Abstract
Purpose To explore cell death in blue light induced retinal damage.
Methods Sprague-Dawley rats reared under cyclic light were exposed continuously to diffuse blue light (400-480 nm) at 0.64 W/m2 for 3 or 6 h after 22 h of dark adaptation. The rats were kept in darkness and killed immediately, 8,16 and 24 h following light exposure. The retinal damage by the blue light was examined with a transmission electron microscope. The cell death was characterised by in situ terminal dUTP nick end labelling (TUNEL) and gel electrophoresis.
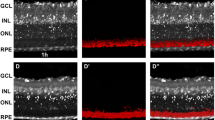
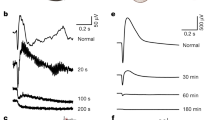
Results During the 24 h following light exposure, photoreceptor cell death was characterised by progressive condensation and margination of the chromatin, shrinkage or convolution and fragmentation of the nucleus, condensation of the cytoplasm, and formation of apoptotic bodies along with rapid removal of dying cells from damaged areas in the absence of inflammatory response. The TUNEL-positive nuclei were scattered individually in the outer nuclear layer just after light exposure. A wave of massive TUNEL labelling of photoreceptor nuclei peaked at 8-16 h and dropped at 24 h following light exposure. The distribution of TUNEL-positive nuclei was located predominantly at the upper temporal region of the retina, which was the most sensitive area to the damage caused by blue light. Furthermore, the multiples of internucleosomal cleavage of 180-200 base pairs were demonstrated at corresponding time points.
Conclusion Photoreceptor cell apoptosis is seen early after the retina is damaged by blue light.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
References
Noell WK, Walker VS, Kang BS, Berman S . Retinal damage by light in rats. Invest Ophthalmol 1966; 5: 450–73.
Ham WT Jr, Mueller HA, Sliney DH . Retinal sensitivity to damage from short wavelength light. Nature 1976; 260: 153–5.
Ham WT Jr, Mueller HA, Ruffolo JJ Jr, Clarke AM . Sensitivity of the retina to radiation damage as a function of wavelength. Photochem Photobiol 1979; 29: 735–43.
Young RW . Pathophysiology of age-related macular degeneration. Surv Ophthalmol 1987; 31: 291–306.
Taylor HR, Munoz B, West S, Bressler NM, Bressler SB, Rosenthal FS . Visible light and risk of age-related macular degeneration. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc 1990; 88: 163–73.
Wang M, Lam TT, Tso MO, Naash MI . Expression of a mutant opsin gene increases the susceptibility of the retina to light damage. Vis Neurosci 1997; 14: 55–62.
Naash ML, Peachey NS, Li ZY, Gryczan CC, Goto Y, Blanks J, Milam AH, Ripps H . Light-induced acceleration of photoreceptor degeneration in transgenic mice expressing mutant rhodopsin. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1996; 37: 775–82.
Noell WK . Possible mechanisms of photoreceptor damage by light in mammalian eyes. Vision Res 1980; 20: 1163–71.
Kerr JF, Wyllie AH, Currie AR . Apoptosis: a basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in tissue kinetics. Br J Cancer 1972; 26: 239–57.
Kerr JF, Gobe GC, Winterford CM, Harmon BV . Anatomical methods in cell death. Methods Cell Biol 1995; 46: 1–27.
Wyllie AH . Glucocorticoid-induced thymocyte apoptosis is associated with endogenous endonuclease activation. Nature 1980; 284: 555–6.
Cohen GM, Sun XM, Snowden RT, Dinsdale D, Skilleter DN . Key morphological features of apoptosis may occur in the absence of internucleosomal DNA fragmentation. Biochem J 1992; 286: 331–4.
Gavrieli Y, Sherman Y, Ben-Sasson SA . Identification of programmed cell death in situ via specific labelling of nuclear DNA fragmentation. J Cell Biol 1992; 119: 493–501.
Webb SJ, Harrison DJ, Wyllie AH . Apoptosis: an overview of the process and its relevance in disease. Adv Pharmacol 1997; 41: 1–34.
