Abstract
Hyperuricemia contributes to renal inflammation. We aimed to investigate the role of Na+–K+–ATPase (NKA) in hyperuricemia-induced renal tubular injury. Human primary proximal tubular epithelial cells (PTECs) were incubated with uric acid (UA) at increasing doses or for increasing lengths of time. PTECs were then stimulated by pre-incubation with an NKA α1 expression vector or small interfering RNA before UA (100 μg ml−1, 48 h) stimulation. Hyperuricemic rats were induced by gastric oxonic acid and treated with febuxostat (Feb). ATP levels, the activity of NKA and expression of its α1 subunit, Src, NOD-like receptor pyrin domain-containing protein 3 (NLRP3) and interleukin 1β (IL-1β) were measured both in vitro and in vivo. Beginning at concentrations of 100 μg ml−1, UA started to dose-dependently reduce NKA activity. UA at a concentration of 100 μg ml−1 time-dependently affected the NKA activity, with the maximal increased NKA activity at 24 h, but the activity started to decrease after 48 h. This inhibitory effect of UA on NKA activity at 48 h was in addition to a decrease in NKA α1 expression in the cell membrane, but an increase in lysosomes. This process also involved the subsequent activation of Src kinase and NLRP3, promoting IL-1β processing. In hyperuricemic rats, renal cortex NKA activity and its α1 expression were upregulated at the 7th week and both decreased at the 10th week, accompanied with increased renal cortex expression of Src, NLRP3 and IL-1β. The UA levels were reduced and renal tubular injuries in hyperuricemic rats were alleviated in the Feb group. Our data suggested that the impairment of NKA and its consequent regulation of Src, NLRP3 and IL-1β in the renal proximal tubule contributed to hyperuricemia-induced renal tubular injury.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Hyperuricemia is an important risk factor for cardiovascular and kidney diseases.1 A study of 177 570 patients lasting more than 25 years showed an independent association between high uric acid (UA) levels and end-stage renal disease.2 Pilot investigations indicated that lowering plasma UA concentrations slowed and delayed the development of chronic kidney disease,3, 4, 5, 6 confirming UA as a critical risk factor for renal injury with tubulointerstitial inflammation commonly detected.7, 8
Approximately two-thirds of UA is excreted by the kidneys, whereas the remaining one-third is produced by intestinal uricolysis.9 The renal proximal tubule is responsible for almost all renal urate transport and is where urate re-absorption primarily occurs.10 Proximal renal tubular epithelial cells (PTECs) excrete urate and express ion and urate transport channels11 and thus are highly metabolic cells containing abundant mitochondria and lysosomes.12 Metabolic disorders have recently been considered to serve as an initial event of inflammation in renal tubular injury13, 14 and interventions for metabolic disorders may provide promising therapies for chronic kidney disease.15, 16, 17 UA has also been shown to induce mitochondrial dysfunction and reduced intracellular ATP in endothelial cells.18 However, whether metabolic disorders induced by hyperuricemia related to it induced renal inflammation19, 20 in renal tubular cells is not clear.
In fact, the driving force of urate transporters in renal PTECs comes from its basolateral sodium potassium ATPase (Na+–K+–ATPase, NKA), which is well-known for its role as a membrane binding ion pump, transporting three Na+ ions out of the cell for every two K+ ions transported into the cell at the cost of one ATP. This active energy-dependent transport provides the diffusion gradient for many other transporters, including urate transporters, and it serves to control the homeostasis of electrolytes and fluids.21, 22 There is now mounting evidence that NKA also has a vital role as a signal transducer, controlling a number of vital cell functions,23, 24 and its role in renal disease has attracted attention in recent years.22 NKA is mainly composed of α, β and γ subunits, each of which has a number of subtypes and has a different physiological role.25 Renal tubular epithelial cells only express the α1 and β1 subtypes.26 In the resting state, the α-subunit of NKA and the protein tyrosine kinase Src are coupled in the cell membrane, which inhibits the activation of Src. Impairment of NKA causes Src dissociation from binding with NKA and activates the Src signaling pathways.22 Src has been shown to mediate NOD-like receptor pyrin domain-containing protein 3 (NLRP3) activation.27 NLRP3 has been shown in our previous studies to be a key factor in renal tubular inflammation under conditions of hyperuricemia.19, 20
As NKA is mainly supplied by mitochondrial ATP and is influenced by mitochondrial function,28 it is possible that NKA may be a bridge linking UA-induced mitochondrial disorders to inflammatory processes in the kidney, especially in renal tubular cells. Hence, in this study, we investigated the NKA activity, expression and signaling involved in cultured human primary PTECs and oxonic acid (OA)-induced hyperuricemic rats, to study the role of NKA in hyperuricemia-induced renal tubular injury.
Materials and methods
Materials and reagents
Human primary renal PTECs and cell culture medium were purchased from ScienCell (San Diego, CA, USA). UA and a uricase inhibitor OA were purchased from Sigma (St. Louis, MO, USA). Enzyme immunoassay kit for detection of interleukin 1β (IL-1β) was purchased from eBioscience (San Diego, CA, USA). A Cell Surface Protein Isolation Kit was purchased from Pierce (Rockford, IL, USA). Anti-NKA α1, anti-Src, anti-phosphor-Src, anti-CIAS1/NALP3, anti-ATP-binding cassette sub-family G member 2 (ABCG2), anti-multidrug resistance-associatedprotein 4 (MRP4), anti-SLC22A6 (OAT1), anti-SLC22A7 (OAT2), anti-SLC22A8 (OAT3), anti-SLC22A11 (OAT4), anti-SLC17A3 (NPT4), anti-SLC13A3, anti-GLUT9, anti-Beclin 1, anti-SQSTM1/p62, anti-lysosomal-associated membrane protein 2 (LAMP2), anti-uncoupling protein 2 (UCP2) antibodies and reactive oxygen species (ROS) production assay kit were purchased from Abcam (Cambridge, UK). Anti-IL-1β and OCTL1 (OAT 10) antibodies were purchased from Santa Cruz (Dallas, Texas, USA). Anti-SLC17A1 (NPT1), anti-SLC2A9 (URAT1), anti-SLC5A8 and anti-SLC5A12 antibodies were purchased from Proteintech (Rosemont, IL, USA). Anti-LC3 antibody was purchased from Novus (Littleton, CO, USA). Anti-mouse and anti-rabbit secondary antibodies were purchased from Sinobio (Shanghai, China). NKA activity kit for cultured cells, mitochondria isolation, mitochondrial membrane potential and respiratory complex I, II, III, IV and V activity kits were purchased from Genmed (Shanghai, China), and the tissue NKA activity kit was purchased from ToYongBio (Shanghai, China). NKA α1 small interfering RNA (siRNA) and expression vectors were purchased from Biotend (Shanghai, China). Lyso-Tracker Red and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release kit were purchased from Beyotime (Shanghai, China). The ATP measurement kit was purchased from Jiwei Biological Technology (Shanghai, China). The Annexin V/Propidium Iodide Flow Cytometry assay kit was purchased from Becton Dickinson (BD, San Jose, CA, USA). Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) and 18S RNA primers were purchased from Invitrogen (Carlsbad, CA, USA). The Sprague–Dawley (SD) rats were from Jiesijie Experimental Animal Co., Ltd (Shanghai, China). Febuxostat (Feb) was kindly provided by Jiangsu Hengrui Medicine Co., Ltd (Shanghai, China).
