Abstract
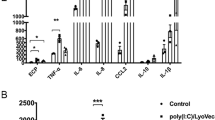
Cystic fibrosis (CF) patients have decreased levels of lung epithelial interleukin (IL)-10 and increased levels of proinflammatory cytokines (tumor necrosis factor-α, IL-4, IL-8 and IL-6). This has also been documented in Cftr (cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator)-deficient mice (Cftr 489X−/−, FABP-hCFTR+/+). Our laboratory has recently characterized a peculiar hyper-IgE phenotype in these mice, in response to Aspergillus fumigatus crude protein extract (Af-cpe). Thus, we hypothesized that sustained systemic circulating IL-10 levels achieved through skeletal muscle transduction with recombinant adeno-associated vectors expressing IL-10 (rAAV1-IL-10) would serve to downregulate Th1 and Th2 cytokine production. This in turn would dampen the allergic response in the Cftr−/−-dependent mouse model of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. After Af-cpe sensitization and airway challenge, mice treated with rAAV1-IL-10 had markedly lower IgE levels when compared to the control-treated rAAV1-GFP group. This was accompanied by a significant reduction in the levels of IL-5, IL-4 and IL-13 in the lung compartment. The lower lung cytokine profiles resulted in a near absence of eosinophil recruitment in the lung and a lower inflammatory response in the lung tissue of mice receiving rAAV1-IL-10. Unfortunately, sustained secretion of IL-10 from transduced muscle did lead to thrombocytopenia and splenomegaly in mice injected with rAAV1-IL-10. These results highlight that while IL-10 gene therapy is very effective for treating allergic responses caution must be taken with the prolonged secretion of IL-10.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ABPA:
-
allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis
- Af-cpe:
-
Aspergillus fumigatus crude protein extract
- CFTR:
-
cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator
- rAAV:
-
recombinant adeno-associated virus.
References
Durie PR, Kent G, Phillips MJ, Ackerley CA . Characteristic multiorgan pathology of cystic fibrosis in a long-living cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator knockout murine model. Am J Pathol 2004; 164: 1481–1493.
Wainwright B . The molecular pathology of cystic fibrosis. Curr Biol 1991; 1: 80–82.
Davidson DJ, Webb S, Teague P, Govan JR, Dorin JR . Lung pathology in response to repeated exposure to Staphylococcus aureus in congenic residual function cystic fibrosis mice does not increase in response to decreased CFTR levels or increased bacterial load. Pathobiology 2004; 71: 152–158.
Lyczak JB, Cannon CL, Pier GB . Lung infections associated with cystic fibrosis. Clin Microbiol Rev 2002; 15: 194–222.
Jiang C, Finkbeiner WE, Widdicombe JH, Miller SS . Fluid transport across cultures of human tracheal glands is altered in cystic fibrosis. J Physiol 1997; 501 (Part 3): 637–647.
Widdicombe JH . Regulation of the depth and composition of airway surface liquid. J Anat 2002; 201: 313–318.
Li C, Naren AP . Macromolecular complexes of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator and its interacting partners. Pharmacol Ther 2005; 108: 208–223.
de Bentzmann S, Roger P, Dupuit F, Bajolet-Laudinat O, Fuchey C, Plotkowski MC et al. Asialo GM1 is a receptor for Pseudomonas aeruginosa adherence to regenerating respiratory epithelial cells. Infect Immun 1996; 64: 1582–1588.
Zar H, Saiman L, Quittell L, Prince A . Binding of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to respiratory epithelial cells from patients with various mutations in the cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator. J Pediatr 1995; 126: 230–233.
Bastonero S, Gargouri M, Ortiou S, Gueant JL, Merten MD . Inhibition by TNF-alpha and IL-4 of cationic lipid mediated gene transfer in cystic fibrosis tracheal gland cells. J Gene Med 2005; 7: 1439–1449.
Terheggen-Lagro SW, Rijkers GT, van der Ent CK . The role of airway epithelium and blood neutrophils in the inflammatory response in cystic fibrosis. J Cyst Fibros 2005; 4 (Suppl 2): 15–23.
Conese M, Copreni E, Di Gioia S, De Rinaldis P, Fumarulo R . Neutrophil recruitment and airway epithelial cell involvement in chronic cystic fibrosis lung disease. J Cyst Fibros 2003; 2: 129–135.
