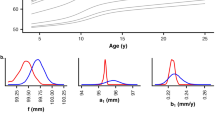
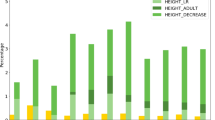
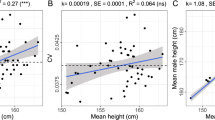
Abstract
Background/Objectives:
Besides large efforts regarding field work, provision of valid databases requires statistical and informational infrastructure to enable long-term access to longitudinal data sets on height, weight and related issues.
Subjects/Methods:
To foster use of longitudinal data sets within the scientific community, provision of valid databases has to address data-protection regulations. It is, therefore, of major importance to hinder identifiability of individuals from publicly available databases. To reach this goal, one possible strategy is to provide a synthetic database to the public allowing for pretesting strategies for data analysis. The synthetic databases can be established using multiple imputation tools. Given the approval of the strategy, verification is based on the original data.
Results:
Multiple imputation by chained equations is illustrated to facilitate provision of synthetic databases as it allows for capturing a wide range of statistical interdependencies. Also missing values, typically occurring within longitudinal databases for reasons of item non-response, can be addressed via multiple imputation when providing databases.
Conclusions:
The provision of synthetic databases using multiple imputation techniques is one possible strategy to ensure data protection, increase visibility of longitudinal databases and enhance the analytical potential.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Campbell P . Data's shameful neglect. Nature 2009; 461: 145.
Cole TJ, Green PJ . Smoothing reference centile curves: the LMS method and penalized likelihood. Stat Med 1992; 11: 1305–1319.
Rubin DB . Multiple Imputation for Nonresponse in Surveys. Wiley-IEEE: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1987.
van Buuren S, Groothuis-Oudshoorn K . MICE: Multivariate Imputation by Chained Equations. J Stat Softw 2011; 45: 1–67.
Preece MA, Baines MJ . A new family of mathematical models describing the human growth curve. Ann Hum Biol 1978; 5: 1–24.
van Buuren S . Fully conditional specification. In: Molenberghs G, Fitzmaurice GM, Kenward MG, Tsiatis AA, Verbeke G (eds), Handbook of Missing Data Methodology. Chapman & Hall/CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015.
Barkow I, Leopold T, Raab M, Schiller D, Wenzig K, Blossfeld HP et al. RemoteNEPS: data dissemination in a collaborative workspace. Z Erziehungswiss 2011; 14: 315–325.
Drechsler J . Synthetic Datasets for Statistical Disclosure Control: Theory and Implementation. Springer, Lecture notes in statistics: Berlin, Germany, 2011.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aßmann, C. Multiple imputation as one tool to provide longitudinal databases for modelling human height and weight development. Eur J Clin Nutr 70, 653–655 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2016.22
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2016.22