Cell culture
Human primary PTECs were cultured in epithelial cell medium, which contains 500 ml of basal medium, 50 ml of fetal bovine serum, 5 ml of epithelial cell growth supplement and 5 ml of penicillin/streptomycin solution. The cells were incubated at 37 °C in 5% CO2 and 95% air. In all experiments, there was a ‘growth arrest’ period of 24 h in serum-free medium before stimulation.
Soluble UA preparation
UA was dissolved in 1 M NaOH at a concentration of 50 mg ml−1, as previously described.19 The solution was examined to ensure that it was free of mycoplasma and filtered (22 μm pore size) before use. Crystals were not detectable using polarizing microscopy, nor did they develop during cell incubation.
Animal model and measurement
Twenty 8-week-old male-specific pathogen-free SD rats weighing 200–250 g were bred at the animal center in the School of Pharmacy at Fudan University. Rats were divided into five groups: (1) Cont 7w (normal diet for 7 weeks), (2) OA 7w (normal diet+gastric OA 750 mg kg−1 per day for 7 weeks), (3) Cont 10w (normal diet for 10 weeks), (4) OA 7w (normal diet+gastric OA 750 mg kg−1 per day for 7 weeks) and (5) Feb 10w (normal diet+gastric OA 750 mg kg−1 per day for 10 weeks +Feb 5 mg kg−1 per day for 4 weeks starting in the 7th week); rats were killed at the 7th or 10th week. Twenty-four-hour urine collection was performed before the day of killing. Serum UA, blood urea nitrogen and serum creatinine concentrations were determined by an enzymatic colorimetric assay method using a fully automatic chemistry analyzer (MODULAR D/P, Roche, Basel, Switzerland). Urinary albumin and creatinine were measured using the sulfosalicylic acid method.
Fresh renal cortex tissues were collected during the killing and proceeded to NKA activity and ATP measurements. Tissues were stained with hematoxylin–eosin for light microscopy and immunoperoxidase staining targeting the NKA α1 was performed, as described previously.29 The rest of the tissues were stored at −80 °C for immunoblotting assays. All animal procedures were in accordance with the National Institute of Health guidelines (NIH Pub. No. 85-23, revised 1996) and were approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Fudan University.
Transfection of siRNA and expression construct of NKA α1 subunit into cultured human PTECs
The complete sequences of Na+/K+ transporting subunit α1 mRNA including both the 5′- and 3′-untranslated regions were from GenBank (ATP1A1 ATPase) Homo sapiens (human)), Gene No. 476). siRNA against NKAα1 (Forward: 5′-GGGAUUAACAUCUGCUCGUdTdT-3′, Reverse: 5′-ACGAGCAGAUGUUAAUCCCdTdT-3′), a control oligoribonucleotide and its α1subunit expression vector were synthesized by Biotend. The uniqueness of the sequences was confirmed using the Genbank/EBI database. Cells were transfected with 50 nmol l−1 NKA a1 siRNA or 30 nmol l−1 NKA α1 expression vector with Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen) and incubated for 30 h before 48 h stimulation of UA.
Detection of cell injury and mitochondrial function
The LDH assay was performed according to the manufacturer’s instructions. LDH released in the culture supernatants was measured with a 30 min coupled enzymatic assay and measured using the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay reader at a wavelength of 490 nm. The percentage of cytotoxicity was calculated using the following equation:

Intracellular ROS production was detected using the Cellular Reactive Oxygen Species Detection Assay Kit (Orange Fluorescence, Abcam). Cells were seeded in a six-well plate and stimulated by NKA α1expression vector or siRNA 30 h before 48 h UA stimulation (100 μg ml−1). After 48 h, cells were treated with 1 μl ROS Orange Stock Solution for 30 min. Then, the cells were collected and resuspended in 200 μl of phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) buffer. Then, intracellular ROS levels were performed by flow cytometry (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA, USA) at 488 nm. All determinations were performed in triplicate.
Apoptosis assays was carried out using flow cytometry to quantify the levels of apoptotic cells. The annexin V assay was performed using the fluorescein isothiocynate–Annexin V Apoptosis Detection Kit according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Briefly, after the treatment, cells were washed twice with ice-cold PBS solution and re-suspended in 1 × 105/100 μl of binding buffer and incubated with 5 μl of Annexin V–fluorescein isothiocynate and 5 μl of Propidium Iodide for 15 min at room temperature in the dark. After 15 min of incubation, 400 μl of binding buffer were added to make 500 μl final volumes and checked with a BD FACS Calibur (San Jose, CA, USA).
Mitochondrial membrane potential and respiratory complexes were measured according to the manufacturer’s instructions after the extraction of mitochondrion from the cells. Mitochondrial membrane potential was detected using JC-1 staining and was read by flow cytometry (BD Biosciences) at 488 nm. The specific enzymatic activity of complex I (NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase) was measured by a reduction of the ubiquinone analog decylubiquinone. For the activity of complex II (succinate-ubiquinone oxidoreductase), the reduction of 2,6-dichlorophenolindophenol, when coupled to complex II-catalyzed reduction of decylubiquinone, was measured. For the specific activity of complex III (ubiquinol/cytochrome c oxidoreductase), the reduction of cytochrome c catalyzed by complex III in the presence of reduced decylubiquinone was monitored. The specific activity of complex IV (cytochrome c oxidase) was measured by following the oxidation of reduced cytochrome c, which had been prepared in the presence of dithionite. The specific activity of complex V (ATP synthase) was measured by a reduction of NADH. All enzymatic activities were expressed as micromoles per minute per milligram protein.30
Primers and probe sets for human mtDNA and 18S RNA were designed from known sequences in the GenBank and the primer sequences were listed in Table 1. GAPDH was used as the endogenous control to normalize the amount of cDNA added to each reaction (ΔCT) and the mean ΔCT of the control samples was used as the calibrator to calculate the ΔΔCT. Quantification of each transcript was calculated by the comparative CT method. In this method, the relative quantity of target mRNA, normalized to the endogenous control and relative to the calibrator, was equal to 2−ΔΔCT.
Examination of autophagy markers, mitochondrial UCP2 and urate transporters
Autophagy markers and urate transporters were detected by western blot analysis as described previously,19 using anti-LC3 (1:2000), anti-Beclin 1 (1:2000), anti-p62 (1:1000), anti-LAMP2 (1:500), anti-UCP2 (1:500), anti-ABCG2 (1:1000), anti-MRP4 (1:500), anti-SLC22A6 (OAT1, 1:500), anti-SLC22A7 (OAT2, 1:500), anti-SLC22A8 (OAT3, 1:1000), anti-SLC22A11 (OAT4, 1:500), anti-SLC17A3 (NPT4, 1:1000), anti-SLC13A3 (1:500), anti-GLUT9 (1:500), anti-OCTL1 (OAT 10, 1:500), anti-SLC17A1 (NPT1, 1:500), anti-SLC2A9 (URAT1, 1:500), anti-SLC5A8 (1:500) and anti-SLC5A12 (1:500) as the primary antibodies, respectively.
NKA enzymatic activity measurement in cultured human PTECs and in rat renal cortex tissue
In culture PTECs, the NKA activity was measured at 340 nm with the NKA activity kit using an amended phosphoenol pyruvate/pyruvatekinase/lactate dehydrogenase coupled assay in the presence of ouabain and NADH.31 The procedures were conducted according to the manufacturer’s instructions. NKA activity refers to the ouabain sensitive NKA activity and was defined as the required NKA amount to oxidize 1 mol l−1 NADH to NAD at 37 °C and pH 7.5 per milligram of protein per minute.