Young RW . Cell death during differentiation of the retina in the mouse. J Comp Neurol 1984; 229: 362–73.
Garcia-Valenzuela E, Gorcyzca W, Darzynkiewicz Z, Sharma SC . Apoptosis in adult retinal ganglion cells after axotomy. J Neurobiol 1994; 25: 431–8.
Rosenbaum DM, Rosenbaum PS, Gupta A, Michaelson MD, Hall DH, Kessler JA . Retinal ischemia leads to apoptosis which is ameliorated by aurintricarboxylic acid. Vision Res 1997; 37: 3445–51.
Chang GQ, Hao Y, Wong F . Apoptosis: final common pathway of photoreceptor death in rd, rds, and rhodopsin mutant mice. Neuron 1993; 11: 595–605.
Portera-Cailliau C, Sung CH, Nathans J, Adler R . Apoptotic photoreceptor cell death in mouse models of retinitis pigmentosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1994; 91: 974–8.
Lolley RN, Rong H, Craft CM . Linkage of photoreceptor degeneration by apoptosis with inherited defect in phototransduction. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1994; 35: 358–62.
Tso MO, Zhang C, Abler AS, Chang CJ, Wong F, Chang GQ, Lam TT . Apoptosis leads to photoreceptor degeneration in inherited retinal dystrophy of RCS rats. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1994; 35: 2693–9.
Smith SB, Bora N, McCool D, Kutty G, Wong P, Kutty RK, Wiggert B . Photoreceptor cells in the vitiligo mouse die by apoptosis. TRPM-2/clusterin expression is increased in the neural retina and in the retinal pigment epithelium. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1995; 36: 2193–201.
Cook B, Lewis GP, Fisher SK, Adler R . Apoptotic photoreceptor degeneration in experimental retinal detachment. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1995; 36: 990–6.
Buchi ER, Bernauer W, Daicker B . Cell death and disposal in retinoblastoma: an electron microscopic study. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 1994; 232: 635–45.
Xu GZ, Li WW, Tso MO . Apoptosis in human retinal degenerations. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc 1996; 94: 411–30.
Chang CJ, Lai WW, Edward DP, Tso MO . Apoptotic photoreceptor cell death after traumatic retinal detachment in humans [see comments]. Arch Ophthalmol 1995; 113: 880–6.
Shahinfar S, Edward DP, Tso MO . A pathologic study of photoreceptor cell death in retinal photic injury. Curr Eye Res 1991; 10: 47–59.
Li S, Chang CJ, Abler AS, Fu J, Tso MO, Lam TT . A comparison of continuous versus intermittent light exposure on apoptosis. Curr Eye Res 1996; 15: 914–22.
Abler AS, Chang CJ, Ful J, Tso MO, Lam TT . Photic injury triggers apoptosis of photoreceptor cells. Res Commun Mol Pathol Pharmacol 1996; 92: 177–89.
Hafezi F, Steinbach JP, Marti A, Munz K, Wang ZQ, Wagner EF, Aguzzi A, Reme CE . The absence of c-fos prevents light-induced apoptotic cell death of photoreceptors in retinal degeneration in vivo [see comments]. Nature Med 1997; 3: 346–9.
Hafezi F, Marti A, Munz K, Reme CE . Light-induced apoptosis: differential timing in the retina and pigment epithelium. Exp Eye Res 1997; 64: 963–70.
Ham WT Jr, Ruffolo JJ Jr, Mueller HA, Guerry D III. The nature of retinal radiation damage: dependence on wavelength, power level and exposure time. Vision Res 1980; 20: 1105–11.
Gorgels TG, van Norren D . Ultraviolet and green light cause different types of damage in rat retina. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1995; 36: 851–63.
Wu J, Chen E, Söderberg PG . Failure of ascorbate to protect broadband blue light induced retinal damage on rat. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 1999; in press.
Organisciak DT, Wang HM, Li ZY, Tso MO . The protective effect of ascorbate in retinal light damage of rats. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1985; 26: 1580–8.
