Abstract
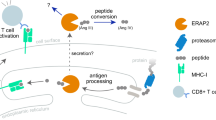
Endosplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase 1 (ERAP1), endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase 2 (ERAP2) and puromycin-sensitive aminopeptidase (NPEPPS) are key zinc metallopeptidases that belong to the oxytocinase subfamily of M1 aminopeptidase family. NPEPPS catalyzes the processing of proteosome-derived peptide repertoire followed by trimming of antigenic peptides by ERAP1 and ERAP2 for presentation on major histocompatibility complex (MHC) Class I molecules. A series of genome-wide association studies have demonstrated associations of these aminopeptidases with a range of immune-mediated diseases such as ankylosing spondylitis, psoriasis, Behçet’s disease, inflammatory bowel disease and type I diabetes, and significantly, genetic interaction between some aminopeptidases and HLA Class I loci with which these diseases are strongly associated. In this review, we highlight the current state of understanding of the genetic associations of this class of genes, their functional role in disease, and potential as therapeutic targets.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $19.83 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rawlings ND, Salvesen G . Handbook of Proteolytic Enzymes. Elsevier, London, UK, 2013.
Rawlings ND, Barrett AJ . Evolutionary families of peptidases. Biochem J. 1993; 290: 205–218.
Kochan G, Krojer T, Harvey D, Fischer R, Chen L, Vollmar M et al. Crystal structures of the endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase-1 (ERAP1) reveal the molecular basis for N-terminal peptide trimming. Proc Natl Acad Sci 2011; 108: 7745–7750.
Nguyen TT, Chang SC, Evnouchidou I, York IA, Zikos C, Rock KL et al. Structural basis for antigenic peptide precursor processing by the endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase ERAP1. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2011; 18: 604–613.
Birtley JR, Saridakis E, Stratikos E, Mavridis IM . The crystal structure of human endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase 2 reveals the atomic basis for distinct roles in antigen processing. Biochemistry 2012; 51: 286–295.
Albiston AL, Ye S, Chai SY . Membrane bound members of the M1 family: more than aminopeptidases. Protein Pept Lett 2004; 11: 491–500.
Fukasawa KM, Fukasawa K, Harada M, Hirose J, Izumi T, Shimizu T . Aminopeptidase B is structurally related to leukotriene-A4 hydrolase but is not a bifunctional enzyme with epoxide hydrolase activity. Biochem J 1999; 339: 497–502.
Saito S, Sakai M, Sasaki Y, Nakashima A, Shiozaki A . Inadequate tolerance induction may induce pre-eclampsia. J Reprod Immunol. 2007; 76: 30–39.
Vanhille DL, Hill LD, Hilliard DD, Lee ED, Teves ME, Srinivas S et al. A novel ERAP2 haplotype structure in a Chilean Population: implications for ERAP2 protein expression and preeclampsia risk. Mol Genet Genomic Med 2013; 1: 98–107.
Mehta AM, Jordanova ES, Kenter GG, Ferrone S, Fleuren GJ . Association of antigen processing machinery and HLA class I defects with clinicopathological outcome in cervical carcinoma. Cancer Immunol Immunother 2008; 57: 197–206.
Mehta AM, Jordanova ES, Corver WE, van Wezel T, Uh HW, Kenter GG et al. Single nucleotide polymorphisms in antigen processing machinery component ERAP1 significantly associate with clinical outcome in cervical carcinoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2009; 48: 410–418.
Fung EY, Smyth DJ, Howson JM, Cooper JD, Walker NM, Stevens H et al. Analysis of 17 autoimmune disease-associated variants in type 1 diabetes identifies 6q23/TNFAIP3 as a susceptibility locus. Genes Immun 2009; 10: 188–191.
Cortes A, Hadler J, Pointon JP, Robinson PC, Karaderi T, Leo P et al. Identification of multiple risk variants for ankylosing spondylitis through high-density genotyping of immune-related loci. Nat Genet 2013; 45: 730–738.
Reveille JD . The genetic basis of ankylosing spondylitis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2006; 18: 332–341.
Brown MA . Genetics of ankylosing spondylitis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2010; 22: 126–132.
