Abstract
Background and Objectives:
Little information is available on severe obesity in childhood. This study estimates the prevalence of severe obesity in 8- to 9-year-old children resident in Italy and its association with gender, age, geographical area and parents’ nutritional status and education using the World Health Organization (WHO) and International Obesity Task Force (IOTF) criteria.
Subjects/Methods:
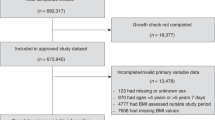
A nationally representative sample of grade 3 Italian students was measured in 2010 (N=42 431) using standardized instruments and methodology. Severe obesity in children was assessed using definitions provided by the WHO and by the IOTF. Prevalence was estimated within categories of sociodemographic variables and their independent effects were estimated using multivariate logistic regression.
Results:
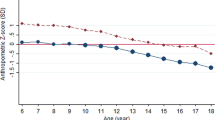
The estimated prevalence of severe obesity in 2010 was 4.5% (95% confidence interval (CI): 4.2–4.7) according to the WHO definition and 2.7% (95% CI: 2.5–2.9) with IOTF cutoffs. These values were slightly lower than those observed in 2008. The prevalence was higher in males, in 8-year-old children and in the South. Parental low education and high body mass index were strongly associated with childhood severe obesity.
Conclusion:
According to the definition used, between 30 000 and 50 000 children aged 8–9 years suffer severe obesity in Italy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pulgarón ER . Childhood obesity: a review of increased risk for physical and psychological comorbidities. Clin Ther 2013; 35: A18–A32.
Reilly JJ, Methven E, McDowell ZC, Hacking B, Alexander D, Stewart L et al. Health consequences of obesity. Arch Dis Child 2003; 88: 748–752.
Reilly JJ, Kelly J . Long-term impact of overweight and obesity in childhood and adolescence on morbidity and premature mortality in adulthood: systematic review. Int J Obes (Lond) 2011; 35: 891–898.
Mamun AA, O'Callaghan MJ, Cramb SM, Najman JM, Williams GM, Bor W . Childhood behavioral problems predict young adults' BMI and obesity: evidence from a birth cohort study. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2009; 17: 761–766.
Freedman DS, Mei Z, Srinivasan SR, Berenson GS, Dietz WH . Cardiovascular risk factors and excess adiposity among overweight children and adolescents: the Bogalusa Heart Study. J Pediatr 2007; 150: 12–17.e2.
Koebnick C, Getahun D, Smith N, Porter AH, Der-Sarkissian JK, Jacobsen SJ . Extreme childhood obesity is associated with increased risk for gastroesophageal reflux disease in a large population-based study. Int J Pediatr Obes 2011; 6: e257–e263.
Norris AL, Steinberger J, Steffen LM, Metzig AM, Schwarzenberg SJ, Kelly AS . Circulating oxidized LDL and inflammation in extreme pediatric obesity. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2011; 19: 1415–1419.
Van Emmerik NM, Renders CM, van de Veer M, van Buuren S, van der Baan-Slootweg OH, Kist-van Holthe JE et al. High cardiovascular risk in severely obese young children and adolescents. Arch Dis Child 2012; 97: 818–821.
Udomittipong K, Chierakul N, Ruttanaumpawan P, Chotinaiwattarakul W, Susiva C, Mahoran K et al. Severe obesity is a risk factor for severe obstructive sleep apnea in obese children. J Med Assoc Thai 2011; 94: 1346–1351.
Scholtens S, Wijga AH, Seidell JC, Brunekreef B, de Jongste JC, Gehring U et al. Overweight and changes in weight status during childhood in relation to asthma symptoms at 8 years of age. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2009; 123: 1312–1318.
Valerio G, Maffeis C, Balsamo A, Del Giudice EM, Brufani C, Grugni G et al. Severe obesity and cardiometabolic risk in children: comparison from two international classification systems. PLoS One 2013; 8: e83793.
Rank M, Siegrist M, Wilks DC, Langhof H, Wolfarth B, Haller B et al. The cardio-metabolic risk of moderate and severe obesity in children and adolescents. J Pediatr 2013; 163: 137–142.
Barlow SE . Expert Committee. Expert committee recommendations regarding the prevention, assessment, and treatment of child and adolescent overweight and obesity: summary report. Pediatrics 2007; 120 (Suppl 4): S164–S192.