Fifty micrograms of fresh renal cortex tissue were collected during the killing of the rats; 50 ml 0.01 mol l−1 PBS (PH 7.4) was added and the renal tissue was homogenized using a homogenizer. Samples were centrifuged at 8000 g for 10 min at 4 °C. The supernatant was collected and proceeded to NKA activity measurement. NKA activity was obtained by measuring inorganic phosphate release using an NKA activity kit (ToYongBio) as in Forbush’smethod.32 The procedures were performed according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Readings were obtained at 660 nm. Enzyme-specific activity was expressed as 1 μmol of inorganic phosphate released per milligram of protein per hour.
Expression of NKA α1 subunit in cell membrane of cultured human PTECs
PTECs were incubated in a T75 flask including 100 μg ml−1 UA with or without transfection of NKA α1 siRNA or an expression vector. The membrane abundance of the endogenous NKA α1 subunit in PTECs was analyzed by surface biotinylation using a Cell Surface Protein Isolation Kit according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Pierce). The surface proteins were eluted and proceeded to western blotting as described previously,19 using mouse anti-NKA α1 (1:500) as the primary antibody.
Immunocytochemistry of NKA α1 in cultured human PTECs and rat renal cortex tissue
Co-localization of NKA α1 and Lyso-Tracker Red was performed by immunocytochemistry as previously described.33 PTECs were incubated with Lyso-Tracker Red diluted 1:1000 for 30 min at 37 °C. Next, the cells were rinsed three times with PBS and fixed in 2% formaldehyde/150 mM NaCl/20 mM Hepes (pH, 7.8) for 30 min at room temperature. After quenching with 50 mM Tris in staining buffer (0.1% Triton X-100/100 mM NaCl/20 mM Hepes pH, 7.8) for 1 h and rinsing with staining buffer, the cells were then incubated overnight at 4 °C with a mouse monoclonal anti-NKA α1 antibody diluted 1:200 in staining buffer. After rinsing in staining buffer, the cells were incubated for 1 h at room temperature with fluorescein isothiocynate-conjugated goat anti mouse secondary antibody diluted 1:500 in staining buffer. Fluorescence was detected using an LSM510 Meta Confocal laser-scanning microscope (Leica, TCS-SP5, Solms, Germany).
Renal tissue immunohistochemistry was performed on 4 μm sections of formaldehyde-fixed and paraffin-embedded renal cortices of rats. Primary antibodies against NKA α1 (1:200) were incubated at 4 °C overnight after the retrieval of antigens, followed by reacting with horseradish peroxidase-labeled secondary antibody (1:200) at 37 °C for 1 h. The color reaction was induced by 3,3'-diaminobenzidine, followed by counterstaining with 10% Mayer’s hematoxylin.
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay of IL-1β protein in cell culture supernatants
Growth-arrested PTECs were incubated with 100 μg ml−1 soluble UA for 48 h with or without previous incubation of siRNA or expression construct of NKA α1. Cell culture supernatants were collected and stored at −70 °C until the protein assay was performed. Protein levels of IL-1β in culture supernatants were determined using a commercial assay kit (eBioscience). The procedures were performed according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Western blot analysis in cultured human PTECs and rat renal cortex tissue
After collecting the cell culture supernatant as mentioned above, the remaining cells were lysed with lysis buffer containing protease inhibitor cocktails (Sigma). Renal cortex tissue of rats was collected and lysed in lysis buffer. The total proteins were collected and western blotting was performed as described previously.19 The concentrations of the primary antibodies used in PTECs were mouse monoclonal anti-CIAS1/NALP3 (1:1000), rabbit polyclonal anti-Src (1:1000) and anti-phosphor-Src (1:1000), whereas in the rat tissues, anti-CIAS1/NALP3 (1:500), anti-IL-1β (1:250), anti-Src (1:500) and anti-NKA α1 (1:4000) were used.
Measurements of ATP in cultured human PTECs and rat renal cortex tissue
After the interfering PTECs of UA with or without transfected siRNA or expression vector of the NKA α1 subunit, cell lysates were collected. Intracellular ATP were measured using an ATP bioluminescence assay kit (Jiwei Biological Technology). Fifty micrograms of fresh rat renal cortex tissue were collected during the killing of the rats and 50 ml of 0.01 mol l−1 PBS (pH 7.4) was added. Renal tissue was homogenized with a homogenizer and centrifuged at 8000 g min−1 for 10 min at 4 °C; next, the supernatant was collected and proceeded to ATP measurement. The procedures were taken according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Statistical analysis and art work
All data are expressed as the means±s.d. unless otherwise specified. Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS v.19.0 for Windows (SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Multivariate analysis of variance was adopted to compare intergroup differences with continuous variables. P<0.05 was considered statistically significant. The art work was drawn using GraphPad prism 5.0.
Results
UA dose- and time-dependently reduced intracellular ATP levels in cultured human PTECs
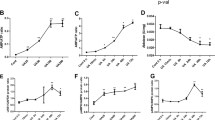
PTECs were incubated with different concentrations of UA (25, 50, 100 and 200 μg ml−1) for 48 h. In the parallel experiment, PTECs were incubated with different time courses of UA (100 μg ml−1) for 15 min, 6 h, 24 h and 48 h, respectively. UA dose- and time-dependently reduced the intracellular ATP levels (Figures 1A and B) in PTECs. No difference was noticed between 24 and 48 h, nor between100 and 200 μg ml−1 treatments of UA.
UA dose- and time-dependently reduced intracellular ATP levels altered NKA activity and its α1 subunit cellular expression in human PTECs. PTECs were incubated with different concentrations of UA (25 to 200 μg ml−1) for 48 h or different time courses (15 min to 48 h of 100 μg ml−1 UA). UA dose- (A) and time-dependently (B) reduced intracellular ATP levels. UA 25 μg ml−1 exhibited a tendency to increase NKA activity, but UA concentrations of 100 μg ml−1 started to dose-dependently reduce the NKA activity (C). UA100 μg ml−1 time-dependently affected the NKA activity, with the maximal increased NKA activity at 24 h that started to decrease until 48 h (D). Immunofluorescence showed that the expression of the α1 subunit of NKA (green) was linearly expressed on the cell surface, but when the cells were incubated with 100 μg ml−1 UA for 48 h, NKA α1 membrane expression was reduced and scattered in the cytoplasm (E). Immunoblotting of cell surface proteins confirmed the changed cell membrane expression of the α1 subunit. Twenty-four hours of incubation of 100 μg ml−1 UA increased the α1 subunit, but 48 h of incubation of UA reduced the α1 subunit expression on the cell surface of PTECs (F). *P<0.05 vs Cont, **P<0.01 vs Cont, #P<0.05 vs UA 24 h.
UA altered NKA activity and its α1 subunit cellular expression in cultured human PTECs
PTECs were incubated with UA as mentioned above. Figure 1C shows that 25 μg ml−1 UA exhibited a tendency of increasing NKA activity, but beginning at 100 μg ml−1, UA dose-dependently reduced the NKA activity. Figure 1D reveals that 100 μg ml−1 UA time-dependently affected the NKA activity, with the maximal increased NKA activity at 24 h that started to decrease until 48 h. No difference was noticed between 100 and 200 μg ml−1 treatments of UA.
