Abstract
Background/objectives:
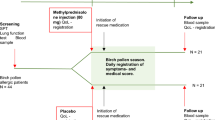
An imbalance between Th1 and Th2 cells is involved in allergic rhinitis (AR) that may be improved by probiotics. To test the efficacy of the probiotic Lactobacillus paracasei subsp. paracasei LP-33, a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized trial was carried out in patients with AR to grass pollen treated with loratadine and presenting altered quality of life.
Subjects/methods:
Subjects with persistent AR, symptomatic during the grass pollen season, and a positive skin test or specific immunoglobulin E to grass pollens were included by general practitioners (GPs). All received loratadine for 5 weeks. The primary end point was the improvement in Rhinitis Quality of Life (RQLQ) global score at the fifth week of LP-33 consumption compared with placebo (in addition to loratadine). Secondary end points included nasal and ocular symptoms (individual and total symptom scores), visual analogue scale and time of first exacerbation of the symptoms when loratadine was stopped.
Results:
A total of 425 subjects were included. Using intent-to-treat analysis, the RQLQ global score decreased significantly more in the LP-33 group than in the placebo group (P=0.0255, difference=−0.286 (95% confidence interval (CI): −0.536; −0.035)). No significant differences were noted for the change of the rhinitis total symptom score 5 global score between groups (P=0.1288, difference=−0.452 (95% CI: −1.036; 0.132)). Significant differences in ocular symptoms (RQLQ) were observed between groups (P=0.0029, difference=−0.4087 (95% CI: −0.6768; −0.1407)).
Conclusions:
This study performed by GPs shows that LP-33 improves the quality of life of subjects with persistent AR who are currently being treated with an oral H1-antihistamine. Whereas nasal symptoms had not changed, ocular symptoms had consistently improved.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bousquet J, Khaltaev N, Cruz AA, Denburg J, Fokkens WJ, Togias A et al. Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma (ARIA) 2008 update (in collaboration with the World Health Organization, GA(2)LEN and AllerGen). Allergy 2008; 63 (Suppl 86), 8–160.
Bousquet J, Bachert C, Canonica GW, Casale TB, Cruz AA, Lockey RJ et al. Unmet needs in severe chronic upper airway disease (SCUAD). J Allergy Clin Immunol 2009; 124: 428–433.
Canonica GW, Bousquet J, Mullol J, Scadding GK, Virchow JC . A survey of the burden of allergic rhinitis in Europe. Allergy 2007; 62 (Suppl 85), 17–25.
Schatz M . A survey of the burden of allergic rhinitis in the USA. Allergy 2007; 62 (Suppl 85), 9–16.
Valovirta E, Ryan D . Patient adherence to allergic rhinitis treatment: results from patient surveys. Medscape J Med 2008; 10: 247.
Virchow JC, Kay S, Demoly P, Mullol J, Canonica W, Higgins V . Impact of ocular symptoms on quality of life (QoL), work productivity and resource utilisation in allergic rhinitis patients—an observational, cross sectional study in four countries in Europe. J Med Econ 2011; 14: 305–314.
Hakansson A, Molin G . Gut microbiota and inflammation. Nutrients 2011; 3: 637–682.
Morita H, He F, Kawase M, Kubota A, Hiramatsu M, Kurisaki J et al. Preliminary human study for possible alteration of serum immunoglobulin E production in perennial allergic rhinitis with fermented milk prepared with Lactobacillus gasseri TMC0356. Microbiol Immunol 2006; 50: 701–706.
Ciprandi G, Vizzaccaro A, Cirillo I, Tosca MA . Bacillus clausii exerts immuno-modulatory activity in allergic subjects: a pilot study. Eur Ann Allergy Clin Immunol 2005; 37: 129–134.
Food and Agriculture Organization and World Health Organization expert consulation. Consultation of Health and Nutritional Properties of Powder Milk and Live Lactic Acid Bacteria. Cordoba, Argentina. http://www.who.int/foodsafety/publications/fs_management/en/probiotics.pdf2001.
Magrone T, Jirillo E . The interplay between the gut immune system and microbiota in health and disease: nutraceutical intervention for restoring homeostasis. Curr Pharm Des 2013; 19: 1329–1342.
Singh A, Hacini-Rachinel F, Gosoniu ML, Bourdeau T, Holvoet S, Doucet-Ladeveze R et al. Immune-modulatory effect of probiotic Bifidobacterium lactis NCC2818 in individual suffering from seasonal allergic rhinitis to grass pollen: an exploratory, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Eur J Clin Nutr 2013; 67: 161–167.
Pochard P, Gosset P, Grangette C, Andre C, Tonnel AB, Pestel J et al. Lactic acid bacteria inhibit TH2 cytokine production by mononuclear cells from allergic patients. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2002; 110: 617–623.