Flegal KM, Wei R, Ogden CL, Freedman DS, Johnson CL, Curtin LR . Characterizing extreme values of body mass index for age by using the 2000 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention growth charts. Am J Clin Nutr 2009; 90: 1314–1320.
Kuczmarski RJ, Ogden CL, Guo SS, Grummer-Strawn LM, Flegal KM, Mei Z et al. 2000. CDC Growth Charts for the United States: methods and development. Vital Health Stat 2002; 11: 1–190.
de Onis M, Onyango AW, Borghi E, Siyam A, Nishida C, Siekmann J . Development of a WHO growth reference for school-aged children and adolescents. Bull World Health Organ 2007; 85: 660–667.
Cole TJ, Lobstein T . Extended international (IOTF) body mass index cut-offs for thinness, overweight and obesity. Pediatr Obes 2012; 7: 284–294.
Cole TJ, Bellizzi MC, Flegal KM, Dietz WH . Establishing a standard definition for child overweight and obesity worldwide: international survey. BMJ 2000; 320: 1240–1243.
Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Kit BK, Flegal KM . Prevalence of obesity and trends in body mass index among US children and adolescents, 1999-2010. JAMA 2012; 307: 483–490.
Skelton JA, Cook SR, Auinger P, Klein JD, Barlow SE . Prevalence and trends of severe obesity among US children and adolescents. Acad Pediatr 2009; 9: 322–329.
Goulding A, Grant AM, Taylor RW, Williams SM, Parnell WR, Wilson N et al. Ethnic differences in extreme obesity. J Pediatr 2007; 151: 542–544.
Società Italiana di Chirurgia dell’Obesità e delle malattie metaboliche. Linee guida e stato dell’arte della chirurgia bariatrica e metabolica in Italia. 2008. Available at http://www.sicob.org/00_materiali/attivita_linee_guida.pdf. Accessed on 26 February 2014.
Fried M, Hainer V, Basdevant A, Buchwald H, Deitel M, Finer N et al. Interdisciplinary European guidelines on surgery of severe obesity. Obes Facts 2008; 1: 52–59.
WHO European Ministerial Conference on Counteracting Obesity. Report of a WHO conference. World Health Organ 2007; 1–30. Available at http://www.euro.who.int/__data/assets/pdf_file/0006/96459/E90143.pdf. Accessed on 26 February 2014.
Binkin N, Fontana G, Lamberti A, Cattaneo C, Baglio G, Perra A et al. A national survey of the prevalence of childhood overweight and obesity in Italy. Obes Rev 2010; 11: 2–10.
Spinelli A, Baglio G, Cattaneo C, Fontana G, Lamberti A . Gruppo OKkio alla SALUTE; Coorte PROFEA anno 2006. Promotion of healthy life style and growth in primary school children (OKkio alla SALUTE). Ann Ig 2008; 20: 337–344.
Wijnhoven TM, van Raaij JM, Spinelli A, Rito AI, Hovengen R, Kunesova M et al. WHO European Childhood Obesity Surveillance Initiative 2008: weight, height and body mass index in 6-9-year-old children. Pediatr Obes 2013; 8: 79–97.
Censi L, Spinelli A, Roccaldo R, Bevilacqua N, Lamberti A, Angelini V et al. Dressed or undressed? How to measure children's body weight in overweight surveillance? Public Health Nutr 2013; 15: 1–6.
Binkin N, Spinelli A, Baglio G, Lamberti A . What is common becomes normal: the effect of obesity prevalence on maternal perception. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 2013; 23: 410–416.
CDC Growth Charts. Percentile Data Files with LMS Values. Available at http://www.cdc.gov/growthcharts/percentile_data_files.htm. Accessed on 26 February 2014.
Blossner M, Siyam A, Borghi E, Onyango A, de Onis M, WHO AnthroPlus for Personal Computers. Software for assessing growth of the world’s children and adolescents. Geneva 2009, Available at http://www.who.int/growthref/tools/who_anthroplus_manual.pdf. Accessed on 26 September 2013.
Istituto Nazionale di Statistica Demografia in cifre. Available at http://demo.istat.it/. Accessed on 26 September 2013.
Obesity: preventing and managing the global epidemic. Report of a WHO consultation. World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser 2000; 894: i-xii 1–253.