Genetic Analysis of Psoriasis Consortium & the Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium 2, Genetic Analysis of Psoriasis Consortium & the Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium 2 Strange A, Genetic Analysis of Psoriasis Consortium & the Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium 2 Capon F, Genetic Analysis of Psoriasis Consortium & the Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium 2 Spencer CC, Genetic Analysis of Psoriasis Consortium & the Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium 2 Knight J, Genetic Analysis of Psoriasis Consortium & the Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium 2 Weale ME et al. A genome-wide association study identifies new psoriasis susceptibility loci and an interaction between HLA-C and ERAP1. Nat Genet 2010; 42: 985–990.
Kirino Y, Bertsias G, Ishigatsubo Y, Mizuki N, Tugal-Tutkun I, Seyahi E et al. Genome-wide association analysis identifies new susceptibility loci for Behçet's disease and epistasis between HLA-B*51 and ERAP1. Nat Genet 2013; 45: 202–207.
Gül A . Genetics of Behçet's disease: lessons learned from genomewide association studies. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2013; 26: 56–63.
Guerini FR, Cagliani R, Forni D, Agliardi C, Caputo D, Cassinotti A et al. A functional variant in ERAP1 predisposes to multiple sclerosis. PLoS ONE 2012; 7: e29931.
Christodoulou K, Wiskin AE, Gibson J, Tapper W, Willis C, Afzal NA et al. Next generation exome sequencing of paediatric inflammatory bowel disease patients identifies rare and novel variants in candidate genes. Gut 2013; 62: 977–984.
Franke A, McGovern DP, Barrett GC, Wang K, Radford-Smith GL, Ahmad T et al. Genome-wide meta-analysis increases to 71 the number of confirmed Crohn's disease susceptibility loci. Nat Genet 2010; 42: 1118–1125.
Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium, Australo-Anglo-American Spondyloarthritis Consortium (TASC), Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium Burton PR, Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium Clayton DG, Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium Cardon LR, Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium Craddock N et al. Association scan of 14,500 nonsynonymous SNPs in four diseases identifies autoimmunity variants. Nat Genet 2007; 39: 1329–1337.
Evans DM, Spencer CC, Pointon JJ, Su Z, Harvey D, Kochan G et al. Interaction between ERAP1 and HLA-B27 in ankylosing spondylitis implicates peptide handling in the mechanism for HLA-B27 in disease susceptibility. Nat Genet 2011; 43: 761–767.
Li C, Lin Z, Xie Y, Guo Z, Huang J, Wei Q et al. ERAP1 is associated with ankylosing Spondylitis in Han Chinese. J Rheumatol 2011; 38: 317–321.
Pazar B, Safrany E, Gergely P, Szanto S, Szekanecz Z, Poor G . Association of ARTS1 gene polymorphisms with ankylosing spondylitis in the Hungarian population: the rs27044 variant is associated with HLA-B*2705 subtype in Hungarian patients with ankylosing spondylitis. J Rheumatol 2010; 37: 379–384.
Pimentel-Santos FM, Ligeiro D, Matos M, Mourao AF, Sousa E, Pinto P et al. Association of IL23R and ERAP1 genes with ankylosing spondylitis in a Portuguese population. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2009; 27: 800–806.
Australo-Anglo-American Spondyloarthritis C, Reveille JD, Sims AM, Danoy P, Evans DM, Leo P et al. Genome-wide association study of ankylosing spondylitis identifies non-MHC susceptibility loci. Nat Genet 2010; 42: 123–127.
Szczypiorska M, Sanchez A, Bartolome N, Arteta D, Sanz J, Brito E et al. ERAP1 polymorphisms and haplotypes are associated with ankylosing spondylitis susceptibility and functional severity in a Spanish population. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2011; 50: 1969–1975.
Davidson SI, Liu Y, Danoy PA, Wu X, Thomas GP, Jiang L et al. Association of STAT3 and TNFRSF1A with ankylosing spondylitis in Han Chinese. Ann Rheum Dis 2011; 70: 289–292.
Davidson SI, Wu X, Liu Y, Wei M, Danoy PA, Thomas G et al. Association of ERAP1, but not IL23R, with ankylosing spondylitis in a Han Chinese population. Arthritis Rheum 2009; 60: 3263–3268.
