Abstract
To identify candidate genes in celiac disease (CD), we reanalyzed the whole Immunochip CD cohort using a different approach that clusters individuals based on immunoancestry prior to disease association analysis, rather than by geographical origin. We detected 636 new associated SNPs (P<7.02 × 10−07) and identified 5 novel genomic regions, extended 8 others previously identified and also detected 18 isolated signals defined by one or very few significant SNPs. To test whether we could identify putative candidate genes, we performed expression analyses of several genes from the top novel region (chr2:134533564–136169524), from a previously identified locus that is now extended, and a gene marked by an isolated SNP, in duodenum biopsies of active and treated CD patients, and non-celiac controls. In the largest novel region, CCNT2 and R3HDM1 were constitutively underexpressed in disease, even after gluten removal. Moreover, several genes within this region were coexpressed in patients, but not in controls. Other novel genes like KIF21B, REL and SORD also showed altered expression in active disease. Apart from the identification of novel CD loci, these results suggest that ancestry-based stratified analysis is an efficient strategy for association studies in complex diseases.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Celiac disease (CD, MIM: 212750) is a chronic, autoimmune disorder caused by intolerance to dietary gluten that develops in genetically susceptible individuals. It is a common disease (around 1% of the population) that is characterized by the presence of autoantibodies against tissue transglutaminase and villous atrophy, crypt hyperplasia and lymphocytic infiltration of the small intestinal mucosa. The major histocompatibility complex region on 6p21 harbors the major contributors to CD risk: in Caucasians, HLA-DQ2/-DQ8 heterodimers are present in >90% of CD patients, but also in around 30% of the general population, so that HLA alone cannot explain all the genetic component.1 Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) and Immunochip project identified 57 association signals from 39 loci, that together contribute 5–7% to the genetic risk.1, 2 More recently, new association signals have been detected in the major histocompatibility complex region, increasing up to 48% proportion of the heritability that is known so far.3 However, the effect of rare, coding variants within the Immunochip genes is minimal,4 and thus the remaining genetic component related to CD should still reside, in part, in common and known variants.
Despite the progress made, it has proven difficult to reconcile the results from association analyses across different populations, and to square SNP association results and expression levels of cis-located genes in patient tissues.5, 6 This limited success could be partly owing to certain genetic heterogeneity within CD, so that not every associated SNP is relevant to all CD cases. Random effects modeling has recently shown that SNPs reported to be associated with the disease (rs1050976C>T in IRF4, h38 chr6:g.408079C>T and rs11851414:C>T in ZFP36L1, h38 chr14:g.68792785T>C) would not have reached the significance threshold if heterogeneity among the different collections analyzed in the Immunochip had been accounted for.7 In the original analysis, a covariate was introduced to indicate collection membership, but not the possible heterogeneity within. We believe that heterogeneity within each one of the Immunochip cohorts could be stronger than what has been assumed. In the present work, we propose taking into consideration the (immuno)genomic background of each individual (revealed by the Immunochip itself) rather than geographical origin, as an alternative strategy for disease association analysis of the Immunochip data.
Subjects and Methods
We reanalyzed the 139 553 SNPs from the Immunochip in 12 041 CD patients and 12 228 non-celiac controls. To stratify individuals according to their genetic background, we first detected 8537 conserved LD blocks of SNPs using Plink8 and selected one random SNP from each block. These 8537 SNPs were used to calculate the possible number of ancestries using Admixture9 and the optimal number was set to 30 because it was the first K with a lower cross-validation value than the next K (Supplementary Figure S1). We then assigned each individual to 1 of the 30 immunogroups (named this way because they are based on the Immunochip SNPs), according to their major ancestry component (Supplementary Figure S2). Immunogroup sizes ranged from 19 to 4178 individuals (Supplementary Table S1), and contained celiac and control individuals from different geographical origins, except for one where all the samples of Indian origin clustered (Supplementary Figure S3), stressing the limitations of the Immunochip for the genetic analysis of non-European populations.10 Finally, we performed an association analysis, correcting for stratification of the 30 immunogroups, using a Cochran–Mantel–Haenszel test implemented in Plink.8 We set the significance cutoff to P<7.02 × 10−07, as there were 71 208 independent tests (8537 LD blocks plus 62 671 SNPs outside them), as calculated previously.10 The results of the association study are available at GWAS Central http://www.gwascentral.org/study/HGVST1839.
