Abstract
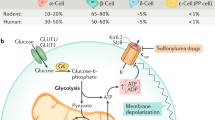
Diabetes mellitus is widely recognised as one of the most serious metabolic diseases worldwide, and its incidence in Asian countries is growing at an alarming rate. Type 2 diabetes (T2DM) is closely associated with age, sedentary lifestyle and poor diet. In T2DM, β-cell dysfunction will occur before hyperglycaemia develops. Excessive levels of glucose, lipid and various inflammatory factors interact at the level of the pancreatic islet to promote β-cell dysfunction. Pancreatic β-cell lines have been widely utilised since the early 1980s and have contributed a large volume of important information regarding molecular, metabolic and genetic mechanisms that regulate insulin secretion. The purpose of this review is to describe the origin and characteristics of the most commonly used β-cell lines and their contribution to discovery of fundamental regulatory processes that control insulin production and release. Pancreatic islets obtained from rodents as well as other animals have additionally provided information on the architecture and three-dimensional design of this endocrine tissue that allows precise regulation of hormone release. Understanding the nature of failure of physiologic and metabolic processes leading to insufficient insulin release and subsequent diabetes has allowed development of novel anti-diabetic therapeutics, now in common use, worldwide.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weir GC, Bonner-Weir S . Finally! A human pancreatic β cell line. J Clin Invest 2011; 121: 3395–3397.
Skelin M, Rupnik M, Cencic A . Pancreatic beta cell lines and their applications in diabetes mellitus research. Altex 2010; 27: 105–113.
Keane KN, Cruzat VF, Carlessi R, de Bittencourt PIH, Newsholme P . Molecular events linking oxidative stress and inflammation to insulin resistance and beta-cell dysfunction. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2015; 2015: 15.
Newsholme P, Rebelato E, Abdulkader F, Krause M, Carpinelli A, Curi R . Reactive oxygen and nitrogen species generation, antioxidant defenses, and beta-cell function: a critical role for amino acids. J Endocrinol 2012; 214: 11–20.
McCluskey JT, Hamid M, Guo-Parke H, McClenaghan NH, Gomis R, Flatt PR . Development and functional characterization of insulin-releasing human pancreatic beta cell lines produced by electrofusion. J Biol Chem 2011; 286: 21982–21992.
Vasu S, McClenaghan NH, McCluskey JT, Flatt PR . Cellular responses of novel human pancreatic beta-cell line, 1.1B4 to hyperglycemia. Islets 2013; 5: 170–177.
Vasu S, McClenaghan NH, McCluskey JT, Flatt PR . Effects of lipotoxicity on a novel insulin-secreting human pancreatic beta-cell line, 1.1B4. Biol Chem 2013; 394: 909–918.
Vasu S, McClenaghan NH, McCluskey JT, Flatt PR . Mechanisms of toxicity by proinflammatory cytokines in a novel human pancreatic beta cell line, 1.1B4. Biochim Biophys Acta 2014; 1840: 136–145.
Ravassard P, Hazhouz Y, Pechberty S, Bricout-Neveu E, Armanet M, Czernichow P et al. A genetically engineered human pancreatic beta cell line exhibiting glucose-inducible insulin secretion. J Clin Invest 2011; 121: 3589–3597.
Andersson LE, Valtat B, Bagge A, Sharoyko VV, Nicholls DG, Ravassard P et al. Characterization of stimulus-secretion coupling in the human pancreatic EndoC-betaH1 beta cell line. PLoS ONE 2015; 10: e0120879.
Mokhtari D, Al-Amin A, Turpaev K, Li T, Idevall-Hagren O, Li J et al. Imatinib mesilate-induced phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signalling and improved survival in insulin-producing cells: role of Src homology 2-containing inositol 5'-phosphatase interaction with c-Abl. Diabetologia 2013; 56: 1327–1338.
Fred RG, Kappe C, Ameur A, Cen J, Bergsten P, Ravassard P et al. Role of the AMP kinase in cytokine-induced human EndoC-betaH1 cell death. Mol Cell Endocrinol 2015; 414: 53–63.
Scharfmann R, Pechberty S, Hazhouz Y, von Bulow M, Bricout-Neveu E, Grenier-Godard M et al. Development of a conditionally immortalized human pancreatic beta cell line. J Clin Invest 2014; 124: 2087–2098.
Benazra M, Lecomte MJ, Colace C, Muller A, Machado C, Pechberty S et al. A human beta cell line with drug inducible excision of immortalizing transgenes. Mol Metab 2015; 4: 916–925.
Guo-Parke H, McCluskey JT, Kelly C, Hamid M, McClenaghan NH, Flatt PR . Configuration of electrofusion-derived human insulin-secreting cell line as pseudoislets enhances functionality and therapeutic utility. J Endocrinol 2012; 214: 257–265.
