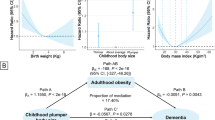
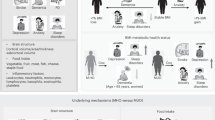
Abstract
This review comprehensively examines the current knowledge on the relationship between body mass index (BMI) and dementia. The association between BMI and cognition is complex: in younger adults, higher BMIs are associated with impaired cognition. Overweight and obesity in middle age are linked to increased future dementia risk in old age. However, when examined in old age, higher BMIs are associated with better cognition and decreased mortality. Little is known about the optimal BMI for well-being and survival in populations already suffering from dementia. Lifetime trends in weight, rather than single measures, might predict prognosis better and help untangle these apparent contradictions. Thus, the need arises to properly monitor BMI trends in affected dementia patients. Registries can include BMI, improving the management of dementia patients throughout the whole course of the disease. The role of central obesity and systemic inflammation on brain pathology and cognitive decline are discussed in this review. Understanding the life-course changes in BMI and their influence on dementia risk, cognitive prognosis and mortality after diagnosis may provide new insights into the underlying pathophysiology of dementia and shape possible intervention and treatment strategies.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Volkert D, Berner YN, Berry E, Cederholm T, Coti Bertrand P, Milne A et al. ESPEN guidelines on enteral nutrition: geriatrics. Clin Nutr 2006; 25: 330–360.
World Health Organization (WHO). Physical status: the use and interpretation of anthropometry. Report of a WHO Expert Committee. World Health Organization (WHO): Geneva, Switzerland, 1995. WHO Technical Report Series 854.
Drubbel I, Bleijenberg N, Kranenburg G, Eijkemans RJ, Schuurmans MJ, de Wit NJ et al. Identifying frailty: do the Frailty Index and Groningen Frailty Indicator cover different clinical perspectives? a cross-sectional study. BMC. Fam Pract 2013; 14: 64.
Freedman DM, Ron E, Ballard-Barbash R, Doody MM, Linet MS . Body mass index and all-cause mortality in a nationwide US cohort. Int J Obes 2006; 30: 822–829.
Quételet A . Sur l'homme et le développement de ses facultés, ou Essai de physique sociale. Vol. 2. Bachelier imprimeur-libraire: Paris, France, 1835.
Janssen I, Heymsfield SB, Ross R . Low relative skeletal muscle mass (sarcopenia) in older persons is associated with functional impairment and physical disability. J Am Geriatr Soc 2002; 50: 889–896.
Flicker L, McCaul KA, Hankey GJ, Jamrozik K, Brown WJ, Byles JE et al. Body mass index and survival in men and women aged 70 to 75. J Am Geriatr Soc 2010; 58: 234–241.
Kvamme JM, Holmen J, Wilsgaard T, Florholmen J, Midthjell K, Jacobsen BK . Body mass index and mortality in elderly men and women: the Tromso and HUNT studies. J Epidemiol Community Health 2012; 66: 611–617.
Dahl AK, Fauth EB, Ernsth-Bravell M, Hassing LB, Ram N, Gerstof D . Body mass index, change in body mass index, and survival in old and very old persons. J Am Geriatr Soc 2013; 61: 512–518.
Janssen I, Mark AE . Elevated body mass index and mortality risk in the elderly. Obes Rev 2007; 8: 41–59.
Fitzpatrick AL, Kuller LH, Lopez OL, Diehr P, O'Meara ES, Longstreth Jr WT et al. Midlife and late-life obesity and the risk of dementia: cardiovascular health study. Arch Neurol 2009; 66: 336–342.
Stewart R, Masaki K, Xue QL, Peila R, Petrovitch H, White LR et al. A 32-year prospective study of change in body weight and incident dementia: the Honolulu-Asia Aging Study. Arch Neurol 2005; 62: 55–60.
Knopman DS, Edland SD, Cha RH, Petersen RC, Rocca WA . Incident dementia in women is preceded by weight loss by at least a decade. Neurology 2007; 69: 739–746.
