Abstract
Background/Objectives:
Few studies have investigated the effects of bariatric surgery on vitamin status in the long term. We examined changes in vitamin status up to 5 years after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery.
Subjects/Methods:
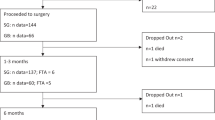
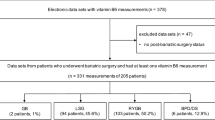
Using a retrospectively maintained database of patients undergoing weight loss surgery, we identified all patients operated with Roux-en-Y gastric bypass at our tertiary care hospital during July 2004–May 2008. Data on vitamin concentrations and patient-reported intake of dietary supplements were collected up to July 2012. Linear mixed models were used to estimate changes in vitamin concentrations during follow-up, adjusting for age and sex. All patients were recommended daily oral multivitamin, calcium/vitamin D and iron supplements and 3-monthly intramuscular B-12 after surgery.
Results:
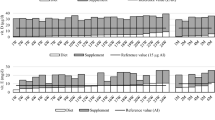
Out of the 443 patients operated with gastric bypass, we included 441 (99.5%) patients with one or more measurements of vitamin concentrations (75.1% women; mean age 41.5 years, mean body mass index 46.1 kg/m2 at baseline). At 5 years after surgery, the patients' estimated mean vitamin concentrations were either significantly higher (vitamin B-6, folic acid, vitamin B-12, vitamin C and vitamin A) or not significantly different (thiamine, 25-hydroxyvitamin D and lipid-adjusted vitamin E) compared with before surgery. Use of multivitamin, calcium/vitamin D and vitamin B-12 supplements was reported by 1–9% of patients before surgery, 79–84% of patients at 1 year and 52–83% of patients 5 years after surgery.
Conclusions:
In patients who underwent gastric bypass surgery, estimated vitamin concentrations were either significantly increased or unchanged up to 5 years after surgery.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buchwald H, Oien DM . Metabolic/bariatric surgery Worldwide 2008. Obes Surg 2009; 19: 1605–1611.
Buchwald H, Buchwald JN . Evolution of operative procedures for the management of morbid obesity 1950-2000. Obes Surg 2002; 12: 705–717.
Carswell KA, Vincent RP, Belgaumkar AP, Sherwood RA, Amiel SA, Patel AG et al. The effect of bariatric surgery on intestinal absorption and transit time. Obes Surg 2014; 24: 796–805.
Odstrcil EA, Martinez JG, Santa Ana CA, Xue B, Schneider RE, Steffer KJ et al. The contribution of malabsorption to the reduction in net energy absorption after long-limb Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Am J Clin Nutr 2010; 92: 704–713.
Aarts EO, van Wageningen B, Janssen IM, Berends FJ . Prevalence of Anemia and Related Deficiencies in the First Year following Laparoscopic Gastric Bypass for Morbid Obesity. J Obes 2012; 2012: 193705.
Ruz M, Carrasco F, Rojas P, Codoceo J, Inostroza J, Rebolledo A et al. Iron absorption and iron status are reduced after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Am J Clin Nutr 2009; 90: 527–532.
Al-Shoha A, Qiu S, Palnitkar S, Rao DS . Osteomalacia with bone marrow fibrosis due to severe vitamin D deficiency after a gastrointestinal bypass operation for severe obesity. Endocr Pract 2009; 15: 528–533.
De Prisco C, Levine SN . Metabolic bone disease after gastric bypass surgery for obesity. Am J Med Sci 2005; 329: 57–61.
Ashourian N, Mousdicas N . Images in clinical medicine. Pellagra-like dermatitis. N Engl J Med 2006; 354: 1614.
Aasheim ET . Wernicke encephalopathy after bariatric surgery: a systematic review. Ann Surg 2008; 248: 714–720.
Grange DK, Finlay JL . Nutritional vitamin B12 deficiency in a breastfed infant following maternal gastric bypass. Pediatr Hematol Oncol 1994; 11: 311–318.
Celiker MY, Chawla A . Congenital B12 deficiency following maternal gastric bypass. J Perinatol 2009; 29: 640–642.
Society for Surgery of the Alimentary Tract. SSAT patient care guidelines. Surgery for obesity. J Gastrointest Surg 2007; 11: 1219–1221.
Mechanick JI, Kushner RF, Sugerman HJ, Gonzalez-Campoy JM, Collazo-Clavell ML, Spitz AF et al. American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists, The Obesity Society, and American Society for Metabolic & Bariatric Surgery medical guidelines for clinical practice for the perioperative nutritional, metabolic, and nonsurgical support of the bariatric surgery patient. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2009; 17: S1–70. v.