Green AD, Vasu S, McClenaghan NH, Flatt PR . Pseudoislet formation enhances gene expression, insulin secretion and cytoprotective mechanisms of clonal human insulin-secreting 1.1B4 cells. Pflugers Arch 2015; 467: 2219–2228.
Lecomte MJ, Pechberty S, Machado C, Da Barroca S, Ravassard P, Scharfmann R et al. Aggregation of engineered human beta-cells into pseudoislets: insulin secretion and gene expression profile in normoxic and hypoxic milieu. Cell Med 2016; 8: 99–112.
Keane KN, Cruzat VF, Carlessi R, de Bittencourt Jr PI, Newsholme P . Molecular events linking oxidative stress and inflammation to insulin resistance and beta-cell dysfunction. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2015; 2015: 181643.
Lacy PE, Kostianovsky M . Method for the isolation of intact islets of Langerhans from the rat pancreas. Diabetes 1967; 16: 35–39.
Ricordi C, Lacy PE, Scharp DW . Automated islet isolation from human pancreas. Diabetes 1989; 38 (Suppl 1), 140–142.
Misler S . The isolated pancreatic islet as a micro-organ and its transplantation to cure diabetes: celebrating the legacy of Paul Lacy. Islets 2010; 2: 210–224.
Newsholme P, Gaudel C, McClenaghan NH . Nutrient regulation of insulin secretion and beta-cell functional integrity. Adv Exp Med Biol 2010; 654: 91–114.
Newsholme P, Cruzat V, Arfuso F, Keane K . Nutrient regulation of insulin secretion and action. J Endocrinol 2014; 221: R105–R120.
Roscioni SS, Migliorini A, Gegg M, Lickert H . Impact of islet architecture on beta-cell heterogeneity, plasticity and function. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2016; 12: 695–709.
Pipeleers D, Kiekens R, Ling Z, Wilikens A, Schuit F . Physiologic relevance of heterogeneity in the pancreatic beta-cell population. Diabetologia 1994; 37 (Suppl 2), S57–S64.
Pipeleers D . The biosociology of pancreatic B cells. Diabetologia 1987; 30: 277–291.
Rutter GA, Hodson DJ . Minireview: intraislet regulation of insulin secretion in humans. Mol Endocrinol 2013; 27: 1984–1995.
Rutter GA, Pullen TJ, Hodson DJ, Martinez-Sanchez A . Pancreatic beta-cell identity, glucose sensing and the control of insulin secretion. Biochem J 2015; 466: 203–218.
Benninger RK, Zhang M, Head WS, Satin LS, Piston DW . Gap junction coupling and calcium waves in the pancreatic islet. Biophys J 2008; 95: 5048–5061.
Johnston NR, Mitchell RK, Haythorne E, Pessoa MP, Semplici F, Ferrer J et al. Beta cell hubs dictate pancreatic islet responses to glucose. Cell Metab 2016; 24: 389–401.
Levitt HE, Cyphert TJ, Pascoe JL, Hollern DA, Abraham N, Lundell RJ et al. Glucose stimulates human beta cell replication in vivo in islets transplanted into NOD-severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) mice. Diabetologia 2011; 54: 572–582.
Rhodes CJ . Type 2 diabetes-a matter of beta-cell life and death? Science 2005; 307: 380–384.
Tang C, Koulajian K, Schuiki I, Zhang L, Desai T, Ivovic A et al. Glucose-induced beta cell dysfunction in vivo in rats: link between oxidative stress and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Diabetologia 2012; 55: 1366–1379.
Maedler K, Sergeev P, Ris F, Oberholzer J, Joller-Jemelka HI, Spinas GA et al. Glucose-induced beta cell production of IL-1beta contributes to glucotoxicity in human pancreatic islets. J Clin Invest 2002; 110: 851–860.
Brun T, Li N, Jourdain AA, Gaudet P, Duhamel D, Meyer J et al. Diabetogenic milieus induce specific changes in mitochondrial transcriptome and differentiation of human pancreatic islets. Hum Mol Genet 2015; 24: 5270–5284.
Poungvarin N, Lee JK, Yechoor VK, Li MV, Assavapokee T, Suksaranjit P et al. Carbohydrate response element-binding protein (ChREBP) plays a pivotal role in beta cell glucotoxicity. Diabetologia 2012; 55: 1783–1796.
Metukuri MR, Zhang P, Basantani MK, Chin C, Stamateris RE, Alonso LC et al. ChREBP mediates glucose-stimulated pancreatic beta-cell proliferation. Diabetes 2012; 61: 2004–2015.
Schmidt SF, Madsen JG, Frafjord KO, Poulsen L, Salo S, Boergesen M et al. Integrative genomics outlines a biphasic glucose response and a ChREBP-RORgamma axis regulating proliferation in beta cells. Cell Rep 2016; 16: 2359–2372.
Henquin JC, Dufrane D, Nenquin M . Nutrient control of insulin secretion in isolated normal human islets. Diabetes 2006; 55: 3470–3477.