The expression of 14 protein-coding genes was measured in intestinal biopsies from 15 CD patients at the time of diagnosis and after >2 years on gluten-free diet (GFD), and from 15 non-celiac controls (Supplementary Table S3). CD was diagnosed according to the ESPGHAN criteria. The study was approved by the Cruces University Hospital, and Basque Clinical Trials and Ethics Committees (CEIC- E09/10 and PI2013072), and biopsies of distal duodenum were obtained by endoscopy after informed consent from all subjects or their parents. Total RNA was extracted using the NucleoSpin microRNA kit (Macherey-Nagel, Düren, Germany) and converted to cDNA using the AffinityScript cDNA Synthesis kit (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA). Gene expression was analyzed using Fluidigm Biomark 48.48 dynamic arrays (Fluidigm Corp., South San Francisco, CA, USA) and commercially available TaqMan Gene Expression assays, including RPLPO as an endogenous control of input RNA (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltham, MA, USA). Relative expression was calculated using the accurate ΔΔCt method and normalized to the average expression value of the control samples. Difference between conditions was tested using nonparametric tests, paired in the case of the comparison between active and treated CD. Gene expression data are available at Gene Expression Omnibus (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo) with accession number GSE84729.
Results and Discussion
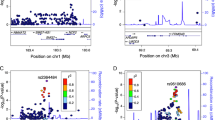
There were 4881 SNPs significantly associated with CD (Supplementary Figure S4), of which 636 had not been detected in the original analysis (Supplementary Figure S5). Only one previously associated region was not detected: hg38 chr14:68,792,689–68,805,252 (P=3.146 × 10−06), where ZFP36L1 had been proposed as the putative candidate gene, a region which was also ‘missed’ by the Random Effects study.7 A total of 500 novel SNPs were located in five previously unidentified genomic regions or close to or within four previously known loci, extending two of them; and there were also several isolated signals defined by one or few significant SNPs (Table 1,Supplementary Table S2). The most strongly associated novel region (hg38 chr2:134,533,564-136,169,524) contains markers and genes that have been associated with type 2 diabetes11 (Figure 1a).
The novel hg38 chr2:134,533,564–136,169,524 region that is associated with celiac disease. (a) Graphical representation of the region made using the Locuszoom online tool (http://locuszoom.sph.umich.edu/locuszoom/). (b) Expression analysis of selected genes from the region. REAC: expression relative to control average; below each gene, Mann–Whitney test P-values, when significant. (c) Spearman correlation analysis of expression levels.
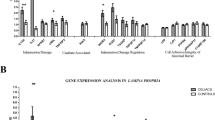
In this region, CCNT2 and R3HDM1 showed decreased expression between CD patients and controls, both at diagnosis and on GFD (Figure 1b), pointing to a constitutive defect. CCNT2 is a cyclin that is involved in cell cycle and RNA transcription. R3HDM1 is a poorly characterized gene that could have a poly(A) RNA-binding function. The expression of the aspartate-tRNA ligase gene DARS was also reduced in patients, although it was not significant in active disease. In addition, the expression of genes within the region was strongly correlated among CD patients but not in controls (Figure 1c), suggesting common, disease-dependent regulatory mechanisms in the region, as has been previously shown.12, 13 The lactase gene LCT showed a pronounced decrease in expression in active CD that recovered after GFD treatment (Supplementary Figure S6), indicative of the lactose intolerance observed in active CD. The other novel regions identified (Table 1) contain genes relevant to the immune response associated with allergy (IL21R),14 Crohn’s disease15 and psoriasis16 (IL23R and IL12RB2).
Our analysis also identified novel SNPs in previously known regions, extending two of them (Supplementary Table S2). In the hg38 chr1:200,901,626–201,054,931 region (Supplementary Figure S7A), C1orf106 is the proposed candidate gene for CD,2 but there were several associated SNPs that extend it 3′-wards up to CACNA1S; including KIF21B, a kinesis related to immune-mediated chronic diseases like multiple sclerosis,17 whose expression was significantly increased in active CD (Supplementary Figure S8A).
In the hg38 chr2:60,850,682–61,644,518 region (Supplementary Figure S7B), PUS10 was the proposed candidate gene,2 but our results extend the region 5′-wards to REL and up to XPO1 on the 3′side. Both genes participate in the NFκB pathway, which is known to be altered in CD.12, 18 The expression of REL (Supplementary Figure S8B), a gene associated with CD,19 was reduced in active CD patients.
There were also seven genes with only one significant SNP (Supplementary Table S2) sometimes because those regions have a very low SNP density. From them, we analyzed the expression of SORD, a gene involved in the interconversion of polyols, that has been related to type 2 diabetic retinopathy,20 and its expression was significantly lower in CD individuals (Supplementary Figure S8C). Finally, a number of novel SNPs were located in intergenic regions, but functional analyses will be necessary to determine their possible role in disease susceptibility.
In conclusion, the immunoancestry-based analysis of the Immunochip data has allowed us to discover novel regions associated with CD that harbor genes that are functionally altered in patient intestinal mucosa. We believe that this type of stratified analysis is applicable to other large-scale genotype data from complex disease association studies and will help to find novel susceptibility genes, and to conciliate genotype and expression data.
References
Ricaño-Ponce I, Wijmenga C, Gutierrez-Achury J : Genetics of celiac disease. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 2015; 29: 399–412.
