Abstract
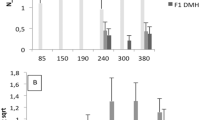
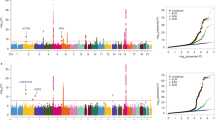
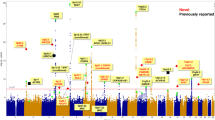
Selective breeding for the acute inflammatory response (AIR) generated two mouse lines characterized by maximum (AIRmax) and minimum (AIRmin) responses, explained by the additive effect of alleles differentially fixed in quantitative trait loci (QTLs). These mice also differ in their susceptibility to lung tumorigenesis, raising the possibility that the same loci are involved in the control of both phenotypes. To map the QTLs responsible for the different phenotypes, we carried out a genome-wide linkage analysis using single-nucleotide polymorphism arrays in a pedigree consisting of 802 mice, including 693 (AIRmax × AIRmin)F2 intercross mice treated with urethane and phenotyped for AIR and lung tumor multiplicity. We mapped five loci on chromosomes 4, 6, 7, 11 and 13 linked to AIR (logarithm of odds (LOD)=3.56, 3.52, 15.74, 7.74 and 3.34, respectively) and two loci linked to lung tumor multiplicity, on chromosomes 6 and 18 (LOD=12.18 and 4.69, respectively). The known pulmonary adenoma susceptibility 1 (Pas1) locus on chromosome 6 was the only locus linked to both phenotypes, suggesting that alleles of this locus were differentially fixed during breeding and selection of AIR mice. These results represent a step toward understanding the link between inflammation and cancer.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $19.83 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Trinchieri G . Cancer and inflammation: an old intuition with rapidly evolving new concepts. Annu Rev Immunol 2012; 30: 677–706.
Sorokin L . The impact of the extracellular matrix on inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol 2010; 10: 712–723.
Soehnlein O, Lindbom L . Phagocyte partnership during the onset and resolution of inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol 2010; 10: 427–439.
Punturieri A, Szabo E, Croxton TL, Shapiro SD, Dubinett SM . Lung cancer and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: needs and opportunities for integrated research. J Natl Cancer Inst 2009; 101: 554–559.
O'Callaghan DS, O'Donnell D, O'Connell F, O'Byrne KJ . The role of inflammation in the pathogenesis of non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 2010; 5: 2024–2036.
Brenner DR, Boffetta P, Duell EJ, Bickeboller H, Rosenberger A, McCormack V et al. Previous lung diseases and lung cancer risk: a pooled analysis from the International Lung Cancer Consortium. Am J Epidemiol 2012; 176: 573–585.
Ibanez OM, Stiffel C, Ribeiro OG, Cabrera WK, Massa S, De Franco M et al. Genetics of nonspecific immunity: I. Bidirectional selective breeding of lines of mice endowed with maximal or minimal inflammatory responsiveness. Eur J Immunol 1992; 22: 2555–2563.
Galvan A, Vorraro F, Cabrera WH, Ribeiro OG, Pazzaglia S, Mancuso M et al. Genetic heterogeneity of inflammatory response and skin tumorigenesis in phenotypically selected mouse lines. Cancer Lett 2010; 295: 54–58.
Ribeiro OG, Maria DA, Adriouch S, Pechberty S, Cabrera WH, Morisset J et al. Convergent alteration of granulopoiesis, chemotactic activity, and neutrophil apoptosis during mouse selection for high acute inflammatory response. J Leukoc Biol 2003; 74: 497–506.
Biozzi G, Ribeiro OG, Saran A, Araujo ML, Maria DA, De Franco M et al. Effect of genetic modification of acute inflammatory responsiveness on tumorigenesis in the mouse. Carcinogenesis 1998; 19: 337–346.
Maria DA, Manenti G, Galbiati F, Ribeiro OG, Cabrera WH, Barrera RG et al. Pulmonary adenoma susceptibility 1 (Pas1) locus affects inflammatory response. Oncogene 2003; 22: 426–432.
Manenti G, Dragani TA . Pas1 haplotype-dependent genetic predisposition to lung tumorigenesis in rodents: a meta-analysis. Carcinogenesis 2005; 26: 875–882.
De Franco M, Colombo F, Galvan A, Cecco LD, Spada E, Milani S et al. Transcriptome of normal lung distinguishes mouse lines with different susceptibility to inflammation and to lung tumorigenesis. Cancer Lett 2010; 294: 187–194.
Vorraro F, Galvan A, Cabrera WH, Carneiro PS, Ribeiro OG, De Franco M et al. Genetic control of IL-1beta production and inflammatory response by the mouse Irm1 locus. J Immunol 2010; 185: 1616–1621.
Manenti G, Acevedo A, Galbiati F, Giannì Barrera R, Noci S, Dragani TA . Cancer modifier alleles inhibiting lung tumorigenesis are common in mouse inbred strains. Int J Cancer 2002; 99: 555–559.
Liljander M, Sallstrom MA, Andersson S, Andersson A, Holmdahl R, Mattsson R . Identification of collagen-induced arthritis loci in aged multiparous female mice. Arthritis Res Ther 2006; 8: R45.
