Abstract
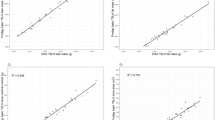
Dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) is considered to be a reference standard for the assessment of body composition, and one particular advantage is its provision of regional body composition parameters. The objective of this study was to determine the in vivo precision of the Lunar iDXA for the measurement of appendicular and trunk lean and fat mass in a heterogeneous group of adults (n=39; age 33.5 (8.3) years; BMI 24.6 (5.4) kg m−2). Two consecutive total body scans were performed on each participant with re-positioning between scans. There was excellent agreement between consecutive scans for measurements of both fat and lean appendicular and trunk composition (R2=0.99). Precision for body composition at all regions was less than 2% coefficient of variation (CV). Precision for bilateral appendicular body composition was less than 4% CV for the arms and less than 2.5% CV for the legs. Our findings indicate that the iDXA is a valuable tool for repeat measurements of regional body composition in adults.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ciangura C, Bouillot JL, Llanet-Linares C, Poitou C, Veyrie N, Basdevant A et al. Dynamics of change in total and regional body composition after gastric bypass in obese patients. Obesity 2012; 18: 760–765.
De Alvaro MTG, Munoz-Calvo MT, Barrios V, Martinez G, Martos-Moreno GA, Hawkins F et al. Regional fat distribution in adolescents with anorexia-nervosa: effect of duration of malnutrition and weight recovery. Eur J Endocrinol 2007; 157: 473–479.
Niedarauer CM, Blinkley TL, Specker BL . Effect of trunchal adiposity on plasma lipid and lipoprotein concentrations. J Nutr Health Aging 2006; 10: 154–160.
Berends AL, Zillikens MC, de Groot CJ, Rivadeneira F, Oostra BA, van Duijn CM et al. Body composition by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry in women with previous pre-eclampsia or small for gestational age offspring. Br J Obste Gyn 2009; 116: 442–445.
Oldroyd B, Smith AH, Truscott JG . Cross calibration of GE/Lunar pencil andfan beam dual energy densitometers – bone mineral density and body composition studies. Eur J Clin Nutr 2003; 57: 977–987.
Krueger DM, Checovich N, Vallarta-Ast D, Gemar D, Blinkley M . Comparison of total body parameters as measured using GE Healthcare Lunar Prodigy and Lunar iDXA densitometers. J Bone Mineral Res 2006; 21: SS225.
Lohman M, Tallroth K, Jyrki A, Marttinen MT . Reproducibility of dual energy X-ray absorptiometry total and regional body composition measurements using different scan positions and definitions of regions. Metabolism 2009; 58: 1663–1668.
Rezzi S, Ginty F, Beaumont A . Body Composition Precision with the Lunar iDXA. ISCD meeting proceedings: March, FL, USA, 2009.
Hind K, Oldroyd B, Truscott J . In-vivo short term precision of the GE Lunar iDXA for the measurement of three compartment total body composition in adults. Eur J Clin Nutr 2011; 65: 140–142.
Rothney MP, Francois-Pierre M, Yi X, Beaumont M, Davis C, Ergun D et al. Precision of GE Lunar iDXA for the measurement of total and regional body composition in nonobese adults. J Clin Densitom 2012; 15: 399–404.
Libber J, Blinkley N, Krueger D . Clinical observations in total body DXA: aspects of positioning and analysis. J Clin Densitom 2012; 15: 282–289.
Mazess RB, Barden H, Bisek JP, Hansen J . Dual energy Xray absorptiometry for total body and regional bone-mineral and soft-tissue composition. Am J Clin Nutr 1990; 51: 1106–1112.
Kiebzak GM, Leamy LJ, Pierson LM, Nord RH, Zang ZY . Measurement precision of body composition variables using the Lunar DPX-L densitometer. J Clin Densitom 2000; 3: 35–41.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hind, K., Oldroyd, B. In-vivo precision of the GE Lunar iDXA densitometer for the measurement of appendicular and trunk lean and fat mass. Eur J Clin Nutr 67, 1331–1333 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2013.210
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2013.210
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Does segmental body composition differ in women with Prader–Willi syndrome compared to women with essential obesity?
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation (2015)