Fried M, Hainer V, Basdevant A, Buchwald H, Deitel M, Finer N et al. Inter-disciplinary European guidelines on surgery of severe obesity. Int J Obes (Lond) 2007; 31: 569–577.
Heber D, Greenway FL, Kaplan LM, Livingston E, Salvador J, Still C . Endocrine and nutritional management of the post-bariatric surgery patient: an Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2010; 95: 4823–4843.
Puzziferri N, Roshek TB 3rd, Mayo HG, Gallagher R, Belle SH, Livingston EH . Long-term follow-up after bariatric surgery: a systematic review. JAMA 2014; 312: 934–942.
Sovik TT, Aasheim ET, Kristinsson J, Schou CF, Diep LM, Nesbakken A et al. Establishing laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: perioperative outcome and characteristics of the learning curve. Obes Surg 2009; 19: 158–165.
Aasheim ET, Bjorkman S, Sovik TT, Engstrom M, Hanvold SE, Mala T et al. Vitamin status after bariatric surgery: a randomized study of gastric bypass and duodenal switch. Am J Clin Nutr 2009; 90: 15–22.
Aasheim ET, Hofso D, Hjelmesaeth J, Birkeland KI, Bohmer T . Vitamin status in morbidly obese patients: a cross-sectional study. Am J Clin Nutr 2008; 87: 362–369.
Meyer HE, Falch JA, Sogaard AJ, Haug E . Vitamin D deficiency and secondary hyperparathyroidism and the association with bone mineral density in persons with Pakistani and Norwegian background living in Oslo, Norway, The Oslo Health Study. Bone 2004; 35: 412–417.
Traber MG, Jialal I . Measurement of lipid-soluble vitamins—further adjustment needed? Lancet 2000; 355: 2013–2014.
Clements RH, Katasani VG, Palepu R, Leeth RR, Leath TD, Roy BP et al. Incidence of vitamin deficiency after laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass in a university hospital setting. Am Surg 2006; 72: 1196–1202. discussion 203-204.
Aasheim ET, Johnson LK, Hofso D, Bohmer T, Hjelmesaeth J . Vitamin status after gastric bypass and lifestyle intervention: a comparative prospective study. Surg Obes Relat Dis 2011; 8: 169–175.
Lakhani SV, Shah HN, Alexander K, Finelli FC, Kirkpatrick JR, Koch TR . Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth and thiamine deficiency after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery in obese patients. Nutr Res 2008; 28: 293–298.
Damms-Machado A, Friedrich A, Kramer KM, Stingel K, Meile T, Kuper MA et al. Pre- and postoperative nutritional deficiencies in obese patients undergoing laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy. Obes Surg 2012; 22: 881–889.
van Rutte PW, Aarts EO, Smulders JF, Nienhuijs SW . Nutrient deficiencies before and after sleeve gastrectomy. Obes Surg 2014; 24: 1639–1646.
Lissner L, Lindroos AK, Sjostrom L . Swedish obese subjects (SOS): an obesity intervention study with a nutritional perspective. Eur J Clin Nutr 1998; 52: 316–322.
Vasilaki AT, McMillan DC, Kinsella J, Duncan A, O'Reilly DS, Talwar D . Relation between pyridoxal and pyridoxal phosphate concentrations in plasma, red cells, and white cells in patients with critical illness. Am J Clin Nutr 2008; 88: 140–146.
Waki M, Kral JG, Mazariegos M, Wang J, Pierson RN Jr, Heymsfield SB . Relative expansion of extracellular fluid in obese vs. nonobese women. Am J Physiol 1991; 261: E199–E203.
Ruz M, Carrasco F, Rojas P, Codoceo J, Inostroza J, Basfi-fer K et al. Zinc absorption and zinc status are reduced after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: a randomized study using 2 supplements. Am J Clin Nutr 2011; 94: 1004–1011.
Ruz M, Carrasco F, Rojas P, Codoceo J, Inostroza J, Basfi-Fer K et al. Heme- and nonheme-iron absorption and iron status 12 mo after sleeve gastrectomy and Roux-en-Y gastric bypass in morbidly obese women. Am J Clin Nutr 2012; 96: 810–817.
Amaral JF, Thompson WR, Caldwell MD, Martin HF, Randall HT . Prospective hematologic evaluation of gastric exclusion surgery for morbid obesity. Ann Surg 1985; 201: 186–193.