Immunofluorescence was performed to assess the localization of the α1 subunit of NKA in PTECs. We used 4′, 6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole (blue) to mark the nucleus. Confocal microscopy immunofluorescence showed that in the control group, NKAα1 (green) was linearly expressed along the cell membrane. After incubation of 100 μg ml−1 UA for 48 h, the NKAα1 subunit was increased in the cytoplasm and reduced in the cell membrane (Figure 1E). Immunoblotting of cell membrane protein extraction was also performed to confirm the change. Twenty-four hours of 100 μg ml−1 UA incubation increased the cell membrane expression of the NKA α1 subunit, but 48 h evidenced the reduction of NKA α1 subunit on the cell surface (Figure 1F). We selected the 100 μg ml−1 UA 48 h stimulation for the following experiments.
NKA α1 expression vector and siRNA altered its activity and subcellular expression in cultured human PTECs
NKA α1 expression vector or siRNA was added to cells for 30 h to over-express or inhibit NKA α1 before the 48 h UA stimulation. The NKA α1 expression vector enhanced NKA activity and its α1cell membrane expression, whereas NKA α1 siRNA reduced its activity (Figures 2A and B). We used Lyso-Tracker Red to label cell lysosomes (red) and then fixed the cells with 4% paraformaldehyde before immunohistochemistry staining of NKAα1 (green). Confocal microscopy immunofluorescence showed that in the control group, NKA α1 was linearly expressed along the cell membrane. After adding UA, NKA α1 translocated into the lysosome. NKA α1 expression vector increased its expression on the cell membrane and decreased its lysosomal expression, whereas NKA α1 siRNA decreased its cell membrane expression and increased its lysosomal expression (Figure 2C).
NKA α1 expression vector and siRNA altered its activity and subcellular expression. To overexpress or inhibit NKA α1 expression, the NKA α1 expression vector or siRNA was added to PTECs for 30 h before 48 h of UA 100 μg ml−1 stimulation. The NKA α1 expression vector enhanced its activity and cell membrane expression, whereas its siRNA reduced its activity (A, B). We used Lyso-Tracker Red to label the lysosomes of cells (red) and then fixed the cells before proceeding to immunohistochemistry staining of NKA α1 (green). Confocal microscopy immunofluorescence showed that, under normal circumstances, NKA α1 was linearly expressed along the cell membrane (C–c). After adding UA, NKA α1 translocated into the cell plasma and were scattered into the lysosomes (C–f). The NKA α1expression vector increased its cell membrane expression and decreased its lysosome expression (C–i), whereas NKA α1 siRNA decreased its cell membrane expression and increased its lysosome expression (C–l). *P<0.05 vs Cont, **P<0.01 vs Cont, #P<0.05 vs UA, ##P<0.01 vs UA.
NKA α1-alleviated UA induced ROS production, autophagy and mitochondrial dysfunction in cultured human PTECs
NKA α1 expression vector or siRNA was added to cells for 30 h to overexpress or inhibit NKA α1 before the 48 h stimulation of UA. UA significantly increased ROS production (Figures 3a and b), LDH release (Figure 3c), early apoptosis (Figures 3d and e), but not late apoptosis (Figures 3d and f), and induced autophagy as indicated by reduced p62 (Figure 3g) and an increased LC3-II/LC3-I ratio (Figure 3h), Beclin-1 (Figure 3i) and LAMP2 (Figure 3j). NKA α1 expression vector significantly alleviated ROS production (Figures 3a and b), increased p62 (Figure 3g), reduced LAMP2 (Figure 3j) and tended to reduce early apoptosis (Figures 3d and e) and the LC3-II/LC3-I ratio (Figure 3h). NKA α1 expression vector had no effect on late apoptosis (Figures 3d and f). UA also significantly reduced the mitochondrial membrane potential (Figures 4a and b), mtDNA copy (Figure 4d), and complex I (Figure 4e) and V (Figure 4i) activities, as well as increased UCP2 expression (Figure 4c). UA did not alter complex II (Figure 4f), III (Figure 4g) and IV (Figure 4h) activities. The NKA α1 expression vector alleviated mitochondrial dysfunction by increased mitochondrial membrane potential (Figures 4a and b) and mtDNA (Figure 4d), and complex I (Figure 4e) and V (Figure 4i) activities, and it reduced UCP2 expression (Figure 4c). The NKA α1 expression vector demonstrated no effect on complex II (Figure 4f), III (Figure 4g) and IV (Figure 4h) activities.
NKA α1 alleviated UA induced ROS production and autophagy in cultured human PTECs. The NKA α1 expression vector or siRNA was added to cells for 30 h to overexpress or inhibit NKA α1 before 48 h UA 100 μg ml−1 stimulation. UA significantly increased ROS production (a, b), LDH release (c), early apoptosis (d, e) and induced autophagy, as indicated by reduced p62 (g) and an increased LC3II/LC3I ratio (h), beclin-1 (i) and LAMP2 (j) when compared with the control. The NKA α1 expression vector significantly alleviated ROS production (a, b) had a tendency to reduce early apoptosis (d, e), but had no effect on late apoptosis (d, f). The NKA α1 expression vector increased p62 expression (g) and reduced LAMP2 expression (j). The NKA α1 expression vector exerted a tendency to reduce the LC3II/LC3I ratio (h). *P<0.05 vs Cont, **P<0.01 vs Cont, #P<0.05 vs UA, ##P<0.01 vs UA.
NKA α1 alleviated UA induced mitochondrial dysfunction in cultured human PTECs. NKA α1 expression vector or siRNA was added to cells for 30 h to overexpress or inhibit NKA α1 before 48 h UA 100 μg ml−1 stimulation. UA significantly reduced mitochondrial membrane potential (a, b), increased UCP2 expression (c), reduced mtDNA copies (d), and complex I (e) and V (I) activities. UA did not change complex II (f), III (g) and IV (h) activities. The NKA α1 expression vector alleviated mitochondrial dysfunction by increasing the mitochondrial membrane potential (a, b), reducing UCP2 expression (c), increasing mtDNA copies (d), as well as complex I (e) and V (i) activities. The NKA α1 expression vector exert no effect on complex II (f), III (g) and IV (h) activities. *P<0.05 vs Cont, **P<0.01 vs Cont, #P<0.05 vs UA, ##P<0.01 vs UA.
NKA α1 altered urate transporter expression in cultured human PTECs
NKA α1 expression vector or siRNA was added to cells for 30 h to over-express or inhibit NKA α1 before 48 h stimulation of UA. Except OAT3 (Figure 5m), UA significantly increased expressions of SLC5A8 (Figure 5a), SLC5A12 (Figure 5b), URAT1 (Figure 5c), OAT10 (Figure 5d), OAT4 (Figure 5e), GLUT9 (Figure 5f), MRP4 (Figure 5g), ABCG2 (Figure 5h), NPT1 (Figure 5i), NPT4 (Figure 5j), OAT2 (Figure 5k), OAT1 (Figure 5l) and SLC13A3 (Figure 5n). NKA α1 expression vector significantly increased UARAT1 (Figure 5c) and reduced NPT4 (Figure 5j) and MRP4 (Figure 5g) expression, whereas it had no effect on other urate transporters. NKA α1 siRNA reduced SLC5A8 (Figure 5a), UARAT1 (Figure 5c) and OAT4 (Figure 5e) expressions, whereas it exerted no effect on other urate transporters.
