Abstract
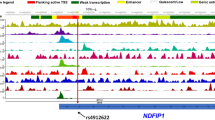
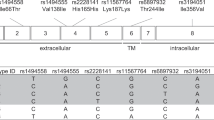
Polymorphisms (single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP)) in the interleukin-7 receptor-α (IL-7Rα)/IL-7 pathway are associated with an increased risk to develop multiple sclerosis (MS). The rs6897932 SNP in the IL-7Rα leads to increased soluble IL-7Rα production. Given the functional interaction between sIL-7Rα, membrane-bound IL-7Rα and IL-7, we assessed IL-7, mIL-7Rα and sIL-7Rα levels in MS patients and healthy controls (HCs). One-hundred and twenty eight MS patients had significantly lower sIL-7Rα levels compared with 73 HCs. The levels of sIL-7Rα increased dose-dependent upon rs6897932 [C] risk allele carriership in both HCs and MS. Next, we hypothesized that lower sIL-7Rα could result in a higher mIL-7Rα to soluble IL-7Rα ratio. Indeed, 52 MS patients had significantly increased mIL-7Rα to sIL-7Rα ratio for both CD4 and CD8 T cells compared with 44 HCs. Given the supposed role of IL-7 in autoimmunity, we determined whether sIL-7Rα influences IL-7 levels. IL-7 levels were significantly decreased in 40 MS patients compared with 40 HCs. In conclusion, MS patients had lower free IL-7 and a higher membrane to soluble IL-7Rα ratio. The soluble IL-7Rα levels correlate with the rs6897932 [C] risk allele carriership. The skew at the IL-7 and IL-7Rα level may influence responsiveness of IL-7Rα+ cells.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $19.83 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hafler DA, Compston A, Sawcer S, Lander ES, Daly MJ, De Jager PL et al. Risk alleles for multiple sclerosis identified by a genomewide study. N Engl J Med 2007; 357: 851–862.
Lundmark F, Duvefelt K, Iacobaeus E, Kockum I, Wallstrom E, Khademi M et al. Variation in interleukin 7 receptor alpha chain (IL7R) influences risk of multiple sclerosis. Nat Genet 2007; 39: 1108–1113.
Gregory SG, Schmidt S, Seth P, Oksenberg JR, Hart J, Prokop A et al. Interleukin 7 receptor alpha chain (IL7R) shows allelic and functional association with multiple sclerosis. Nat Genet 2007; 39: 1083–1091.
Zuvich RL, McCauley JL, Oksenberg JR, Sawcer SJ, De Jager PL, Aubin C et al. Genetic variation in the IL7RA/IL7 pathway increases multiple sclerosis susceptibility. Hum Genet 2010; 127: 525–535.
Mazzucchelli R, Durum SK . Interleukin-7 receptor expression: intelligent design. Nat Rev Immunol 2007; 7: 144–154.
O’Doherty C, Alloza I, Rooney M, Vandenbroeck K . IL7RA polymorphisms and chronic inflammatory arthropathies. Tissue Antigen 2009; 74: 429–431.
Concannon P, Rich SS, Nepom GT . Genetics of type 1A diabetes. N Engl J Med 2009; 360: 1646–1654.
Hartgring SA, van Roon JA, Wenting-van Wijk M, Jacobs KM, Jahangier ZN, Willis CR et al. Elevated expression of interleukin-7 receptor in inflamed joints mediates interleukin-7-induced immune activation in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2009; 60: 2595–2605.
Hoe E, McKay FC, Schibeci SD, Gandhi K, Heard RN, Stewart GJ et al. Functionally significant differences in expression of disease-associated IL-7 receptor alpha haplotypes in CD4 T cells and dendritic cells. J Immunol 2010; 184: 2512–2517.
Haas J, Korporal M, Schwarz A, Balint B, Wildemann B . The interleukin-7 receptor alpha chain contributes to altered homeostasis of regulatory T cells in multiple sclerosis. Eur J Immunol 2011; 41: 845–853.