Gasteyger C, Suter M, Gaillard RC, Giusti V . Nutritional deficiencies after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass for morbid obesity often cannot be prevented by standard multivitamin supplementation. Am J Clin Nutr 2008; 87: 1128–1133.
Alexandrou A, Armeni E, Kouskouni E, Tsoka E, Diamantis T, Lambrinoudaki I . Cross-sectional long-term micronutrient deficiencies after sleeve gastrectomy versus Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: A pilot study. Surg Obes Relat Dis 2014; 10: 262–268.
Marcuard SP, Sinar DR, Swanson MS, Silverman JF, Levine JS . Absence of luminal intrinsic factor after gastric bypass surgery for morbid obesity. Dig Dis Sci 1989; 34: 1238–1242.
Karefylakis C, Naslund I, Edholm D, Sundbom M, Karlsson FA, Rask E . Vitamin D status 10 years after primary gastric bypass: gravely high prevalence of hypovitaminosis D and raised PTH levels. Obes Surg 2014; 24: 343–348.
Duran de Campos C, Dalcanale L, Pajecki D, Garrido AB Jr, Halpern A . Calcium intake and metabolic bone disease after eight years of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Obes Surg 2008; 18: 386–390.
Dalcanale L, Oliveira CP, Faintuch J, Nogueira MA, Rondo P, Lima VM et al. Long-term nutritional outcome after gastric bypass. Obes Surg 2010; 20: 181–187.
Hewitt S, Sovik TT, Aasheim ET, Kristinsson J, Jahnsen J, Birketvedt GS et al. Secondary hyperparathyroidism, vitamin D sufficiency, and serum calcium 5 years after gastric bypass and duodenal switch. Obes Surg 2013; 23: 384–390.
Goldner WS, Stoner JA, Lyden E, Thompson J, Taylor K, Larson L, Erickson J, McBride C . Finding the optimal dose of vitamin D following Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: a prospective, randomized pilot clinical trial. Obes Surg 2009; 19: 173–179.
Faure H, Preziosi P, Roussel AM, Bertrais S, Galan P, Hercberg S et al. Factors influencing blood concentration of retinol, alpha-tocopherol, vitamin C, and beta-carotene in the French participants of the SU.VI.MAX trial. Eur J Clin Nutr 2006; 60: 706–717.
Galan P, Viteri FE, Bertrais S, Czernichow S, Faure H, Arnaud J et al. Serum concentrations of beta-carotene, vitamins C and E, zinc and selenium are influenced by sex, age, diet, smoking status, alcohol consumption and corpulence in a general French adult population. Eur J Clin Nutr 2005; 59: 1181–1190.
Ford ES, Mokdad AH, Giles WH, Brown DW . The metabolic syndrome and antioxidant concentrations: findings from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Diabetes 2003; 52: 2346–2352.
Pfeiffer CM, Sternberg MR, Schleicher RL, Rybak ME . Dietary supplement use and smoking are important correlates of biomarkers of water-soluble vitamin status after adjusting for sociodemographic and lifestyle variables in a representative sample of U.S. adults. J Nutr 2013; 143: 957S–965S.
Hansen EP, Metzsche C, Henningsen E, Toft P . Severe scurvy after gastric bypass surgery and a poor postoperative diet. J Clin Med Res 2012; 4: 135–137.
Acknowledgements
EA (guarantor) and ETA collected the data; EA, A-MA, TM and ETA contributed to the study design and planned the study; EA cross-checked the data; EA and MWF carried out the statistical analysis; EA and ETA wrote the manuscript; TM, A-MA and ETA supervised the study. All authors contributed to the interpretation of results, critically revised the manuscript and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on European Journal of Clinical Nutrition website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aaseth, E., Fagerland, M., Aas, AM. et al. Vitamin concentrations 5 years after gastric bypass. Eur J Clin Nutr 69, 1249–1255 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2015.82
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2015.82
This article is cited by
-
Vitamin and Mineral Deficiency 12 Years After Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass a Cross-Sectional Multicenter Study
Obesity Surgery (2023)
-
Changes in Body Composition and Biochemical Parameters Following Laparoscopic One Anastomosis Gastric Bypass: 1-Year Follow-Up
Obesity Surgery (2021)
-
Psychopharmacological Medication Has No Influence on Vitamin Status After Bariatric Surgery in Long-term Follow-up
Obesity Surgery (2020)
-
Relationships Between Vitamin D Status and PTH over 5 Years After Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass: a Longitudinal Cohort Study
Obesity Surgery (2020)
-
Long-Term Results of the Mediterranean Diet After Sleeve Gastrectomy
Obesity Surgery (2020)