NKAα1 altered urate transporter expression in cultured human PTECs. NKA α1 expression vector or siRNA was added to cells for 30 h to overexpress or inhibit NKA α1 before 48 h of UA 100 μg ml−1 stimulation. Except OAT3 (m), UA significantly increased the expressions of SLC5A8 (a), SLC5A12 (b), URAT1 (c), OAT10 (d), OAT4 (e), GLUT9 (f), MRP4 (g), ABCG2 (h), NPT1 (i), NPT4 (j), OAT2 (k), OAT1 (l) and SLC13A3 (n). NKA α1 expression vector significantly increased UARAT1 (c) and reduced MRP4 (g) and NPT4 (j) expressions, whereas it had no effect on other urate transporters. NKA α1 siRNA reduced SLC5A8 (a), UARAT1 (c) and OAT4 (e) expressions, wheresa it had no effect on other urate transporters. *P<0.05 vs Cont, **P<0.01 vs Cont, #P<0.05 vs UA, ##P<0.01 vs UA.
NKA α1-mediated Src activation and NLRP3-IL-1β signaling in UA-activated human PTECs
UA significantly induced the activation of Src (recognized as phosphor-Src/Src, Figure 6a), increased the expressions of NLRP3 (Figure 6b) and IL-1β (Figure 6c), and reduced the intracellular ATP level (Figure 6d). NKA α1 siRNA significantly increased the intracellular ATP level, but it did not change the Src, NLRP3 or IL-1β activation induced by UA, whereas the NKA α1 expression vector had no effect on the intracellular ATP level, but it significantly suppressed UA-induced Src, NLRP3 and IL-1β activation.
Src activation and NLRP3-IL-1β signaling in UA activated PTECs and hyperuricemic rats. UA (100 μg ml−1, 48 h) stimulation significantly activated Src (indicated as phosphor-Src (pSrc)/Src, a), NLRP3 (b) and IL-1β (c), and reduced intracellular ATP (d). The NKA α1 expression vector or siRNA was added to PTECs for 30 h before 48 h UA 100 μg ml−1 stimulation. NKA α1 siRNA significantly increased intracellular ATP level; however, it did not alleviate Src, NLRP3 and IL-1β activation induced by UA, whereas NKA α1 expression vector had no effect on intracellular ATP level, but significantly alleviated Src, NLRP3 and IL-1β activation induced by UA. (a–d) *P<0.05 vs Cont, **P<0.01 vs Cont, #P<0.05 vs UA, ##P<0.01 vs UA. Renal cortex expressions of Src, NLRP3 and IL-1β were detected by western blotting. Src (e), NLRP3 (f) and IL-1β (g) in OA-treated rats started to increase at week 7 and significantly higher than that of the control group at week 10. The expression of Src, NLRP3 and IL-1β were lower in the febuxostat group. Renal cortex ATP levels (h) were not different among Cont 10w, OA10w and Feb 10w groups. (e, f) *P<0.05 vs Cont, **P<0.01 vs Cont, #P<0.05 vs OA 10w.
Hyperuricemicrats developed microalbuminuria and slight mesangial expansion
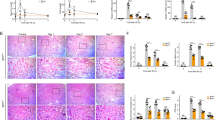
Male SD rats that were administered with gastric OA for 10 weeks showed significantly increased serum UA levels(Figure 7A). The rat blood urea nitrogen and serum creatinine levels of all the groups did not differ (data not shown). Urinary UA levels were not different among the Cont 10w, OA 10w and Feb 10w groups (Figure 7B). OA began to elevate the urinary albumin/creatinine ratio in rats at the 4th week and kept rising until the 10th week (Figure 7C). Feb treatment showed a tendency to reduce urinary albumin/creatinine ratio in hyperuricemic rats (Figure 7D). OA induced a slight increase in rat glomerular size and mesangial expansion at the 7th week and more significant changes were observed at the 10th week (Figure 7E). Feb treatment reduced serum UA levels and renal mesangial expansion in OA-dosed rats (Figure 7).
Hyperuricemicrats developed microalbuminuria and slight mesangial expansion. OA gastric administration for 7 weeks showed a tendency of elevated UA levels and significantly increased serum UA level at the 10th week in SD rats (A). Urinary UA were not different among Cont 10w, OA 10w and Feb 10w groups (B). OA started to increase urinary albumin/creatinine ratio (ACR) at the 4th week and maintained this effect till the 10th week (C). Feb treatment showed a tendency of reducing urinary ACR in hyperuricemic rats (D). OA induced a slight increase in glomerular size and mesangial expansion at the 7th week and the changes were more significant at the 10th week (E). Feb treatment reduced serum UA levels and renal mesangial expansion in OA-administered rats.*P<0.05 vs Cont, **P<0.01 vs Cont, ##P<0.01 vs OA 10w.
Impairment of NKA in hyperuricemic rats
The NKA activity in the renal cortex of rats in the OA group was higher than in the control group at the 7th week, but it was lower than the activity in the control group at the 10th week. Feb treatment in OA rats significantly increased renal cortex NKA activity compared with rats administered only OA (Figure 8A). At the 7th week, NKA α1 expression in the OA groups showed an increasing tendency versus the control group, but it was lower than the activity in the control group at the 10th week (Figure 8B). Immunohistochemistry showed that the NKA α1 subunit was expressed on the basolateral side of PTECs and was higher in the OA 7w group than in the Cont 7w group, but the NKA α1 subunit was lower in the OA 10w group than in the Cont 10w group (Figure 8C).
Impairment of NKA in hyperuricemic rats. The activity of NKA in the renal cortex of rats was higher than in the control group at the 7th week, but was lower than that in the normal group at the 10th week. Feb treatment increased NKA activity compared with the OA group (A). The renal cortex expression of the NKA α1 subunit was correlated with its activity and the NKA α1 subunit expression showed an increased tendency in the OA versus the control group at the 7th week, but it was lower in the OA group than in the control group at the 10th week. Feb treatment increased NKA α1 subunit expression in OA administered rats (B). Immunohistochemistry showed that NKA α1subunit expression was expressed on the basolateral side of the proximal tubular epithelial cells and was higher in the OA 7w group than in the Cont 7w group, but NKA α1 subunit expression was lower in the OA 10w group than in the Cont 10w group (C). *P<0.05 vs Cont.
Activation of Src-NLRP3-IL-1β in hyperuricemic rats
Western blotting showed that renal cortex expressions of Src (Figure 6e), NLRP3 (Figure 6f) and IL-1β (Figure 6g) in OA-treated rats started to increase at week 7 and were significantly higher than in the control group at week 10. The expression of Src, NLRP3 and IL-1β were lower in the Feb group when compared with the group treated only with OA (Figure 6). Renal cortex ATP levels were not different among the Cont 10w, OA10w and Feb 10w groups (Figure 6h).
Discussion
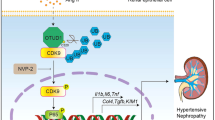
In this study, we examined the role of NKA in UA-stimulated PTECs and in a hyperuricemic rat model induced by oral OA. Our results demonstrated that UA induced dysregulation of NKA activity and its α1 subunit subcellular expression. There was also reduced intracellular ATP levels and cell injury, as well as further activation of Src, NLRP3 and IL-1β. Overexpressing NKA α1 by an expression construct increased its expression on the cell membrane, enhanced its activity and alleviated cell injury and the Src-NLRP3-IL-1β signaling pathway induced by UA. To our knowledge, this study is the first to demonstrate that impairment of NKA signaling is critically involved in the pathogenesis of hyperuricemia-induced renal tubular injury.