Hare KJ, Jenkinson EJ, Anderson G . An essential role for the IL-7 receptor during intrathymic expansion of the positively selected neonatal T cell repertoire. J Immunol 2000; 165: 2410–2414.
Hug A, Korporal M, Schroder I, Haas J, Glatz K, Storch-Hagenlocher B et al. Thymic export function and T cell homeostasis in patients with relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis. J Immunol 2003; 171: 432–437.
Mazzucchelli R, Hixon JA, Spolski R, Chen X, Li WQ, Hall VL et al. Development of regulatory T cells requires IL-7Ralpha stimulation by IL-7 or TSLP. Blood 2008; 112: 3283–3292.
Rose T, Lambotte O, Pallier C, Delfraissy JF, Colle JH . Identification and biochemical characterization of human plasma soluble IL-7R: lower concentrations in HIV-1-infected patients. J Immunol 2009; 182: 7389–7397.
Crawley AM, Faucher S, Angel JB . Soluble IL-7R alpha (sCD127) inhibits IL-7 activity and is increased in HIV infection. J Immunol 2010; 184: 4679–4687.
Kreft KL, Verbraak E, Wierenga-Wolf AF, van Meurs M, Oostra BA, Laman JD et al. The IL-7Ralpha pathway is quantitatively and functionally altered in CD8 T cells in multiple sclerosis. J Immunol 2012; 188: 1874–1883.
Halwani R, Doroudchi M, Yassine-Diab B, Janbazian L, Shi Y, Said EA et al. Generation and maintenance of human memory cells during viral infection. Springer Semin Immunopathol 2006; 28: 197–208.
Kaneko S, Mastaglio S, Bondanza A, Ponzoni M, Sanvito F, Aldrighetti L et al. IL-7 and IL-15 allow the generation of suicide gene-modified alloreactive self-renewing central memory human T lymphocytes. Blood 2009; 113: 1006–1015.
Kremlev SG, Gaurnier-Hausser AL, Del Valle L, Perez-Liz G, Dimitrov S, Tuszynski G . Angiocidin promotes pro-inflammatory cytokine production and antigen presentation in multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol 2008; 194: 132–142.
Sawa S, Kamimura D, Jin GH, Morikawa H, Kamon H, Nishihara M et al. Autoimmune arthritis associated with mutated interleukin (IL)-6 receptor gp130 is driven by STAT3/IL-7-dependent homeostatic proliferation of CD4+ T cells. J Exp Med 2006; 203: 1459–1470.
Polman CH, Reingold SC, Edan G, Filippi M, Hartung HP, Kappos L et al. Diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: 2005 revisions to the ‘McDonald Criteria’. Ann Neurol 2005; 58: 840–846.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Marvin van Luijn (MSc) for critically reading the manuscript and Sandra de Bruin-Versteeg for editorial assistance with the figures. This work was supported by the MS Research Foundation, The Netherlands with an academic grant (07–630 MS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kreft, K., Verbraak, E., Wierenga-Wolf, A. et al. Decreased systemic IL-7 and soluble IL-7Rα in multiple sclerosis patients. Genes Immun 13, 587–592 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2012.34
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2012.34
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
IL-7/IL7R axis dysfunction in adults with severe community-acquired pneumonia (CAP): a cross-sectional study
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
IL7RA genetic variants differentially affect IL-7Rα expression and alternative splicing: a role in autoimmune and infectious diseases?
Genes & Immunity (2020)
-
Genetic variation in interleukin-7 is associated with a reduced erythropoietic response in Kenyan children infected with Plasmodium falciparum
BMC Medical Genetics (2019)
-
Association between the IL7R T244I polymorphism and multiple sclerosis risk: a meta analysis
Neurological Sciences (2016)
-
Association between IL7R polymorphisms and severe liver disease in HIV/HCV coinfected patients: a cross-sectional study
Journal of Translational Medicine (2015)