Ghadimi D, Folster-Holst R, de Vrese M, Winkler P, Heller KJ, Schrezenmeir J . Effects of probiotic bacteria and their genomic DNA on TH1/TH2-cytokine production by peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) of healthy and allergic subjects. Immunobiology 2008; 213: 677–692.
von Mutius E . A fascinating look at the world with a new microscope. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2012; 129: 1202–1203.
Jensen MP, Meldrum S, Taylor AL, Dunstan JA, Prescott SL . Early probiotic supplementation for allergy prevention: Long-term outcomes. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2012; 130: 1209–1211.
Prescott S, Nowak-Wegrzyn A . Strategies to prevent or reduce allergic disease. Ann Nutr Metab 2011; 59 (Suppl 1), 28–42.
Ivory K, Chambers SJ, Pin C, Prieto E, Arques JL, Nicoletti C . Oral delivery of Lactobacillus casei Shirota modifies allergen-induced immune responses in allergic rhinitis. Clin Exp Allergy 2008; 38: 1282–1289.
Kawase M, He F, Kubota A, Hiramatsu M, Saito H, Ishii T et al. Effect of fermented milk prepared with two probiotic strains on Japanese cedar pollinosis in a double-blind placebo-controlled clinical study. Int J Food Microbiol 2009; 128: 429–434.
Ouwehand AC, Nermes M, Collado MC, Rautonen N, Salminen S, Isolauri E . Specific probiotics alleviate allergic rhinitis during the birch pollen season. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15: 3261–3268.
Kalliomaki M, Antoine JM, Herz U, Rijkers GT, Wells JM, Mercenier A . Guidance for substantiating the evidence for beneficial effects of probiotics: prevention and management of allergic diseases by probiotics. J Nutr 2010; 140: 713S–721SS.
Rijkers GT, Bengmark S, Enck P, Haller D, Herz U, Kalliomaki M et al. Guidance for substantiating the evidence for beneficial effects of probiotics: current status and recommendations for future research. J Nutr 2010; 140: 671S–676SS.
Vliagoftis H, Kouranos VD, Betsi GI, Falagas ME . Probiotics for the treatment of allergic rhinitis and asthma: systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 2008; 101: 570–579.
Peng GC, Hsu CH . The efficacy and safety of heat-killed Lactobacillus paracasei for treatment of perennial allergic rhinitis induced by house-dust mite. Pediatr Allergy Immunol 2005; 16: 433–438.
Wang MF, Lin HC, Wang YY, Hsu CH . Treatment of perennial allergic rhinitis with lactic acid bacteria. Pediatr Allergy Immunol 2004; 15: 152–158.
Lin TY, Chen CJ, Chen LK, Wen SH, Jan RHA . Randomized prospective double blind controlled trial of the effect of probiotics on allergic rhinitis confined to Df, Dp or dust-sensitive children. Indian Pediatr 2013; 50: 209–213.
Lue KH, Sun HL, Lu KH, Ku MS, Sheu JN, Chan CH et al. A trial of adding Lactobacillus johnsonii EM1 to levocetirizine for treatment of perennial allergic rhinitis in children aged 7–12 years. Int J Ped Otorhinolaryngol 2012; 76: 994–1001.
Wassenberg J, Nutten S, Audran R, Barbier N, Aubert V, Moulin J et al. Effect of Lactobacillus paracasei ST11 on a nasal provocation test with grass pollen in allergic rhinitis. Clin Exp Allergy 2011; 41: 565–573.
Snel J, Vissers YM, Smit BA, Jongen JM, van der Meulen ET, Zwijsen R et al. Strain-specific immunomodulatory effects of Lactobacillus plantarum strains on birch-pollen-allergic subjects out of season. Clin Exp Allergy 2011; 41: 232–242.
Vissers YM, Snel J, Zuurendonk PF, Kleerebezem M, Wichers HJ, Savelkoul HF . Lactobacillus strains differentially modulate cytokine production by hPBMC from pollen-allergic patients. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 2011; 61: 28–40.
Juniper EF . Measuring health-related quality of life in rhinitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 1997; 99: S742–S749.
Bousquet J, Bachert C, Canonica GW, Mullol J, Van Cauwenberge P, Bindslev Jensen C et al. Efficacy of desloratadine in intermittent allergic rhinitis: a GALEN study. Allergy 2009; 64: 1516–1523.
Bousquet J, Bachert C, Canonica GW, Mullol J, Van Cauwenberge P, Jensen CB et al. Efficacy of desloratadine in persistent allergic rhinitis—a GA(2)LEN study. Int Arch Allergy Immunology 2010; 153: 395–402.
International Consensus Report on Diagnosis and Management of Rhinitis. International Rhinitis Management Working Group. Allergy 1994; 49 (19 Suppl), 1–34.
Bousquet J, Van Cauwenberge P, Khaltaev N . Allergic rhinitis and its impact on asthma. The J Allergy Clin Immunol 2001; 108 (5 Suppl), S147–S334.