Sagel SD, Accurso FJ . Monitoring inflammation in CF. Cytokines. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 2002; 23: 41–57.
Venkatakrishnan A, Stecenko AA, King G, Blackwell TR, Brigham KL, Christman JW et al. Exaggerated activation of nuclear factor-kappaB and altered IkappaB-beta processing in cystic fibrosis bronchial epithelial cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2000; 23: 396–403.
Moss RB, Bocian RC, Hsu YP, Dong YJ, Kemna M, Wei T et al. Reduced IL-10 secretion by CD4+ T lymphocytes expressing mutant cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR). Clin Exp Immunol 1996; 106: 374–388.
Bonfield TL, Konstan MW, Burfeind P, Panuska JR, Hilliard JB, Berger M . Normal bronchial epithelial cells constitutively produce the anti-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-10, which is downregulated in cystic fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 1995; 13: 257–261.
Bonfield TL, Konstan MW, Berger M . Altered respiratory epithelial cell cytokine production in cystic fibrosis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 1999; 104: 72–78.
Dosanjh AK, Elashoff D, Robbins RC . The bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of cystic fibrosis lung transplant recipients demonstrates increased interleukin-8 and elastase and decreased IL-10. J Interferon Cytokine Res 1998; 18: 851–854.
Bonfield TL, Panuska JR, Konstan MW, Hilliard KA, Hilliard JB, Ghnaim H et al. Inflammatory cytokines in cystic fibrosis lungs. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1995; 152 (6 Part 1): 2111–2118.
Osika E, Cavaillon JM, Chadelat K, Boule M, Fitting C, Tournier G et al. Distinct sputum cytokine profiles in cystic fibrosis and other chronic inflammatory airway disease. Eur Respir J 1999; 14: 339–346.
Soltys J, Bonfield T, Chmiel J, Berger M . Functional IL-10 deficiency in the lung of cystic fibrosis (Cftr(−/−)) and IL-10 knockout mice causes increased expression and function of B7 costimulatory molecules on alveolar macrophages. J Immunol 2002; 168: 1903–1910.
Chmiel JF, Konstan MW, Saadane A, Krenicky JE, Lester Kirchner H, Berger M . Prolonged inflammatory response to acute Pseudomonas challenge in interleukin-10 knockout mice. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2002; 165: 1176–1181.
Grunig G, Corry DB, Leach MW, Seymour BW, Kurup VP, Rennick DM . Interleukin-10 is a natural suppressor of cytokine production and inflammation in a murine model of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. J Exp Med 1997; 185: 1089–1099.
Kurup VP, Grunig G . Animal models of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. Mycopathologia 2002; 153: 165–177.
Knutsen AP, Hutchinson PS, Albers GM, Consolino J, Smick J, Kurup VP . Increased sensitivity to IL-4 in cystic fibrosis patients with allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. Allergy 2004; 59: 81–87.
Hartl D, Griese M, Kappler M, Zissel G, Reinhardt D, Rebhan C et al. Pulmonary T(H)2 response in Pseudomonas aeruginosa-infected patients with cystic fibrosis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2006; 117: 204–211.
Galietta LJ, Pagesy P, Folli C, Caci E, Romio L, Costes B et al. IL-4 is a potent modulator of ion transport in the human bronchial epithelium in vitro. J Immunol 2002; 168: 839–845.
Hauber HP, Gholami D, Koppermann G, Heuer HE, Meyer A, Pforte A . Increased expression of interleukin-13 but not interleukin-4 in cystic fibrosis patients. J Cyst Fibros 2003; 2: 189–194.
Ormerod LP, Thomson RA, Anderson CM, Stableforth DE . Reversible airway obstruction in cystic fibrosis. Thorax 1980; 35: 768–772.
Alison JA, Donnelly PM, Lennon M, Parker S, Torzillo P, Mellis C et al. The effect of a comprehensive, intensive inpatient treatment program on lung function and exercise capacity in patients with cystic fibrosis. Phys Ther 1994; 74: 583–591; discussion 91–93.
Zimmerman B, Feanny S, Reisman J, Hak H, Rashed N, McLaughlin FJ et al. Allergy in asthma. I. The dose relationship of allergy to severity of childhood asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 1988; 81: 63–70.
Balfour-Lynn IM, Lees B, Hall P, Phillips G, Khan M, Flather M et al. Multicenter randomized controlled trial of withdrawal of inhaled corticosteroids in cystic fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2006; 173: 1356–1362.
