmeier W . Hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor induces a variety of tissue-specific morphogenic programs in epithelial cells. J Cell Biol 1995; 131: 1573–1586.
Kountouras J, Boura P, Lygidakis NJ . Liver regeneration after hepatectomy. Hepatogastroenterology 2001; 48: 556–562.
Laurent S, Otsuka M, De Saeger C, Maiter D, Lambotte L, Horsmans Y . Expression of presumed specific early and late factors associated with liver regeneration in different rat surgical models. Lab Invest 2001; 81: 1299–1307.
Wang H, Zhang Y, Heuckeroth RO . Tissue-type plasminogen activator deficiency exacerbates cholestatic liver injury mice. Hepatology 2007; 45: 1527–1537.
Bissell DM, Roulot D, George J . Transforming growth factor β and the liver. Hepatology 2001; 34: 859–867.
Gressner AM, Weiskirchen R, Breitkopf K, Dooley S . Roles of TGF-β in hepatic fibrosis. Front Biosci 2002; 7: d793–d807.
Wiercinska E, Wickert L, Denecke B, Said HM, Hamzavi J, Gressner AM et al. Id1 is a critical mediator in TGF-β-induced transdifferentiation of rat hepatic stellate cells. Hepatology 2006; 43: 1032–1041.
Bucher NLR . Regeneration of mammalian liver. Int Rev Cytol 1963; 15: 245–300.
Masumoto A, Yamamoto N . Sequestration of a hepatocyte growth factor in extracellular matrix in normal adult rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1991; 174: 90–95.
Liu ML, Mars WM, Zarnegar R, Michalopoulos GK . Uptake and distribution of hepatocyte growth factor in normal and regenerating adult rat liver. Am J Pathol 1994; 144: 129–140.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported, in part, by a grant from the Research and Development Program for New Bio-industry Initiatives and by a Grant-in-Aid for High Technology Research, no. 09309011, from the Ministry of Education, Science, Sports, and Culture, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nishibe, Y., Kaneko, H., Suzuki, H. et al. Baculovirus-mediated interferon alleviates dimethylnitrosamine-induced liver cirrhosis symptoms in a murine model. Gene Ther 15, 990–997 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2008.29
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2008.29
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Generation of functional human hepatocytes in vitro: current status and future prospects
Inflammation and Regeneration (2019)
-
Recombinant baculovirus expressing the FrC-OVA protein induces protective antitumor immunity in an EG7-OVA mouse model
Journal of Biological Engineering (2019)
-
Baculovirus directly activates murine NK cells via TLR9
Cancer Gene Therapy (2017)
-
Local Immune Stimulation by Intravesical Instillation of Baculovirus to Enable Bladder Cancer Therapy
Scientific Reports (2016)
-
Antitumor effects of baculovirus-infected dendritic cells against human pancreatic carcinoma
Gene Therapy (2014)