Abstract
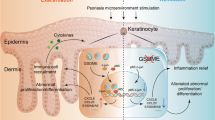
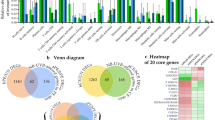
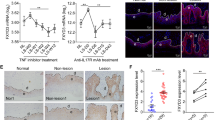
Liver X receptor-alpha (LXR-α), being a member of the nuclear receptor/transcription factor family, has been widely recognized to have a pleiotropic effect in the regulation of genes involved in innate immunity, inflammation and cholesterol homeostasis. Keeping in view the fact that psoriasis is a chronic, inflammatory and autoimmune disease with a high turnover of keratinocytes, this study was addressed to understand the functional RNomics of the LXR-α gene in cultured primary keratinocytes derived from skin biopsies of human psoriatic lesions, and from symptomless skin of psoriatic patients and clinically healthy subjects. The results of this study revealed for the first time that the LXR-α gene has an inherent capacity to regulate genes coding for inflammatory cytokines, cell cycle, immunomodulation and reactive oxygen species scavenging within human keratinocytes. Moreover, LXR-α gene knockdown within normal human keratinocytes simulated the genomic profile observed in psoriatic skin lesions. On the basis of our study, we propose that restoration of LXR-α expression/function within a psoriatic lesion may help to switch the transition from psoriatic to symptomless skin.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $19.83 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vena GA, Cassano N . Emerging drugs for psoriasis. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs 2006; 11: 567–596.
Hanley K, Komuves LG, Bass NM, He SS, Jiang Y, Crumrine D et al. Fetal epidermal differentiation and barrier development in vivo is accelerated by nuclear hormone receptor activators. J Invest Dermatol 1999; 113: 788–795.
Hanley K, Ng DC, He SS, Lau P, Min K, Elias PM et al. Oxysterols induce differentiation in human keratinocytes and increase Ap-1-dependent involucrin transcription. J Invest Dermatol 2000; 114: 545–553.
Zelcer N, Tontonoz P . Liver X receptor as integrators of metabolic and inflammatory signaling. J Clin Inves 2006; 116: 607–614.
Liu Y, Krueger JG, Bowcock AM . Psoriasis: genetic associations and immune system changes. Genes Immun 2007; 8: 1–12.
Sabat R, Philipp S, Hoflich C, Kreutzer S, Wallace E, Asadullh K et al. Immunopathogenesis of psoriasis. Exp Dermatol 2007; 16: 779–798.
Tontonoz P, Mangelsdorf DJ . Liver X receptor signaling pathways in cardiovascular disease. Mol Endocrinol 2003; 6: 985–993.
Russell LE, Harrison WJ, Bahta AW, Zouboulis CC, Burrin JM, Philpott MP . Characterisation of liver X receptor expression and function in human skin and pilosebaceous unit. Exp Dermatol 2007; 16: 844–852.
Jiang YJ, Kim P, Elias PM, Feingold KR . LXR and PPAR activators stimulate cholesterol sulfotransferase (SULT2B1b) in human keratinocytes. J Lipid Res 2005; 46: 2657–2666.
Hanley K, Ng DC, He SS, Lau P, Min K, Elias PM et al. Oxysterols induce differentiation in human keratinocytes and increase Ap-1-dependent involucrin transcription. J Invest Dermatol 2000; 114: 545–553.
Kömüves LG, Schmuth M, Fowler AJ, Elias PM, Hanley K, Man MQ et al. Oxysterol stimulation of epidermal differentiation is mediated by liver X receptor-beta in murine epidermis. J Invest Dermatol 2002; 118: 25–34.
Schmuth M, Elias PM, Hanley K, Lau P, Moser A, Willson TM et al. The effect of LXR activators on AP-1 proteins in keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol 2004; 123: 41–48.
Fowler AJ, Sheu MY, Schmuth M, Kao J, Fluhr JW, Rhein L et al. Liver X receptor activators display anti-inflammatory activity in irritant and allergic contact dermatitis models: liver-X-receptor-specific inhibition of inflammation and primary cytokine production. J Invest Dermatol 2003; 120: viii–x.
