Abstract
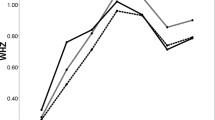
Exclusive breastfeeding is recommended for infants during the first 6 months of life. The aim of this analysis was to examine time trends in breastfeeding between 1990 and 2013 in Germany using data from the DONALD (Dortmund Nutritional and Anthropometric Longitudinally Designed) Study. Although partial breastfeeding was observed to constantly increase over time in both 3-month and 6-month-old infants, fully breastfeeding rates did not further increase in 3-month-old infants since 2002, and even showed a tendency to decrease in 6-month-old infants. In conclusion, this finding emphasises the need for improvements in breastfeeding promotion in Germany, which currently seems to be ineffective in case of continuation of full breastfeeding until the age of 6 months.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agostoni C, Braegger C, Decsi T, Kolacek S, Koletzko B, Michaelsen KF et al. Breast-feeding: a commentary by the ESPGHAN Committee on Nutrition. J. Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2009; 49: 112–125.
Weissenborn A, Abou-Dakn M, Bergmann R, Both D, Gresens R, Hahn B et al. Stillhäufigkeit und Stilldauer in Deutschland—eine systematische Übersicht. Gesundheitswesen 2015; 78: 695–707.
World Health Organization (WHO) Report of the Expert Consultation on the Optimal Duration of Exclusive Breastfeeding. World Health Organisation (WHO): Switzerland, 2001.
Hilbig A, Kersting M . Effects of age and time on energy and macronutrient intake in German infants and young children: results of the DONALD study. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2006; 43: 518–524.
Lange C, Schenk L, Bergmann R . Verbreitung, Dauer und zeitlicher Trend des Stillens in Deutschland. Ergebnisse des Kinder- und Jugendgesundheitssurveys (KiGGS). Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz 2007; 50: 624–633.
Kroke A, Manz F, Kersting M, Remer T, Sichert-Hellert W, Alexy U et al. The DONALD Study. History, current status and future perspectives. Eur J Nutr 2004; 43: 45–54.
Libuda L, Stimming M, Mesch C, Warschburger P, Kalhoff H, Koletzko BV et al. Frequencies and demographic determinants of breastfeeding and DHA supplementation in a nationwide sample of mothers in Germany. Eur J Nutr 2014; 53: 1335–1344.
von der Lippe E, Brettschneider A-K, Gutsche J, Poethko-Müller C . Einflussfaktoren auf Verbreitung und Dauer des Stillens in Deutschland: Ergebnisse der KiGGS-Studie—Erste Folgebefragung (KiGGS Welle 1). Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz 2014; 57: 849–859.
Buyken AE, Alexy U, Kersting M, Remer T . Die DONALD Kohorte. Ein aktueller Überblick zu 25 Jahren Forschung im Rahmen der Dortmund Nutritional and Anthropometric Longitudinally Designed Study. Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz 2012; 55: 875–884.
Acknowledgements
Sources of financial support: The DONALD Study is supported by the Ministry of Science and Research of North Rhine Westphalia, Germany.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Libuda, L., Bolzenius, K. & Alexy, U. Breastfeeding trends in healthy infants since 1990—results of the DONALD study. Eur J Clin Nutr 71, 1016–1018 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2017.106
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2017.106
This article is cited by
-
Stillverhalten in Deutschland – Neues aus KiGGS Welle 2
Bundesgesundheitsblatt - Gesundheitsforschung - Gesundheitsschutz (2018)