Manenti G, Gariboldi M, Elango R, Fiorino A, De Gregorio L, Falvella FS et al. Genetic mapping of a pulmonary adenoma resistance locus (Par1) in mouse. Nat Genet 1996; 12: 455–457.
Obata M, Nishimori H, Ogawa K, Lee GH . Identification of the Par2 (Pulmonary adenoma resistance) locus on mouse chromosome 18, a major genetic determinant for lung carcinogen resistance in BALB/cByJ mice. Oncogene 1996; 13: 1599–1604.
Manenti G, Gariboldi M, Fiorino A, Zanesi N, Pierotti MA, Dragani TA . Genetic mapping of lung cancer modifier loci specifically affecting tumor initiation and progression. Cancer Res 1997; 57: 4164–4166.
Liu PY, Vikis H, James M, Lu Y, Wang DL, Liu HB et al. Identification of Las2, a major modifier gene affecting the Pas1 mouse lung tumor susceptibility locus. Cancer Res 2009; 69: 6290–6298.
Gariboldi M, Manenti G, Canzian F, Falvella FS, Radice MT, Pierotti MA et al. A major susceptibility locus to murine lung carcinogenesis maps on chromosome 6. Nat Genet 1993; 3: 132–136.
Manenti G, Gariboldi M, Fiorino A, Zedda AI, Pierotti MA, Dragani TA . Pas1 is a common lung cancer susceptibility locus in three mouse strains. Mamm Genome 1997; 8: 801–809.
Manolio TA, Collins FS, Cox NJ, Goldstein DB, Hindorff LA, Hunter DJ et al. Finding the missing heritability of complex diseases. Nature 2009; 461: 747–753.
Zuk O, Hechter E, Sunyaev SR, Lander ES . The mystery of missing heritability: genetic interactions create phantom heritability. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2012; 109: 1193–1198.
Manenti G, Galbiati F, Giannì Barrera R, Pettinicchio A, Acevedo A, Dragani TA . Haplotype sharing suggests that a genomic segment containing six genes accounts for the pulmonary adenoma susceptibility 1 (Pas1) locus activity in mice. Oncogene 2004; 23: 4495–4504.
Ji H, Houghton AM, Mariani TJ, Perera S, Kim CB, Padera R et al. K-ras activation generates an inflammatory response in lung tumors. Oncogene 2006; 25: 2105–2112.
Wang JH, Newbury LJ, Knisely AS, Monia B, Hendry BM, Sharpe CC . Antisense knockdown of Kras inhibits fibrosis in a rat model of unilateral ureteric obstruction. Am J Pathol 2012; 180: 82–90.
Hersh CP, Silverman EK, Gascon J, Bhattacharya S, Klanderman BJ, Litonjua AA et al. SOX5 is a candidate gene for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease susceptibility and is necessary for lung development. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2011; 183: 1482–1489.
Galvan A, Dragani TA . Nicotine dependence may link the 15q25 locus to lung cancer risk. Carcinogenesis 2009; 31: 331–333.
Saccone NL, Culverhouse RC, Schwantes-An TH, Cannon DS, Chen X, Cichon S et al. Multiple independent loci at chromosome 15q25.1 affect smoking quantity: a meta-analysis and comparison with lung cancer and COPD. PLoS Genet 2010; 6: e1001053.
Castaldi PJ, Cho MH, Litonjua AA, Bakke P, Gulsvik A, Lomas DA et al. The association of genome-wide significant spirometric loci with COPD susceptibility. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2011; 45: 1147–1153.
Moffatt MF, Gut IG, Demenais F, Strachan DP, Bouzigon E, Heath S et al. A large-scale, consortium-based genomewide association study of asthma. N Engl J Med 2010; 363: 1211–1221.
Wang Y, Broderick P, Webb E, Wu X, Vijayakrishnan J, Matakidou A et al. Common 5p15.33 and 6p21.33 variants influence lung cancer risk. Nat Genet 2008; 40: 1407–1409.
Shen R, Fan JB, Campbell D, Chang W, Chen J, Doucet D et al. High-throughput SNP genotyping on universal bead arrays. Mutat Res 2005; 573: 70–82.
Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K, Thomas L, Ferreira MA, Bender D et al. PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet 2007; 81: 559–575.
Hernandez-Sanchez J, Grunchec JA, Knott S . A web application to perform linkage disequilibrium and linkage analyses on a computational grid. Bioinformatics 2009; 25: 1377–1383.
Wei WH, Knott S, Haley CS, de Koning DJ . Controlling false positives in the mapping of epistatic QTL. Heredity (Edinb) 2010; 104: 401–409.
Acknowledgements
We thank Valerie Matarese for scientific editing. This work was funded in part by grants from the Italian Association for Cancer Research (AIRC) and the Italian Foundation for Cancer Research (FIRC) to GM, from the Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP) to OCMI, from the Conselho Nacional de Pesquisas (CNPq) to OCMI, MDF, OGR and NS, and from Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC) supporting the work of SK in the GridQTL project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Galvan, A., Cabrera, W., Vorraro, F. et al. Genetic linkage analysis identifies Pas1 as the common locus modulating lung tumorigenesis and acute inflammatory response in mice. Genes Immun 14, 512–517 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2013.49
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2013.49