In the current study, we found that UA significantly induced PTEC injury as indicated by increased LDH release, ROS production and apoptosis. UA also induced autophagy as demonstrated by LC3-II/LC3-I, Beclin-1 and LAMP2 increase, and a decrease in p62, which is similar to the finding that UA could induce autophagy activation via an mammalian target of rapamycin-dependent signaling in PC12 cells.34 In human articular chondrocytes, monosodium urate crystals may also cause the death of chondrocytes through the activation of the autophagic process rather than apoptosis or ER stress.35 In human osteoblasts, monosodium urate activate phagocytosis and NLRP3-dependent autophagy.36 NKA significantly alleviated UA-induced autophagy with increased p62 and reduced LAMP2 by NKA α1 expression vector pre-incubation. In addition, NKA reduced ROS production and demonstrated a tendency to reduce both apoptosis and LDH release, suggesting that NKA has a protective role in UA-induced renal tubular cell injury.
As PTECs are equipped with urate transporters,37 we wondered whether UA changed urate transporter expression and thus led to the malfunction of urate transport. The urate transport pathways in PTECs are urate reabsorption and secretion. In the urate reabsorption process, it is the basolateral NKA that provides the driving force of the Na+ concentration.37 Na+-dependent anion transport by apical side SLC5A8 and SLC5A12 increases intracellular concentrations of anions that exchange with urate transporters URAT1, OAT10 and OAT4 on the apicalside.37 GLUT9 acts as the exit pathway for urate at the basolateral membrane and mediates the transport of urate into the blood.37 In the process of urate secretion, urate enters the cell at the basolateral membrane in exchange with α-ketoglutarate, mediated by OAT1 and OAT3, or in exchange with unknown anions via OAT2.37 At the apical membrane, urate is secreted via MRP4, ABCG2, NPT1 and/or NPT4, in which MRP4 and ABCG2 are ATP driven.37 In our study, we have measured all these urate transporters and found that, with the exception of OAT3, UA significantly increased the expressions of all other urate transporters, suggesting that the UA stimulated the cells to actively transport UA. Pre-incubation of the NKA α1 expression vector further increased UARAT1, but reduced NPT4 and MRP4 expressions when compared with UA stimulation alone. As UART1 is the most important urate resorption transporter and works on a tertiary mechanism dependent on NKA, our findings further support the mechanism that NKA is the driving force for urate absorption. As for the mechanism of NKA regulating MRP4, it is possible as MRP4 is also ATP dependent; when the NKA α1 expression vector was added to the cells and it competitively utilized cellular ATP, MRP4 function could not be further maintained without adequate amounts of ATP. These findings further supported a role of NKA in regulating urate transporters. However, since PTECs are polarized cells, the specific regulation of NKA on urate transporters should be examined with single layer culture of PTECs, which needs further studies to clarify.
Recent evidence has suggested that mitochondria have an important role in the pathogenesis of different forms of renal disease by affecting several cellular pathways, leading to increased oxidative stress, apoptosis, microvascular loss and fibrosis, all of which compromise renal function.38 To increase mitochondrial ATP production could reduce the level of mitochondrial ROS and alleviate renal injury.39 UA has been shown to induce mitochondrial ROS in hepatic steatosis40 as well as mitochondrial alterations and decreased intracellular ATP in endothelial cells.18 It has been suggested that the decreased mitochondrial mass and increased mitochondrial uncoupling, which can be indicated by UCP2, led to the reduced mitochondrial production of ATP and that this result might explain the lower basal concentrations of ATP in cells exposed to UA.18 In the present study, we found the dose and time dependent effects of UA on intracellular ATP level in PTECs and we also found that UA significantly induced mitochondrial dysfunction demonstrated by reduced mtDNA, membrane potential and respiratory complex I and V activities, and increased UCP2 expression.41 As NKA is mainly fueled by mitochondrial ATP and its activity is coupled with mitochondrial function,28 NKA may also be regulated by UA. In the present study, we found that the NKA activity of PTECs was first increased (at 24 h) and then decreased (at 48 h) in cultured human PTECs under UA stimulation. This phenomenon was also observed in the tubular cells of the porcine kidney with albumin stimulation.42 The authors suggested that as the albumin load increased, NKA first compensatorily increased, but with continuous stimulation, NKA activity ultimately decreased, which was possibly due to the imbalance between the energy supply and cell demand.42 Similarly, it is possible in our study that the NKA activity in PTECs under high concentrations of UA was first increased to better function, but with the increased mitochondrial injury and reduced mitochondrial ATP production induced by UA, the fuel for NKA to maintain its activity de-compensated and NKA was finally suppressed. However, when adding the NKA α1 construct prior to the incubation of UA, NKA protected cells from UA-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and alleviated mtDNA, mitochondrial membrane potential, UCP2 expression and complex I and V activity abnormalities, further supporting the coupling mechanism between NKA and mitochondria.
NKA is expressed on the cell membrane and its activity is mainly regulated by the subcellular locations of its α1 subunit, which can be regulated by different stimuli.25 In renal PTECs incubated by pathophysiological concentrations of albumin, NKA was observed in the cytoplasm but not on the cell surface.42 Angiotensin II stimulation increased the trafficking of NKA to the plasma membrane in opossum kidney cells,43 whereas gastrin increased NKA endocytosis in the Rab5 and Rab7 endosomes.44 Using Lyso-Tracker Red to mark cell lysosomes, we also found that with UA incubation, NKA α1 aggregated in the lysosome for degradation, instead of its normal expressing on the cell surface, and this change of NKA α1 subcellular expression is in accordance with the NKA activity mediated by UA. Thus, our findings add new evidence that UA may also regulate NKA activity through its α1 subcellular expressions. We have further confirmed that UA regulated NKA in an in vivo model and successfully established mild hyperuricemia rats with glomerular hypertrophy and mesangial matrix proliferation but no obvious interstitial lesions, which was consistent with the previous studies.45, 46 However, we found that NKA activity and the expression of its α1 subunit were already upregulated and then reduced in the renal cortex in the absence of obvious pathological injury of the renal tubule. Our findings suggested that hyperuricemia might already develop tubular NKA dysfunction without obvious pathological injury.
In addition, the impairment of NKA activity and its expression not only affect its own function, but NKA may also act as a novel class of membrane receptors in a multi-protein complex and modify target molecules such as Src kinase.47 Src kinase is an important signaling molecule on the cell membrane. Under physiological conditions, it binds to NKA and the Src function is inhibited. Once dissociated with NKA, Src is activated and induces multiple inflammatory pathways, including nuclear factor-κB.48 The NKA/Src complex has been shown to be activated in the kidney to address excess salt, and the trade-off could be the development of salt-induced hypertension,49 renal tissue inflammation50 and fibrosis.51 In addition, NKA α1 polypeptide can be used as a Src inhibitor, blocking the role of Src directly.52 Src was also increased in the macrophages and monocytes stimulated by UA and it was a key factor in the inflammatory response induced by UA.53 In this study, we noted that UA increased the Src activation and the NKA α1 expression construct significantly inhibited UA-induced Src activation, suggesting that when NKA is adequately expressed on the cell surface, it may bind Src and inhibit Src activation. In addition to many inflammatory pathways, Src activation could also mediate NLRP3 activation.54 We have previously demonstrated that NLRP3 is vital in hyperuricemia-induced renal injuries.19, 20, 55 In the present study, we also confirmed the enhanced overproduction of NLRP3 and its downstream effector IL-1β under conditions of hyperuricemia in vivo and in vitro. Adding the NKA α1 expression construct in UA stimulated PTECs, the reduced intracellular ATP by UA was not relieved, but UA-induced Src, NLRP3 and IL-1β overexpression was significantly reduced. However, NKA α1 siRNA significantly increased the intracellular level of ATP in UA stimulated PTECs, but it could not alleviate UA induced Src, NLRP3 and IL-1β overexpression. Our in vivo hyperuricemic rat model also demonstrated the decline of NKA activity and its α1 expression in the renal cortex accompanying the increased Src, NLRP3 and IL-1β expressions in the 10th week OA rats; Feb treatment significantly reduced serum UA levels induced by OA and the renal cortex of rats in this group demonstrated increased NKA activity and its expression, as well as decreased renal cortex Src-NLRP3-IL-1β activation. Thus, our findings suggested that the UA induced reduction of intracellular ATP may result from the impairment of NKA signaling, rather than by directly injuring the cells in hyperuricemia-induced renal tubular injury.