Faxen-Irving G, Basun H, Cederholm T . Nutritional and cognitive relationships and long-term mortality in patients with various dementia disorders. Age Ageing 2005; 34: 136–141.
Bergman RN, Stefanovski D, Buchanan TA, Sumner AE, Reynolds JC, Sebring NG et al. A better index of body adiposity. Obesity 2011; 19: 1083–1089.
Lichtash CT, Cui J, Guo X, Chen YD, Hsueh WA, Rotter JI et al. Body adiposity index versus body mass index and other anthropometric traits as correlates of cardiometabolic risk factors. PLoS One 2013; 8: e65954.
Arsenault BJ, Beaumont EP, Despres JP, Larose E . Mapping body fat distribution: a key step towards the identification of the vulnerable patient? Ann Med 2012; 44: 758–772.
Shuster A, Patlas M, Pinthus JH, Mourtzakis M . The clinical importance of visceral adiposity: a critical review of methods for visceral adipose tissue analysis. Br J Radiol 2012; 85: 1–10.
The European Society for Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism Basics in clinical nutrition, Sobotka L, Allison SP, Forbes A, Ljungqvist O, Meier RF, Pertkiewicz M et al. (eds). 4th edn. Galén: Prague, Czech Republic, 2011.
Masters RK, Powers DA, Link BG . Obesity and US mortality risk over the adult life course. Am J Epidemiol 2013; 177: 431–442.
Flegal KM, Graubard BI, Williamson DF, Gail MH . Cause-specific excess deaths associated with underweight, overweight, and obesity. JAMA 2007; 298: 2028–2037.
Janssen I . Morbidity and mortality risk associated with an overweight BMI in older men and women. Obesity 2007; 15: 1827–1840.
Albanese E, Taylor C, Siervo M, Stewart R, Prince MJ, Acosta D . Dementia severity and weight loss: A comparison across eight cohorts. The 10/66 study. Alzheimers Dement 2013; 9: 649–656.
Luchsinger JA, Patel B, Tang MX, Schupf N, Mayeux R . Body mass index, dementia and mortality in the elderly. J Nutr Health Aging 2008; 12: 127–131.
Buchman AS, Wilson RS, Bienias JL, Shah RC, Evans DA, Bennett DA . Change in body mass index and risk of incident Alzheimer disease. Neurology 2005; 65: 892–897.
Silver HJ, Niswender KD, Kullberg J, Berglund J, Johansson L, Bruvold M et al. Comparison of gross body fat-water magnetic resonance imaging at 3 Tesla to dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry in obese women. Obesity 2013; 21: 765–774.
Cameron AJ, Magliano DJ, Soderberg S . A systematic review of the impact of including both waist and hip circumference in risk models for cardiovascular diseases, diabetes and mortality. Obes Rev 2013; 14: 86–94.
Freedman DS, Blanck HM, Dietz WH, DasMahapatra P, Srinivasan SR, Berenson GS . Is the body adiposity index (hip circumference/height(1.5)) more strongly related to skinfold thicknesses and risk factor levels than is BMI? The Bogalusa Heart Study. Br J Nutr 2013; 109: 338–345.
Snijder MB, Nicolaou M, van Valkengoed IG, Brewster LM, Stronks K . Newly proposed body adiposity index (bai) by Bergman et al. is not strongly related to cardiovascular health risk. Obesity 2012; 20: 1138–1139.
Lavie CJ, Milani RV, Ventura HO . Obesity and cardiovascular disease: risk factor, paradox, and impact of weight loss. J Am Coll Cardiol 2009; 53: 1925–1932.
Kopple JD . The phenomenon of altered risk factor patterns or reverse epidemiology in persons with advanced chronic kidney failure. Am J Clin Nutr 2005; 81: 1257–1266.
Anand N, S CC, Alam MN . The malnutrition inflammation complex syndrome-the micsing factor in the perio-chronic kidney disease interlink. J Clin Diagn Res 2013; 7: 763–767.
Kalantar-Zadeh K, Kilpatrick RD, Kuwae N, Wu DY . Reverse epidemiology: a spurious hypothesis or a hardcore reality? Blood Purif 2005; 23: 57–63.