Physical status: the use and interpretation of anthropometry. Report of a WHO Expert Committee. World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser 1995; 854: 1–452.
de Onis M, Martínez-Costa C, Núñez F, Nguefack-Tsague G, Montal A, Brines J . Association between WHO cut-offs for childhood overweight and obesity and cardiometabolic risk. Public Health Nutr 2013; 16: 625–630.
Kakinami L, Henderson M, Delvin EE, Levy E, O'Loughlin J, Lambert M et al. Association between different growth curve definitions of overweight and obesity and cardiometabolic risk in children. CMAJ 2012; 184: e539–e550.
Olds T, Maher C, Zumin S, Péneau S, Lioret S, Castetbon K et al. Evidence that the prevalence of childhood overweight is plateauing: data from nine countries. Int J Pediatr Obes 2011; 6: 342–360.
Maffeis C, Talamini G, Tatò L . Influence of diet, physical activity and parents' obesity on children's adiposity: a four-year longitudinal study. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1998; 22: 758–764.
Morandi A, Meyre D, Lobbens S, Kleinman K, Kaakinen M, Sheryl L et al. Estimation of newborn risk for child or adolescent obesity: lessons from longitudinal birth cohorts. PLoS One 2012; 7: e49919.
Shrewsbury V, Wardle J . Socioeconomic status and adiposity in childhood: a systematic review of cross-sectional studies 1990-2005. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2008; 16: 275–284.
Acknowledgements
The following are the other members of the OKkio alla SALUTE Group 2010: G Baglio, M Bucciarelli, S Andreozzi, M Pediconi, S Rubimarca, C Cattaneo, B De Mei (National Centre for Epidemiology, Surveillance and Health Promotion of the National Institute of Health); D Galeone, MT Menzano, MT Scotti, L Spizzichino (Ministry of Health); MT Silani, S Teti (Regional Office for Education—Lazio); L Censi, D D’Addesa, A De Luca (National Research Institute on Food and Nutrition); F Cavallo (Department of Public Health and Microbiology, University of Turin); A Ciglia, M Di Giacomo (Abruzzo Region), G Ammirati, G Cauzillo, G Sorrentino (Basilicata Region), C Azzarito, M La Rocca, G Perri (Calabria Region), R Pizzuti (Campania Region), P Angelini, E Di Martino, M Fridel (Emilia Romagna Region), C Carletti, A Cattaneo (Friuli Venezia Giulia Region), G Cairella, E Castronuovo (Lazio Region), F Pascali, S Schiaffino (Liguria Region), AR Silvestri (ASL Milano, Lombardia Region), E Benedetti, S De Introna, G Giostra (Marche Region), TM Selvaggi, O Valentini, C Di Nucci (Molise Region), M Caputo, P Ferrari (Piemonte Region), S Anelli, G Rosa, E Viesti (Puglia), S Meloni, R Masala, ML Senis (Sardegna Region), A Cernigliaro, S Rizzo (Sicilia Region), M Giacchi (Toscana Region), M Cristofori, M Brinchi, MD Giaimo (Umbria Region), AM Covarino, G D’Alessandro (Valle D’Aosta Region), R Galesso (Veneto Region), A Fanolla, L Lucchin, S Weiss (Bolzano Autonomous Province), S Piffer (Trento Autonomous Province). The Surveillance System OKkio alla SALUTE is funded by the Italian Ministry of Health/Centre for Disease Prevention and Control.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lombardo, F., Spinelli, A., Lazzeri, G. et al. Severe obesity prevalence in 8- to 9-year-old Italian children: a large population-based study. Eur J Clin Nutr 69, 603–608 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2014.188
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2014.188
This article is cited by
-
Improving the overall sustainability of the school meal chain: the role of portion sizes
Eating and Weight Disorders - Studies on Anorexia, Bulimia and Obesity (2020)
-
Decline of childhood overweight and obesity in Italy from 2008 to 2016: results from 5 rounds of the population-based surveillance system
BMC Public Health (2019)
-
Advances in pediatrics in 2017: current practices and challenges in allergy, endocrinology, gastroenterology, genetics, immunology, infectious diseases, neonatology, nephrology, neurology, pulmonology from the perspective of Italian Journal of Pediatrics
Italian Journal of Pediatrics (2018)
-
Early severe obesity in children
Nature Reviews Endocrinology (2018)
-
Healthy lifestyle promotion in primary schools through the board game Kaledo: a pilot cluster randomized trial
European Journal of Pediatrics (2018)