In summary, this study demonstrated that the impairment of NKA and its consequent regulation of Src, NLRP3 and IL-1βin the renal proximal tubule contributed to hyperuricemia-induced renal tubular injury, providing a molecular bridge connecting a cellular energy disorder to downstream inflammatory processes.
References
Bellomo G . The relationship between uric acid, allopurinol, cardiovascular events, and kidney disease progression: a step forward. Am J Kidney Dis 2015; 65: 525–527.
Hsu CY, Iribarren C, McCulloch CE, Darbinian J, Go AS . Risk factors for end-stage renal disease: 25-year follow-up. Arch Intern Med 2009; 169: 342–350.
Shi Y, Chen W, Jalal D, Li Z, Mao H, Yang Q et al. Clinical outcome of hyperuricemia in IgA nephropathy: a retrospective cohort study and randomized controlled trial. Kidney Blood Press Res 2012; 35: 153–160.
Wang S, Shu Z, Tao Q, Yu C, Zhan S, Li L . Uric acid and incident chronic kidney disease in a large health check-up population in Taiwan. Nephrology (Carlton) 2011; 16: 767–776.
Mok Y, Lee SJ, Kim MS, Cui W, Moon YM, Jee SH . Serum uric acid and chronic kidney disease: the Severance cohort study. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2012; 27: 1831–1835.
Sircar D, Chatterjee S, Waikhom R, Golay V, Raychaudhury A, Chatterjee S et al. Efficacy of febuxostat for slowing the gfr decline in patients with CKD and asymptomatic hyperuricemia: a 6-month, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Am J Kidney Dis 2015; 66: 945–950.
Zhou Y, Fang L, Jiang L, Wen P, Cao H, He W et al. Uric acid induces renal inflammation via activating tubular NF-kappaB signaling pathway. PLoS ONE 2012; 7: e39738.
Kang DH, Nakagawa T, Feng L, Watanabe S, Han L, Mazzali M et al. A role for uric acid in the progression of renal disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 2002; 13: 2888–2897.
Jalal DI . Hyperuricemia, the kidneys, and the spectrum of associated diseases: a narrative review. Curr Med Res Opin 2016; 32: 1863–1869.
Lipkowitz MS . Regulation of uric acid excretion by the kidney. Curr Rheumatol Rep 2012; 14: 179–188.
Bobulescu IA, Moe OW . Renal transport of uric acid: evolving concepts and uncertainties. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis 2012; 19: 358–371.
Rolfe DF, Brown GC . Cellular energy utilization and molecular origin of standard metabolic rate in mammals. Physiol Rev 1997; 77: 731–758.
Kang HM, Ahn SH, Choi P, Ko YA, Han SH, Chinga F et al. Defective fatty acid oxidation in renal tubular epithelial cells has a key role in kidney fibrosis development. Nat Med 2015; 21: 37–46.
Han SH, Malaga-Dieguez L, Chinga F, Kang HM, Tao J, Reidy K et al. Deletion of Lkb1 in renal tubular epithelial cells leads to CKD by altering metabolism. J Am Soc Nephrol 2016; 27: 439–453.
Decleves AE, Sharma K . Novel targets of antifibrotic and anti-inflammatory treatment in CKD. Nat Rev Nephrol 2014; 10: 257–267.
Sanchez-Calvo B, Cassina A, Rios N, Peluffo G, Boggia J, Radi R et al. Nitro-arachidonic acid prevents angiotensin ii-induced mitochondrial dysfunction in a cell line of kidney proximal tubular cells. PLoS ONE 2016; 11: e0150459.
Nowak G, Takacsova-Bakajsova D, Megyesi J . Deletion of protein kinase C-epsilon attenuates mitochondrial dysfunction and ameliorates ischemic renal injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 2017; 312: F109–F120.
Sanchez-Lozada LG, Lanaspa MA, Cristobal-Garcia M, Garcia-Arroyo F, Soto V, Cruz-Robles D et al. Uric acid-induced endothelial dysfunction is associated with mitochondrial alterations and decreased intracellular ATP concentrations. Nephron Exp Nephrol 2012; 121: e71–e78.
Xiao J, Zhang XL, Fu C, Han R, Chen W, Lu Y et al. Soluble uric acid increases NALP3 inflammasome and interleukin-1beta expression in human primary renal proximal tubule epithelial cells through the Toll-like receptor 4-mediated pathway. Int J Mol Med 2015; 35: 1347–1354.
Xiao JZX, Han R, Fu CS, Chen WJ, Ye ZB . Uric acid induces TLR4-dependent innate immune response but not HLA-DR and CD40 activation in renal proximal tubular epithelial cells. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016; 2016 9: 940–949.
Kaplan JH . Biochemistry of Na,K-ATPase. Annu Rev Biochem 2002; 71: 511–535.
Xie JX, Li X, Xie Z . Regulation of renal function and structure by the signaling Na/K-ATPase. IUBMB Life 2013; 65: 991–998.
Pierre SV, Xie Z . The Na,K-ATPase receptor complex: its organization and membership. Cell Biochem Biophys 2006; 46: 303–316.
Lingrel JB . The physiological significance of the cardiotonic steroid/ouabain-binding site of the Na,K-ATPase. Annu Rev Physiol 2010; 72: 395–412.
Obradovic M, Bjelogrlic P, Rizzo M, Katsiki N, Haidara M, Stewart AJ et al. Effects of obesity and estradiol on Na+/K+-ATPase and their relevance to cardiovascular diseases. J Endocrinol 2013; 218: R13–R23.
Feraille E, Doucet A . Sodium-potassium-adenosinetriphosphatase-dependent sodium transport in the kidney: hormonal control. Physiol Rev 2001; 81: 345–418.
Kankkunen P, Valimaki E, Rintahaka J, Palomaki J, Nyman T, Alenius H et al. Trichothecene mycotoxins activate NLRP3 inflammasome through a P2X7 receptor and Src tyrosine kinase dependent pathway. Hum Immunol 2014; 75: 134–140.
Fernandez-Moncada I, Barros LF . Non-preferential fuelling of the Na(+)/K(+)-ATPase pump. Biochem J 2014; 460: 353–361.
Liu N, Guo JK, Pang M, Tolbert E, Ponnusamy M, Gong R et al. Genetic or pharmacologic blockade of EGFR inhibits renal fibrosis. J Am Soc Nephrol 2012; 23: 854–867.
Ikeuchi M, Matsusaka H, Kang D, Matsushima S, Ide T, Kubota T et al. Overexpression of mitochondrial transcription factor a ameliorates mitochondrial deficiencies and cardiac failure after myocardial infarction. Circulation 2005; 112: 683–690.