Henquin JC, Nenquin M . Dynamics and regulation of insulin secretion in pancreatic islets from normal young children. PLoS ONE 2016; 11: e0165961.
Newsholme P, Keane D, Welters HJ, Morgan NG . Life and death decisions of the pancreatic beta-cell: the role of fatty acids. Clin Sci 2007; 112: 27–42.
McNelis JC, Lee YS, Mayoral R, van der Kant R, Johnson AM, Wollam J et al. GPR43 potentiates beta-cell function in obesity. Diabetes 2015; 64: 3203–3217.
Yabe D, Seino Y . Two incretin hormones GLP-1 and GIP: comparison of their actions in insulin secretion and beta cell preservation. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 2011; 107: 248–256.
Chon S, Gautier JF . An update on the effect of incretin-based therapies on beta-cell function and mass. Diabetes Metab J 2016; 40: 99–114.
Carlessi R, Lemos NE, Dias AL, Oliveira FS, Brondani LA, Canani LH et al. Exendin-4 protects rat islets against loss of viability and function induced by brain death. Mol Cell Endocrinol 2015; 412: 239–250.
Benninger RK, Piston DW . Cellular communication and heterogeneity in pancreatic islet insulin secretion dynamics. Trends Endocrinol Metab 2014; 25: 399–406.
Oleson BJ, McGraw JA, Broniowska KA, Annamalai M, Chen J, Bushkofsky JR et al. Distinct differences in the responses of the human pancreatic beta-cell line EndoC-betaH1 and human islets to proinflammatory cytokines. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2015; 309: R525–R534.
Brissova M, Fowler MJ, Nicholson WE, Chu A, Hirshberg B, Harlan DM et al. Assessment of human pancreatic islet architecture and composition by laser scanning confocal microscopy. J Histochem Cytochem 2005; 53: 1087–1097.
Plentz RR, Palagani V, Wiedemann A, Diekmann U, Glage S, Naujok O et al. Islet microarchitecture and glucose transporter expression of the pancreas of the marmoset monkey display similarities to the human. Islets 2012; 4: 123–129.
Cabrera O, Berman DM, Kenyon NS, Ricordi C, Berggren PO, Caicedo A . The unique cytoarchitecture of human pancreatic islets has implications for islet cell function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 2334–2339.
Wieczorek G, Pospischil A, Perentes E . A comparative immunohistochemical study of pancreatic islets in laboratory animals (rats, dogs, minipigs, nonhuman primates). Exp Toxicol Pathol 1998; 50: 151–172.
Dolensek J, Rupnik MS, Stozer A . Structural similarities and differences between the human and the mouse pancreas. Islets 2015; 7: e1024405.
Wojtusciszyn A, Armanet M, Morel P, Berney T, Bosco D . Insulin secretion from human beta cells is heterogeneous and dependent on cell-to-cell contacts. Diabetologia 2008; 51: 1843–1852.
Hodson DJ, Mitchell RK, Bellomo EA, Sun G, Vinet L, Meda P et al. Lipotoxicity disrupts incretin-regulated human beta cell connectivity. J Clin Invest 2013; 123: 4182–4194.
Hodson DJ, Tarasov AI, Gimeno Brias S, Mitchell RK, Johnston NR, Haghollahi S et al. Incretin-modulated beta cell energetics in intact islets of Langerhans. Mol Endocrinol 2014; 28: 860–871.
Eizirik DL, Pipeleers DG, Ling Z, Welsh N, Hellerstrom C, Andersson A . Major species differences between humans and rodents in the susceptibility to pancreatic beta-cell injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1994; 91: 9253–9256.
Welsh N, Margulis B, Borg LA, Wiklund HJ, Saldeen J, Flodstrom M et al. Differences in the expression of heat-shock proteins and antioxidant enzymes between human and rodent pancreatic islets: implications for the pathogenesis of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Mol Med 1995; 1: 806–820.
Martens GA . Species-related differences in the proteome of rat and human pancreatic beta cells. J Diabetes Res 2015; 2015: 549818.
Mueller KR, Balamurugan AN, Cline GW, Pongratz RL, Hooper RL, Weegman BP et al. Differences in glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in vitro of islets from human, nonhuman primate, and porcine origin. Xenotransplantation 2013; 20: 75–81.
Acknowledgements
We thank the School of Biomedical Sciences and CHIRI for excellent research support and research facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carlessi, R., Keane, K., Mamotte, C. et al. Nutrient regulation of β-cell function: what do islet cell/animal studies tell us?. Eur J Clin Nutr 71, 890–895 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2017.49
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2017.49
This article is cited by
-
Cluster-assembled zirconia substrates promote long-term differentiation and functioning of human islets of Langerhans
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
An 8-week diet high in cereal fiber and coffee but free of red meat does not improve beta-cell function in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized controlled trial
Nutrition & Metabolism (2018)
-
Type 2 diabetes in Asia: where do we go from here?
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2017)