Bachert C, Maspero J . Efficacy of second-generation antihistamines in patients with allergic rhinitis and comorbid asthma. J Asthma 2011; 48: 965–973.
Babre D . Medical coding in clinical trials. Perspect Clin Res 2010; 1: 29–32.
Bousquet PJ, Combescure C, Neukirch F, Klossek JM, Mechin H, Daures JP et al. Visual analog scales can assess the severity of rhinitis graded according to ARIA guidelines. Allergy 2007; 62: 367–372.
Bousquet PJ, Fabbro-Peray P, Janin N, Annesi-Maesano I, Neukirch F, Daures JP et al. Pilot study assessing the impact of smoking on nasal-specific quality of life. Allergy 2004; 59: 1015–1016.
Bousquet PJ, Combescure C, Klossek JM, Daures JP, Bousquet J . Change in visual analog scale score in a pragmatic randomized cluster trial of allergic rhinitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2009; 123: 1349–1354.
Bousquet J, Bodez T, Gehano P, Klossek JM, Liard F, Neukirch F et al. Implementation of guidelines for allergic rhinitis in specialist practices. a randomized pragmatic controlled trial. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 2009; 150: 75–82.
Ciprandi G, Canonica WG, Grosclaude M, Ostinelli J, Brazzola GG, Bousquet J . Effects of budesonide and fluticasone propionate in a placebo-controlled study on symptoms and quality of life in seasonal allergic rhinitis. Allergy 2002; 57: 586–591.
Walter Canonica G, Bousquet J, Van Hammee G, Bachert C, Durham SR, Klimek L et al. Levocetirizine improves health-related quality of life and health status in persistent allergic rhinitis. Respir Med 2006; 100: 1706–1715.
Brozek JL, Bousquet J, Baena-Cagnani CE, Bonini S, Canonica GW, Casale TB et al. Allergic Rhinitis and its impact on Asthma (ARIA) guidelines: 2010 revision. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2010; 126: 466–476.
Bachert C, Bousquet J, Canonica GW, Durham SR, Klimek L, Mullol J et al. Levocetirizine improves quality of life and reduces costs in long-term management of persistent allergic rhinitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2004; 114: 838–844.
Ciprandi G, Klersy C, Cirillo I, Marseglia GL . Quality of life in allergic rhinitis: relationship with clinical, immunological, and functional aspects. Clin Exp Allergy 2007; 37: 1528–1535.
Juniper EF, Guyatt GH, Willan A, Griffith LE . Determining a minimal important change in a disease-specific Quality of Life Questionnaire. J Clin Epidemiol 1994; 47: 81–87.
Acknowledgements
BIOFORTIS managed all administrative and logistic procedures. The study was funded by Merck Medication Familiale and Chr Hansen A/S. The investigators who collaborated in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
DJC received fees for consultancy from Merck Medication Familiale. PM received fees for consultancy, and lectures for Biocodex, Danone Merck Medication Familiale. LKP recieved fees for consultancy from Merck Medication Familiale. EH recieved fees for consultancy, and lectures for Milupa, Danone Merck Medication Familiale. MC, BH and SL are employees of Biofortis. MS is an employee of Chr. Hansen A/S. PM is an employee of Merck Medication Familiale. SC is an employee of Merck Medication Familiale. JB recieved fees for participation in scientific and advisory boards, giving lectures and press engagements from Actelion, Almirall, AstraZeneca, Chiesi, GlaxoSmithKline, Meda, Merck Sharpe & Dohme, Merck Medication Familiale Novartis, oM Pharma, Sanofi-Aventis, Schering Plough, Stallergènes, Takeda, Teva and Uriach. MA declares no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Costa, D., Marteau, P., Amouyal, M. et al. Efficacy and safety of the probiotic Lactobacillus paracasei LP-33 in allergic rhinitis: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial (GA2LEN Study). Eur J Clin Nutr 68, 602–607 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2014.13
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2014.13
This article is cited by
-
Comparative Case Study of Efficacy of Oral Bilastine Monotherapy to Concomittant Administration of Oral Bilastine with Probiotic in Patients with Allergic Rhinitis
Indian Journal of Otolaryngology and Head & Neck Surgery (2023)
-
Effects of therapeutic probiotics on modulation of microRNAs
Cell Communication and Signaling (2021)
-
Chinese herbal medicine bi min fang for allergic rhinitis: protocol for a double-blind, double-dummy, randomized controlled trial
Trials (2019)
-
House dust mite-related respiratory allergies and probiotics: a narrative review
Clinical and Molecular Allergy (2018)
-
Oral administration of Lactobacillus paracasei NCC 2461 for the modulation of grass pollen allergic rhinitis: a randomized, placebo‐controlled study during the pollen season
Clinical and Translational Allergy (2015)