Strange A, Capon F, Spencer CC, Knight J, Weale ME, Allen MH et al. A genome-wide association study identifies new psoriasis susceptibility loci and an interaction between HLA-C and ERAP1. Nat Genet 2010; 42: 985–990.
Hinks A, Cobb J, Marion MC, Prahalad S, Sudman M, Bowes J et al. Dense genotyping of immune-related disease regions identifies 14 new susceptibility loci for juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Nat Genet 2013; 45: 664–669.
Krige D, Needham LA, Bawden LJ, Flores N, Farmer H, Miles LE et al. CHR-2797: an antiproliferative aminopeptidase inhibitor that leads to amino acid deprivation in human leukemic cells. Cancer Res 2008; 68: 6669–6679.
Hitzerd SM, Verbrugge SE, Ossenkoppele G, Jansen G, Peters GJ . Positioning of aminopeptidase inhibitors in next generation cancer therapy. Amino Acids 2014; 46: 793–808.
Saric T, Chang SC, Hattori A, York IA, Markant S, Rock KL et al. An IFN-gamma-induced aminopeptidase in the ER, ERAP1, trims precursors to MHC class I-presented peptides. Nat Immunol 2002; 3: 1169–1176.
York IA, Chang SC, Saric T, Keys JA, Favreau JM, Goldberg AL et al. The ER aminopeptidase ERAP1 enhances or limits antigen presentation by trimming epitopes to 8-9 residues. Nat Immunol 2002; 3: 1177–1184.
Ouyang C, Smith DD, Krontiris TG . Evolutionary signatures of common human cis-regulatory haplotypes. PLoS ONE 2008; 3: e3362.
Harvey D, Pointon JJ, Evans DM, Karaderi T, Farrar C, Appleton LH et al. Investigating the genetic association between ERAP1 and ankylosing spondylitis. Hum Mol Genet 2009; 18: 4204–4212.
Nguyen TT, Chang SC, Evnouchidou I, York IA, Zikos C, Rock KL et al. Structural basis for antigenic peptide precursor processing by the endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase ERAP1. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2011; 18: 604–613.
Stratikos E, Stern LJ . Antigenic peptide trimming by ER aminopeptidases—insights from structural studies. Mol Immunol 2013; 55: 212–219.
Goto Y, Tanji H, Hattori A, Tsujimoto M . Glutamine-181 is crucial in the enzymatic activity and substrate specificity of human endoplasmic-reticulum aminopeptidase-1. Biochem J 2008; 416: 109–116.
Gibbs RA, Weinstock GM, Metzker ML, Muzny DM, Sodergren EJ, Scherer S et al. Genome sequence of the Brown Norway rat yields insights into mammalian evolution. Nature 2004; 428: 493–521.
Haroon N, Inman RD . Endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidases: Biology and pathogenic potential. Nat Rev Rheumatol 2010; 6: 461–467.
Ascher DB, Polekhina G, Parker MW . Crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction analysis of human endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase 2. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun 2012; 68: 468–471.
Zervoudi E, Papakyriakou A, Georgiadou D, Evnouchidou I, Gajda A, Poreba M et al. Probing the S1 specificity pocket of the aminopeptidases that generate antigenic peptides. Biochem J 2011; 435: 411–420.
Saveanu L, Carroll O, Lindo V, Del Val M, Lopez D, Lepelletier Y et al. Concerted peptide trimming by human ERAP1 and ERAP2 aminopeptidase complexes in the endoplasmic reticulum. Nat Immunol 2005; 6: 689–697.
Andres AM, Dennis MY, Kretzschmar WW, Cannons JL, Lee-Lin SQ, Hurle B et al. Balancing selection maintains a form of ERAP2 that undergoes nonsense-mediated decay and affects antigen presentation. PLoS Genet 2010; 6: e1001157.
Evnouchidou I, Birtley J, Seregin S, Papakyriakou A, Zervoudi E, Samiotaki M et al. A common single nucleotide polymorphism in endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase 2 induces a specificity switch that leads to altered antigen processing. J Immunol 2012; 189: 2383–2392.