Ellis CN, Varani J, Fisher GJ, Zeigler ME, Pershadsingh HA, Benson SC et al. Troglitazone improves psoriasis and normalizes models of proliferative skin disease: ligands for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma inhibit keratinocyte proliferation. Arch Dermatol 2000; 136: 609–616.
Young CN, Koepke JI, Terlecky LJ, Borkin MS, Boyd Savoy L, Terlecky SR . Reactive oxygen species in tumor necrosis factor-α activated primary human keratinocytes: implications of psoriasis an inflammatory skin disease. J Invest Dermatol 2008; 128: 2606–2614.
Yildirim M, Inaloz HS, Baysal V, Delibas N . The role of oxidants and antioxidants in psoriasis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2003; 17: 34–36.
Kapp A . Activated granulocytes as producers of reactive oxygen species—their significance for inflammatory reaction. Hautarzt 1990; 41: 196–203.
Adorini L . Intervention in autoimmunity: the potential of vitamin D receptor agonists. Cell Immunol 2005; 233: 115–124.
Wolters M . Diet and psoriasis: experimental data and clinical evidence. Br J Dermatol 2005; 153: 706–714.
Reichrath J . Vitamin D and skin: an ancient friend, revisited. Exp Dermatol 2007; 16: 618–625.
Schulz BS, Michel G, Wagner S, Süss R, Beetz A, Peter RU et al. Increased expression of epidermal IL-8 receptor in psoriasis. Down-regulation by FK-506 in vitro. J Immunol 1993; 151: 4399–4406.
Tursen K, Kupper T, Degenstein L, William I, Fuchs E . Interleukin 6: insights to its function in skin by overexpression in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1992; 89: 5068–5072.
Asadullah K, Docke WD, Volk HD, Sterry W . The pathophysiological role of cytokines in psoriasis. Drugs Today (Barc) 1999; 35: 913–924.
Biedermann T, Röcken M, Carballido JM . TH1 and TH2 lymphocyte development and regulation of TH cell-mediated immune responses of the skin. J Invest Dermatol 2004; 9: 5–14.
Schleyer V, Landthaler M, Szeimies RM . Novel pharmacological approaches in the treatment of psoriasis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2005; 19: 1–20.
Gniadecki R, Calverley MJ . Emerging drugs in psoriasis. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs 2002; 7: 69–90.
Piskin G, Tursen U, Bos JD, Teunissen MB . IL-4 expression by neutrophils in psoriasis lesional skin upon high-dose UVB exposure. Dermatology 2003; 207: 51–53.
Tamura K, Chen YE, Horiuchi M, Chen Q, Daviet L, Yang Z et al. LXRa functions as a cAMP-responsive transcriptional regulator of gene expression. PNAS 2000; 97: 8513–8518.
Echigo T, Hasegawa M, Shimada Y, Takehara K, Sato S . Expression of fractalkine and its receptor, CX3CR1, in atopic dermatitis: possible contribution to skin inflammation. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2004; 113: 940–948.
Chomczynsky P, Sacchi N . Single step method for RNA isolation by acid guanidium thiocyanate phenol chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem 1987; 162: 156–159.
Laemmli UK . Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970; 227: 680–685.
Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidman JG, Smith JA et al. Short Protocols in Molecular Biology. John Wiley Inc.: USA, 1999.
Luck H . Catalase. In: Bergmeyer HU (ed). Methods of Enzymatic Analysis. Academic Press: New York and London, 1965, pp 885–888.
Acknowledgements
Financial support was received from the Department of Biotechnology, Ministry of Science and Technology, Government of India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, D., Kaul, D., Kanwar, A. et al. Psoriasis: crucial role of LXR-α RNomics. Genes Immun 11, 37–44 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2009.63
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2009.63
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The trisaccharide raffinose modulates epidermal differentiation through activation of liver X receptor
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Modulation of LXR-α and the effector genes by Ascorbic acid and Statins in psoriatic keratinocytes
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2014)
-
Role of Tissue Liver X-Receptors Level in Skin Diseases
International Journal of Peptide Research and Therapeutics (2013)
-
Gene armour against psoriasis
Nature India (2010)