Huang JC, Chen SC, Su HM, Chang JM, Hwang SJ, Chen HC . Performance of the Framingham risk score in patients receiving hemodialysis. Nephrology 2013; 18: 510–515.
Guder G, Frantz S, Bauersachs J, Allolio B, Wanner C, Koller MT et al. Reverse epidemiology in systolic and nonsystolic heart failure: cumulative prognostic benefit of classical cardiovascular risk factors. Circ Heart Fail 2009; 2: 563–571.
Kalantar-Zadeh K, Block G, Horwich T, Fonarow GC . Reverse epidemiology of conventional cardiovascular risk factors in patients with chronic heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol 2004; 43: 1439–1444.
Andersen KK, Olsen TS . Body mass index and stroke: overweight and obesity less often associated with stroke recurrence. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 2013; 22: e576–e581.
Stevens J, Cai J, Pamuk ER, Williamson DF, Thun MJ, Wood JL . The effect of age on the association between body-mass index and mortality. N Engl J Med 1998; 338: 1–7.
Landi F, Onder G, Gambassi G, Pedone C, Carbonin P, Bernabei R . Body mass index and mortality among hospitalized patients. Arch Intern Med 2000; 160: 2641–2644.
Thies W, Bleiler L . 2013 Alzheimer's disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement 2013; 9: 208–245.
Levin NW, Handelman GJ, Coresh J, Port FK, Kaysen GA . Reverse epidemiology: a confusing, confounding, and inaccurate term. Semin Dial 2007; 20: 586–592.
Park SY, Wilkens LR, Murphy SP, Monroe KR, Henderson BE, Kolonel LN . Body mass index and mortality in an ethnically diverse population: the Multiethnic Cohort Study. Eur J Epidemiol 2012; 27: 489–497.
Fedor A, Gunstad J . Higher BMI is associated with reduced cognitive performance in division I athletes. Obes Facts 2013; 6: 185–192.
Marques-Iturria I, Pueyo R, Garolera M, Segura B, Junque C, Garcia-Garcia I et al. Frontal cortical thinning and subcortical volume reductions in early adulthood obesity. Psychiatry Res 2013; 214: 109–115.
Kivipelto M, Ngandu T, Fratiglioni L, Viitanen M, Kareholt I, Winblad B et al. Obesity and vascular risk factors at midlife and the risk of dementia and Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol 2005; 62: 1556–1560.
Whitmer RA, Gunderson EP, Barrett-Connor E, Quesenberry Jr CP, Yaffe K . Obesity in middle age and future risk of dementia: a 27 year longitudinal population based study. BMJ 2005; 330: 1360.
Rosengren A, Skoog I, Gustafson D, Wilhelmsen L . Body mass index, other cardiovascular risk factors, and hospitalization for dementia. Arch Intern Med 2005; 165: 321–326.
Gelber RP, Petrovitch H, Masaki KH, Abbott RD, Ross GW, Launer LJ et al. Lifestyle and the risk of dementia in Japanese-american men. J Am Geriatr Soc 2012; 60: 118–123.
Beydoun MA, Lhotsky A, Wang Y, Dal Forno G, An Y, Metter EJ et al. Association of adiposity status and changes in early to mid-adulthood with incidence of Alzheimer's disease. Am J Epidemiol 2008; 168: 1179–1189.
Strand BH, Langballe EM, Hjellvik V, Handal M, Naess O, Knudsen GP et al. Midlife vascular risk factors and their association with dementia deaths: results from a Norwegian prospective study followed up for 35 years. J Neurol Sci 2013; 324: 124–130.
Gustafson DR, Backman K, Joas E, Waern M, Ostling S, Guo X et al. 37 years of body mass index and dementia: observations from the prospective population study of women in Gothenburg, Sweden. J Alzheimers Dis 2012; 28: 163–171.
Luchsinger JA, Patel B, Tang MX, Schupf N, Mayeux R . Measures of adiposity and dementia risk in elderly persons. Arch Neurol 2007; 64: 392–398.