Trynka G, Hunt K, Bockett N et al: Dense genotyping identifies and localizes multiple common and rare variant association signals in celiac disease. Nat Genet 2011; 43: 1193–1201.
Gutierrez-Achury J, Zhernakova A, Pulit SL et al: Fine mapping in the MHC region accounts for 18% additional genetic risk for celiac disease. Nat Genet 2015; 47: 577–578.
Hunt K, Mistry V, Bockett N et al: Negligible impact of rare autoimmune-locus coding-region variants on missing heritability. Nature 2013; 498: 232–235.
Plaza-Izurieta L, Castellanos-Rubio A, Irastorza I et al: Revisiting genome wide association studies (GWAS) in coeliac disease: replication study in Spanish population and expression analysis of candidate genes. J Med Genet 2011; 48: 493–496.
Plaza-Izurieta L, Fernandez-Jimenez N, Irastorza I et al: Expression analysis in intestinal mucosa reveals complex relations among genes under the association peaks in celiac disease. Eur J Hum Genet 2015; 23: 1100–1105.
Ahn RS, Garner C : A case study of fixed-effects and random-effects meta-analysis models for genome-wide association studies in celiac disease. Hum Hered 2015; 80: 51–61.
Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K et al: PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet 2007; 81: 559–575.
Alexander DH, Novembre J, Lange K : Fast model-based estimation of ancestry in unrelated individuals. Genome Res 2009; 19: 1655–1664.
Senapati S, Gutierrez-Achury J, Sood A et al: Evaluation of European coeliac disease risk variants in a north Indian population. Eur J Hum Genet 2014; 23: 530–535.
Tabassum R, Chauhan G, Dwivedi OP et al: Genome-wide association study for type 2 diabetes in Indians identifies a new susceptibility locus at 2q21. Diabetes 2013; 62: 977–986.
Fernandez-Jimenez N, Castellanos-Rubio A, Plaza-Izurieta L et al: Coregulation and modulation of NFκB-related genes in celiac disease: uncovered aspects of gut mucosal inflammation. Hum Mol Genet 2014; 23: 1298–1310.
Bondar C, Plaza-Izurieta L, Fernandez-Jimenez N et al: THEMIS and PTPRK in celiac intestinal mucosa: coexpression in disease and after in vitro gliadin challenge. Eur J Hum Genet 2014; 22: 358–362.
Hinds DA, McMahon G, Kiefer AK et al: A genome-wide association meta-analysis of self-reported allergy identifies shared and allergy-specific susceptibility loci. Nat Genet 2013; 45: 907–911.
Julià A, Domènech E, Ricart E et al: A genome-wide association study on a southern European population identifies a new Crohn’s disease susceptibility locus at RBX1-EP300. Gut 2013; 62: 1440–1445.
Nair RP, Duffin KC, Helms C et al: Genome-wide scan reveals association of psoriasis with IL-23 and NF-kappaB pathways. Nat Genet 2009; 41: 199–204.
Goris A, Boonen S, D’hooghe M-B, Dubois B : Replication of KIF21B as a susceptibility locus for multiple sclerosis. J Med Genet 2010; 47: 775–776.
Castellanos-Rubio A, Santin I, Martin-Pagola A et al: Long-term and acute effects of gliadin on small intestine of patients on potentially pathogenic networks in celiac disease. Autoimmunity 2010; 43: 131–139.
Trynka G, Zhernakova A, Romanos J et al: Coeliac disease-associated risk variants in TNFAIP3 and REL implicate altered NF-kappaB signalling. Gut 2009; 58: 1078–1083.
Szaflik JP, Majsterek I, Kowalski M et al: Association between sorbitol dehydrogenase gene polymorphisms and type 2 diabetic retinopathy. Exp Eye Res 2008; 86: 647–652.
Acknowledgements
JRB is funded by Research Grants PI13/01201 (within the National Plan for Scientific Research, Development and Technological Innovation 2013–2016, cofinanced by the Spanish Ministry Economy and Competitiveness, and the European Regional Development Fund) and 2011/111034 from the Basque Department of Health. IR-G and AJ-M are predoctoral fellows supported by grants from the University of the Basque Country (UPV/EHU) and the Basque Department of Education, respectively. This study makes use of data generated by the Wellcome Trust Case-Control Consortium (WTCC data sets EGAD00010000246, EGAD00010000248 and EGAD00010000250). A full list of the investigators who contributed to the generation of the data is available from http://www.wtccc.org.uk. Funding for the project was provided by the Wellcome Trust under awards 076113, 085475 and 090355. We thank the technical and human support provided by SGIker of the UPV/EHU.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on European Journal of Human Genetics website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garcia-Etxebarria, K., Jauregi-Miguel, A., Romero-Garmendia, I. et al. Ancestry-based stratified analysis of Immunochip data identifies novel associations with celiac disease. Eur J Hum Genet 24, 1831–1834 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2016.120
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2016.120