McLellan S, Dyer SH, Rodriguez G, Hersh LB . Studies on the tissue distribution of the puromycin-sensitive enkephalin-degrading aminopeptidases. J Neurochem 1988; 51: 1552–1559.
Dyer SH, Slaughter CA, Orth K, Moomaw CR, Hersh LB . Comparison of the soluble and membrane-bound forms of the puromycin-sensitive enkephalin-degrading aminopeptidases from rat. J Neurochem 1990; 54: 547–554.
Johnson GD, Hersh LB . Studies on the subsite specificity of the rat brain puromycin-sensitive aminopeptidase. Arch Biochem Biophys 1990; 276: 305–309.
Safavi A, Hersh LB . Degradation of dynorphin-related peptides by the puromycin-sensitive aminopeptidase and aminopeptidase M. J Neurochem 1995; 65: 389–395.
Kudo LC, Parfenova L, Ren G, Vi N, Hui M, Ma Z et al. Puromycin-sensitive aminopeptidase (PSA/NPEPPS) impedes development of neuropathology in hPSA/TAU(P301L) double-transgenic mice. Hum Mol Genet 2011; 20: 1820–1833.
Thompson MW, Govindaswami M, Hersh LB . Mutation of active site residues of the puromycin-sensitive aminopeptidase: conversion of the enzyme into a catalytically inactive binding protein. Arch Biochem Biophys 2003; 413: 236–242.
Haroon N, Tsui FW, Uchanska-Ziegler B, Ziegler A, Inman RD . Endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase 1 (ERAP1) exhibits functionally significant interaction with HLA-B27 and relates to subtype specificity in ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis 2012; 71: 589–595.
Alvarez-Navarro C, López de Castro JA . ERAP1 structure, function and pathogenetic role in ankylosing spondylitis and other MHC-associated diseases. Mol Immunol 2013; 57 (1): 12–21.
García-Medel N, Sanz-Bravo A, Van Nguyen D, Galocha B, Gómez-Molina P, Martín-Esteban A et al. Functional interaction of the ankylosing spondylitis-associated endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase 1 polymorphism and HLA-B27 in vivo. Mol Cell Proteomics 2012; 11: 1416–1429.
Martín-Esteban A, Gómez-Molina P, Sanz-Bravo A, López de Castro J . Combined effects of ankylosing spondylitis-associated ERAP1 polymorphisms outside the catalytic and peptide-binding sites on the processing of natural HLA-B27 ligands. J Biol Chem 2014; 289: 3978–3990.
Alvarez-Navarro C, López de Castro J . ERAP1 in ankylosing spondylitis: genetics, biology and pathogenetic role. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2013; 25: 419–425.
Chen L, Fischer R, Peng Y, Reeves E, McHugh K, Ternette N et al. Critical role of endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase 1 in determining the length and sequence of peptides bound and presented by HLA-B27. Arthritis Rheumatol 2014; 66: 284–294.
Akram A, Lin A, Gracey E, Streutker CJ, Inman RD . HLA-B27, but not HLA-B7, immunodominance to Influenza is ERAP dependent. J Immunol 2014; 192 (12): 5520–5528.
Akram A, Inman RD . Co-expression of HLA-B7 and HLA-B27 alleles is associated with B7-restricted immunodominant responses following influenza infection. Eur J Immunol 2013; 43: 3254–3267.
Cortes A, de Bakker P, Brown MA . Fine-mapping major histocompatibility complex variation associated with ankylosing spondylitis susceptibility. In American College of Rheumatology. Arthritis Rheum 2013; 12: 1706.
Albiston AL, Morton CJ, Ng HL, Pham V, Yeatman HR, Ye S et al. Identification and characterization of a new cognitive enhancer based on inhibition of insulin-regulated aminopeptidase. FASEB J 2008; 22: 4209–4217.
Ocain TD, Rich DH . L-lysinethiol: a subnanomolar inhibitor of aminopeptidase B. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1987; 145: 1038–1042.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on Genes and Immunity website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Agrawal, N., Brown, M. Genetic associations and functional characterization of M1 aminopeptidases and immune-mediated diseases. Genes Immun 15, 521–527 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2014.46
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2014.46