Dahl AK, Lopponen M, Isoaho R, Berg S, Kivela SL . Overweight and obesity in old age are not associated with greater dementia risk. J Am Geriatr Soc 2008; 56: 2261–2266.
Hughes TF, Borenstein AR, Schofield E, Wu Y, Larson EB . Association between late-life body mass index and dementia: The Kame Project. Neurology 2009; 72: 1741–1746.
Kuo HK, Jones RN, Milberg WP, Tennstedt S, Talbot L, Morris JN et al. Cognitive function in normal-weight, overweight, and obese older adults: an analysis of the Advanced Cognitive Training for Independent and Vital Elderly cohort. J Am Geriatr Soc 2006; 54: 97–103.
Sperling RA, Aisen PS, Beckett LA, Bennett DA, Craft S, Fagan AM et al. Toward defining the preclinical stages of Alzheimer's disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer's Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement 2011; 7: 280–292.
Gustafson D, Rothenberg E, Blennow K, Steen B, Skoog I . An 18-year follow-up of overweight and risk of Alzheimer disease. Arch Intern Med 2003; 163: 1524–1528.
Gillette Guyonnet S, Abellan Van Kan G, Alix E, Andrieu S, Belmin J, Berrut G et al. IANA (international academy on nutrition and aging) expert group: weight loss and Alzheimer's disease. J Nutr Health Aging 2007; 11: 38–48.
Cuerda C, Velasco C, Merchan-Naranjo J, Garcia-Peris P, Arango C . The effects of second-generation antipsychotics on food intake, resting energy expenditure and physical activity. Eur J Clin Nutr 2014; 68: 146–152.
Allen VJ, Methven L, Gosney MA . Use of nutritional complete supplements in older adults with dementia: systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical outcomes. Clin Nutr 2013; 32: 950–957.
Liu W, Cheon J, Thomas SA . Interventions on mealtime difficulties in older adults with dementia: a systematic review. Int J Nurs Stud 2014; 51: 14–27.
Watson R, Green SM . Feeding and dementia: a systematic literature review. J Adv Nurs 2006; 54: 86–93.
Gu Y, Scarmeas N, Cosentino S, Brandt J, Albert M, Blacker D et al. Change in body mass index before and after alzheimer's disease onset. Curr Alzheimer Res 2013; e-pub ahead of print 19 November 2013; doi:10.2174/1567205010666131120110930.
Hayden KM, Zandi PP, Lyketsos CG, Khachaturian AS, Bastian LA, Charoonruk G et al. Vascular risk factors for incident Alzheimer disease and vascular dementia: the Cache County study. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 2006; 20: 93–100.
Whitmer RA, Sidney S, Selby J, Johnston SC, Yaffe K . Midlife cardiovascular risk factors and risk of dementia in late life. Neurology 2005; 64: 277–281.
Whitmer RA, Gustafson DR, Barrett-Connor E, Haan MN, Gunderson EP, Yaffe K . Central obesity and increased risk of dementia more than three decades later. Neurology 2008; 71: 1057–1064.
Schmidt R, Schmidt H, Curb JD, Masaki K, White LR, Launer LJ . Early inflammation and dementia: a 25-year follow-up of the Honolulu-Asia Aging Study. Ann Neurol 2002; 52: 168–174.
Prins JB . Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 2002; 16: 639–651.
Das UN . Is obesity an inflammatory condition? Nutrition 2001; 17: 953–966.
Yaffe K, Lindquist K, Penninx BW, Simonsick EM, Pahor M, Kritchevsky S et al. Inflammatory markers and cognition in well-functioning African-American and white elders. Neurology 2003; 61: 76–80.
Gustafson D, Lissner L, Bengtsson C, Bjorkelund C, Skoog I . A 24-year follow-up of body mass index and cerebral atrophy. Neurology 2004; 63: 1876–1881.
Gustafson DR, Steen B, Skoog I . Body mass index and white matter lesions in elderly women. An 18-year longitudinal study. Int Psychogeriatr 2004; 16: 327–336.