Powalska E, Janosch S, Kinne-Saffran E, Kinne RK, Fontes CF, Mignaco JA et al. Fluorescence spectroscopic studies of pressure effects on Na+,K(+)-ATPase reconstituted into phospholipid bilayers and model raft mixtures. Biochemistry 2007; 46: 1672–1683.
Forbush B 3rd . Characterization of right-side-out membrane vesicles rich in (Na,K)-ATPase and isolated from dog kidney outer medulla. J Biol Chem 1982; 257: 12678–12684.
Cherniavsky-Lev M, Golani O, Karlish SJ, Garty H . Ouabain-induced internalization and lysosomal degradation of the Na+/K+-ATPase. J Biol Chem 2014; 289: 1049–1059.
Sheng YL, Chen X, Hou XO, Yuan X, Yuan BS, Yuan YQ et al. Urate promotes SNCA/alpha-synuclein clearance via regulating mTOR-dependent macroautophagy. Exp Neurol 2017; 297: 138–147.
Hwang HS, Yang CM, Park SJ, Kim HA . Monosodium urate crystal-induced chondrocyte death via autophagic process. Int J Mol Sci 2015; 16: 29265–29277.
Allaeys I, Marceau F, Poubelle PE . NLRP3 promotes autophagy of urate crystals phagocytized by human osteoblasts. Arthritis Res Ther 2013; 15: R176.
Mandal AK, Mount DB . The molecular physiology of uric acid homeostasis. Annu Rev Physiol 2015; 77: 323–345.
Eirin A, Lerman A, Lerman LO . The emerging role of mitochondrial targeting in kidney disease. Handb Exp Pharmacol 2017; 240: 229–250.
Suzuki T, Yamaguchi H, Kikusato M, Hashizume O, Nagatoishi S, Matsuo A et al. Mitochonic acid 5 binds mitochondria and ameliorates renal tubular and cardiac myocyte damage. J Am Soc Nephrol 2016; 27: 1925–1932.
Lanaspa MA, Sanchez-Lozada LG, Choi YJ, Cicerchi C, Kanbay M, Roncal-Jimenez CA et al. Uric acid induces hepatic steatosis by generation of mitochondrial oxidative stress: potential role in fructose-dependent and -independent fatty liver. J Biol Chem 2012; 287: 40732–40744.
Donadelli M, Dando I, Fiorini C, Palmieri M . UCP2, a mitochondrial protein regulated at multiple levels. Cell Mol Life Sci 2014; 71: 1171–1190.
Peruchetti DB, Pinheiro AA, Landgraf SS, Wengert M, Takiya CM, Guggino WB et al. Na++K+)-ATPase is a target for phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B and protein kinase C pathways triggered by albumin. J Biol Chem 2011; 286: 45041–45047.
Massey KJ, Li Q, Rossi NF, Keezer SM, Mattingly RR, Yingst DR . Phosphorylation of rat kidney Na-K pump at Ser938 is required for rapid angiotensin II-dependent stimulation of activity and trafficking in proximal tubule cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2016; 310: C227–C232.
Liu T, Konkalmatt PR, Yang Y, Jose PA . Gastrin decreases Na+,K+-ATPase activity via a PI 3-kinase- and PKC-dependent pathway in human renal proximal tubule cells. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2016; 310: E565–E571.
Nakagawa T, Mazzali M, Kang DH, Kanellis J, Watanabe S, Sanchez-Lozada LG et al. Hyperuricemia causes glomerular hypertrophy in the rat. Am J Nephrol 2003; 23: 2–7.
Sanchez-Lozada LG, Tapia E, Soto V, Avila-Casado C, Franco M, Zhao L et al. Treatment with the xanthine oxidase inhibitor febuxostat lowers uric acid and alleviates systemic and glomerular hypertension in experimental hyperuricaemia. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2008; 23: 1179–1185.
Aperia A, Akkuratov EE, Fontana JM, Brismar H . Na+-K+-ATPase, a new class of plasma membrane receptors. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2016; 310: C491–C495.
Wang Y, Ye Q, Liu C, Xie JX, Yan Y, Lai F et al. Involvement of Na/K-ATPase in hydrogen peroxide-induced activation of the Src/ERK pathway in LLC-PK1 cells. Free Radic Biol Med 2014; 71: 415–426.
Liu J, Yan Y, Liu L, Xie Z, Malhotra D, Joe B et al. Impairment of Na/K-ATPase signaling in renal proximal tubule contributes to Dahl salt-sensitive hypertension. J Biol Chem 2011; 286: 22806–22813.
Kennedy DJ, Chen Y, Huang W, Viterna J, Liu J, Westfall K et al. CD36 and Na/K-ATPase-alpha1 form a proinflammatory signaling loop in kidney. Hypertension 2013; 61: 216–224.
Fedorova LV, Raju V, El-Okdi N, Shidyak A, Kennedy DJ, Vetteth S et al. The cardiotonic steroid hormone marinobufagenin induces renal fibrosis: implication of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 2009; 296: F922–F934.
Li Z, Cai T, Tian J, Xie JX, Zhao X, Liu L et al. NaKtide, a Na/K-ATPase-derived peptide Src inhibitor, antagonizes ouabain-activated signal transduction in cultured cells. J Biol Chem 2009; 284: 21066–21076.
Valimaki E, Miettinen JJ, Lietzen N, Matikainen S, Nyman TA . Monosodium urate activates Src/Pyk2/PI3 kinase and cathepsin dependent unconventional protein secretion from human primary macrophages. Mol Cell Proteomics 2013; 12: 749–763.
Guo W, Ye P, Yu H, Liu Z, Yang P, Hunter N . CD24 activates the NLRP3 inflammasome through c-Src kinase activity in a model of the lining epithelium of inflamed periodontal tissues. Immun Inflamm Dis 2014; 2: 239–253.
Xiao J, Fu C, Zhang X, Zhu D, Chen W, Lu Y et al. Soluble monosodium urate, but not its crystal, induces toll like receptor 4-dependent immune activation in renal mesangial cells. Mol Immunol 2015; 66: 310–318.
Acknowledgements
The results in this study were presented in poster form at the 6th Oriental Congress of Nephrology 2016 (1 September to 4 September, Shanghai, China). This research is supported by the Shanghai Municipal Commission of Health and Family Planning (Grant number 20134075) and the Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (Grant number 17ZR1409100). This manuscript has been approved by all authors and is not under consideration for publication elsewhere in a similar form or in any language.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note:
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 4.0 International License. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in the credit line; if the material is not included under the Creative Commons license, users will need to obtain permission from the license holder to reproduce the material. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, J., Zhang, X., Fu, C. et al. Impaired Na+−K+-ATPase signaling in renal proximal tubule contributes to hyperuricemia-induced renal tubular injury. Exp Mol Med 50, e452 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2017.287
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2017.287
This article is cited by
-
The effect of lipid metabolism disorder on patients with hyperuricemia using Multi-Omics analysis
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
The role of Nod-like receptor protein 3 inflammasome activated by ion channels in multiple diseases
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2023)
-
The roles of NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated signaling pathways in hyperuricemic nephropathy
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2021)
-
The association of urinary uric acid excretion with ambulatory blood pressure values in patients with chronic kidney disease
Clinical Hypertension (2020)
-
The association of renal tubular inflammatory and injury markers with uric acid excretion in chronic kidney disease patients
International Urology and Nephrology (2020)