Nelson LA, Callerame ML, Schwartz RH . Aspergillosis and atopy in cystic fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis 1979; 120: 863–873.
Feanny S, Forsyth S, Corey M, Levison H, Zimmerman B . Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis in cystic fibrosis: a secretory immune response to a colonizing organism. Ann Allergy 1988; 60: 64–68.
Ip MS, So SY, Lam WK, Yam L, Liong E . High prevalence of asthma in patients with bronchiectasis in Hong Kong. Eur Respir J 1992; 5: 418–423.
Wu P, de Fiebre CM, Millard WJ, King MA, Wang S, Bryant SO et al. An AAV promoter-driven neuropeptide Y gene delivery system using Sendai virosomes for neurons and rat brain. Gene Therapy 1996; 3: 246–253.
Wagner JA, Nepomuceno IB, Shah N, Messner AH, Moran ML, Norbash AM et al. Maxillary sinusitis as a surrogate model for CF gene therapy clinical trials in patients with antrostomies. J Gene Med 1999; 1: 13–21.
Becker JW, Burke W, McDonald G, Greenberger PA, Henderson WR, Aitken ML . Prevalence of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis and atopy in adult patients with cystic fibrosis. Chest 1996; 109: 1536–1540.
Mussaffi H, Greif J, Kornreich L, Ashkenazi S, Levy Y, Schonfeld T et al. Severe allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis in an infant with cystic fibrosis and her asthmatic father. Pediatr Pulmonol 2000; 29: 155–159.
Skov M, McKay K, Koch C, Cooper PJ . Prevalence of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis in cystic fibrosis in an area with a high frequency of atopy. Respir Med 2005; 99: 887–893.
Djukanovic R, Roche WR, Wilson JW, Beasley CR, Twentyman OP, Howarth RH et al. Mucosal inflammation in asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis 1990; 142: 434–457.
Kay AB . Asthma and inflammation. J Allergy Clin Immunol 1991; 87: 893–910.
Galietta LJ, Folli C, Marchetti C, Romano L, Carpani D, Conese M et al. Modification of transepithelial ion transport in human cultured bronchial epithelial cells by interferon-gamma. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2000; 278: L1186–L1194.
Moss RB, Hsu YP, Olds L . Cytokine dysregulation in activated cystic fibrosis (CF) peripheral lymphocytes. Clin Exp Immunol 2000; 120: 518–525.
Stecenko AA, King G, Torii K, Breyer RM, Dworski R, Blackwell TS et al. Dysregulated cytokine production in human cystic fibrosis bronchial epithelial cells. Inflammation 2001; 25: 145–155.
Aldallal N, McNaughton EE, Manzel LJ, Richards AM, Zabner J, Ferkol TW et al. Inflammatory response in airway epithelial cells isolated from patients with cystic fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2002; 166: 1248–1256.
Ghildyal N, McNeil HP, Stechschulte S, Austen KF, Silberstein D, Gurish MF et al. IL-10 induces transcription of the gene for mouse mast cell protease-1, a serine protease preferentially expressed in mucosal mast cells of Trichinella spiralis-infected mice. J Immunol 1992; 149: 2123–2129.
Asadullah K, Sterry W, Volk HD . Interleukin-10 therapy—review of a new approach. Pharmacol Rev 2003; 55: 241–269.
Antoniv TT, Park-Min KH, Ivashkiv LB . Kinetics of IL-10-induced gene expression in human macrophages. Immunobiology 2005; 210: 87–95.
Williams L, Jarai G, Smith A, Finan P . IL-10 expression profiling in human monocytes. J Leukoc Biol 2002; 72: 800–809.
Kiem HP, Darovsky B, von Kalle C, Goehle S, Stewart D, Graham T et al. Retrovirus-mediated gene transduction into canine peripheral blood repopulating cells. Blood 1994; 83: 1467–1473.
Heeckeren A, Walenga R, Konstan MW, Bonfield T, Davis PB, Ferkol T . Excessive inflammatory response of cystic fibrosis mice to bronchopulmonary infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Clin Invest 1997; 100: 2810–2815.
Muller C, Braag SA, Herlihy JD, Wasserfall CH, Chesrown SE, Nick HS et al. Enhanced IgE allergic response to Aspergillus fumigatus in CFTR−/− mice. Lab Invest 2006; 86: 130–140.