Abbott RD, Ross GW, White LR, Nelson JS, Masaki KH, Tanner CM et al. Midlife adiposity and the future risk of Parkinson's disease. Neurology 2002; 59: 1051–1057.
Gao S, Nguyen JT, Hendrie HC, Unverzagt FW, Hake A, Smith-Gamble V et al. Accelerated weight loss and incident dementia in an elderly African-American cohort. J Am Geriatr Soc 2011; 59: 18–25.
Harvey J, Shanley LJ, O'Malley D, Irving AJ . Leptin: a potential cognitive enhancer? Biochem Soc Trans 2005; 33: 1029–1032.
Irving AJ, Harvey J . Leptin regulation of hippocampal synaptic function in health and disease. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 2014; 369: 20130155.
Doherty GH, Beccano-Kelly D, Yan SD, Gunn-Moore FJ, Harvey J . Leptin prevents hippocampal synaptic disruption and neuronal cell death induced by amyloid beta. Neurobiol Aging 2013; 34: 226–237.
Power DA, Noel J, Collins R, O'Neill D . Circulating leptin levels and weight loss in Alzheimer's disease patients. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 2001; 12: 167–170.
Song J, Lee JE . Adiponectin as a new paradigm for approaching Alzheimer's disease. Anat Cell Biol 2013; 46: 229–234.
Marwarha G, Ghribi O . Leptin signaling and Alzheimer's disease. Am J Neurodegener Dis 2012; 1: 245–265.
Teixeira AL, Diniz BS, Campos AC, Miranda AS, Rocha NP, Talib LL et al. Decreased levels of circulating adiponectin in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease. Neuromol Med 2013; 15: 115–121.
Warren MW, Hynan LS, Weiner MF . Lipids and adipokines as risk factors for Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis 2012; 29: 151–157.
Une K, Takei YA, Tomita N, Asamura T, Ohrui T, Furukawa K et al. Adiponectin in plasma and cerebrospinal fluid in MCI and Alzheimer's disease. Eur J Neurol 2011; 18: 1006–1009.
Lieb W, Beiser AS, Vasan RS, Tan ZS, Au R, Harris TB et al. Association of plasma leptin levels with incident Alzheimer disease and MRI measures of brain aging. JAMA 2009; 302: 2565–2572.
Paz-Filho G, Wong ML, Licinio J . Leptin levels and Alzheimer disease. JAMA 2010; 303: 1478; author reply -9.
Ferreira ST, Clarke JR, Bomfim TR, De Felice FG . Inflammation, defective insulin signaling, and neuronal dysfunction in Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement 2014; 10: S76–S83.
Liu Y, Coresh J, Eustace JA, Longenecker JC, Jaar B, Fink NE et al. Association between cholesterol level and mortality in dialysis patients: role of inflammation and malnutrition. JAMA 2004; 291: 451–459.
Kivipelto M, Ngandu T, Fratiglioni L, Viitanen M, Kareholt I, Winblad B et al. Obesity and vascular risk factors at midlife and the risk of dementia and Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol 2005; 62: 1556–1556.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Swedish research council, the Swedish Brain Power consortium, the Swedish Society of Medicine and Foundation for Geriatric Diseases at Karolinska Institutet, the Swedish Dementia Foundation, Alzheimerfonden and the Swedish Association of Local Authorities and Regions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
García-Ptacek, S., Faxén-Irving, G., Čermáková, P. et al. Body mass index in dementia. Eur J Clin Nutr 68, 1204–1209 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2014.199
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2014.199
This article is cited by
-
Association between BMI trajectories in late-middle age and subsequent dementia risk in older age: a 26-year population-based cohort study
BMC Geriatrics (2023)
-
Machine learning algorithms for identifying predictive variables of mortality risk following dementia diagnosis: a longitudinal cohort study
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Brain CT can predict low lean mass in the elderly with cognitive impairment: a community-dwelling study
BMC Geriatrics (2022)
-
Associations of five obesity indicators with cognitive performance in 30,697 Taiwan Biobank participants
BMC Geriatrics (2022)
-
BMI, functional and cognitive status in a cohort of nonagenarians: results from the Mugello study
European Geriatric Medicine (2021)