Chen E, Wu J . A novel device that keeps rats' eyes open during light exposure. Lasers Light Ophthalmol 1999; in press.
Buchi ER . Cell death in rat retina after pressure-induced ischaemia-reperfusion insult: electron microscopic study. II. Outer nuclear layer. Jpn J Ophthalmol 1992; 36: 62–8.
Buchi ER . Cell death in the rat retina after a pressure-induced ischaemia-reperfusion insult: an electron microscopic study. I. Ganglion cell layer and inner nuclear layer. Exp Eye Res 1992; 55: 605–13.
Penfold PL, Provis JM . Cell death in the development of the human retina: phagocytosis of pyknotic and apoptotic bodies by retinal cells. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 1986; 224: 549–53.
Egensperger R, Maslim J, Bisti S, Hollander H, Stone J . Fate of DNA from retinal cells dying during development: uptake by microglia and macroglia (Muller cells). Brain Res Dev Brain Res 1996; 97: 1–8.
Pautler EL, Morita M, Beezley D . Hemoprotein(s) mediate blue light damage in the retinal pigment epithelium. Photochem Photobiol 1990; 51: 599–605.
Pautler EL, Morita M, Beezley D . Reversible and irreversible blue light damage to the isolated, mammalian pigment epithelium. Prog Clin Biol Res 1989; 314: 555–67.
Ninnemann H, Butler WL, Epel BL . Inhibition of respiration and destruction of cytochrome A3 by light in mitochondria and cytochrome oxidase from beef heart. Biochim Biophys Acta 1970; 205: 507–12.
Ninnemann H, Butler WL, Epel BL . Inhibition of respiration in yeast by light. Biochim Biophys Acta 1970; 205: 499–506.
Lawwill T . Three major pathologic processes caused by light in the primate retina: a search for mechanisms. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc 1982; 80: 517–79.
Chen E . Inhibition of enzymes by short-wave optical radiation and its effect on the retina. Acta Ophthalmol Suppl 1993; 71: 1–50.
Chen E, Pallon J, Forslind B . Distribution of calcium and sulphur in the blue-light-exposed rat retina. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 1995; 233: 163–7.
Zamzami N, Susin SA, Marchetti P, Hirsch T, Gomez-Monterrey I, Castedo M, Kroem G . Mitochondrial control of nuclear apoptosis [see comments]. J Exp Med 1996; 183: 1533–44.
Richter C . Reactive oxygen and nitrogen species regulate mitochondrial Ca2+ homeostasis and respiration. Biosci Rep 1997; 17: 53–66.
McConkey DJ, Orrenius S . Signal transduction pathways in apoptosis. Stem Cells 1996; 14: 619–31.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This study was supported by Karolinska Institutets Forskningsfonder, Edwin Jordans Stiftelse för Oftalmologisk Forskning, Einar och Anna Keys Resebidragsstiftelse, Carmen och Bertil Regners Stiftelse för Forskning inom Området Ögonsjukdomar, Stiftelsen Kronprinsessan Margaretas Arbetsnämnd för Synskadade
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, J., Seregard, S., Spångberg, B. et al. Blue light induced apoptosis in rat retina. Eye 13, 577–583 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/eye.1999.142
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/eye.1999.142
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Blue Light Exposure: Ocular Hazards and Prevention—A Narrative Review
Ophthalmology and Therapy (2023)
-
Over-expression of CNTF in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells protects RPE cells from short-wavelength, blue-light injury
In Vitro Cellular & Developmental Biology - Animal (2018)
-
Bystander effects elicited by single-cell photo-oxidative blue-light stimulation in retinal pigment epithelium cell networks
Cell Death Discovery (2017)
-
Scleral cross-linking by riboflavin and blue light application in young rabbits: damage threshold and eye growth inhibition
Graefe's Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology (2016)
-
AcrySof Natural filter decreases blue light-induced apoptosis in human retinal pigment epithelium
Graefe's Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology (2008)