Drazan KE, Wu L, Bullington D, Shaked A . Viral IL-10 gene therapy inhibits TNF-alpha and IL-1 beta, not IL-6, in the newborn endotoxemic mouse. J Pediatr Surg 1996; 31: 411–414.
Lindsay J, Van Montfrans C, Brennan F, Van Deventer S, Drillenburg P, Hodgson H et al. IL-10 gene therapy prevents TNBS-induced colitis. Gene Therapy 2002; 9: 1715–1721.
Zhang YC, Pileggi A, Agarwal A, Molano RD, Powers M, Brusko T et al. Adeno-associated virus-mediated IL-10 gene therapy inhibits diabetes recurrence in syngeneic islet cell transplantation of NOD mice. Diabetes 2003; 52: 708–716.
Goudy KS, Burkhardt BR, Wasserfall C, Song S, Campbell-Thompson ML, Brusko T et al. Systemic overexpression of IL-10 induces CD4+CD25+ cell populations in vivo and ameliorates type 1 diabetes in nonobese diabetic mice in a dose-dependent fashion. J Immunol 2003; 171: 2270–2278.
Fu CL, Chuang YH, Chau LY, Chiang BL . Effects of adenovirus-expressing IL-10 in alleviating airway inflammation in asthma. J Gene Med 2006; 8: 1393–1399.
Fedorak RN, Gangl A, Elson CO, Rutgeerts P, Schreiber S, Wild G et al. Recombinant human interleukin 10 in the treatment of patients with mild to moderately active Crohn's disease. The Interleukin 10 Inflammatory Bowel Disease Cooperative Study Group. Gastroenterology 2000; 119: 1473–1482.
Song S, Morgan M, Ellis T, Poirier A, Chesnut K, Wang J et al. Sustained secretion of human alpha-1-antitrypsin from murine muscle transduced with adeno-associated virus vectors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998; 95: 14384–14388.
Goudy K, Song S, Wasserfall C, Zhang YC, Kapturczak M, Muir A et al. Adeno-associated virus vector-mediated IL-10 gene delivery prevents type 1 diabetes in NOD mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001; 98: 13913–13918.
Chmiel JF, Konstan MW, Knesebeck JE, Hilliard JB, Bonfield TL, Dawson DV et al. IL-10 attenuates excessive inflammation in chronic Pseudomonas infection in mice. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1999; 160: 2040–2047.
Dosanjh AK, Elashoff D, Robbins RC . The bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of cystic fibrosis lung transplant recipients demonstrates increased interleukin-8 and elastase and decreased IL-10 (In Process Citation). J Interferon Cytokine Res 1998; 18: 851–854.
Sosman JA, Verma A, Moss S, Sorokin P, Blend M, Bradlow B et al. Interleukin 10-induced thrombocytopenia in normal healthy adult volunteers: evidence for decreased platelet production. Br J Haematol 2000; 111: 104–111.
Brouard J, Knauer N, Boelle PY, Corvol H, Henrion-Caude A, Flamant C et al. Influence of interleukin-10 on Aspergillus fumigatus infection in patients with cystic fibrosis. J Infect Dis 2005; 191: 1988–1991.
Grubb BR, Pickles RJ, Ye H, Yankaskas JR, Vick RN, Engelhardt JF et al. Inefficient gene transfer by adenovirus vector to cystic fibrosis airway epithelia of mice and humans. Nature 1994; 371: 802–806.
Acknowledgements
We thank Mark Atkinson, Clive Wasserfall and Todd Brusko for their helpful comments and insights. This study was supported by grants for NHLBI (HL51811) and the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mueller, C., Braag, S., Martino, A. et al. The pros and cons of immunomodulatory IL-10 gene therapy with recombinant AAV in a Cftr−/−-dependent allergy mouse model. Gene Ther 16, 172–183 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2008.156
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2008.156
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Combination therapy for melanoma with BRAF/MEK inhibitor and immune checkpoint inhibitor: a mathematical model
BMC Systems Biology (2017)
-
β-Cell-targeted blockage of PD1 and CTLA4 pathways prevents development of autoimmune diabetes and acute allogeneic islets rejection
Gene Therapy (2015)
-
Modulation of Exaggerated-IgE Allergic Responses by Gene Transfer-mediated Antagonism of IL-13 and IL-17e
Molecular Therapy (2010)