Abstract
Background/Objectives:
The EPIC-Soft 24-h recall (the software developed to conduct 24-h dietary recalls (24-HDRs) in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC) Study) has been used in several regional/national dietary monitoring surveys. The main objective of the study was to present and discuss design, settings, logistics, data management and quality controls of dietary monitoring surveys that used EPIC-Soft for the collection of food consumption data.
Subjects/Methods:
Within European Food Consumption Validation (EFCOVAL), a questionnaire including questions on current/past EPIC-Soft experiences and requirements for the future was developed and sent to all institutes that used EPIC-Soft in their food consumption survey(s) (five surveys in four different countries).
Results:
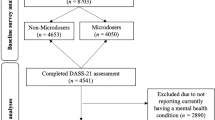
EPIC-Soft was used in the national food consumption survey in Belgium (⩾15–97 years), Germany (14–80 years), the Netherlands (19–30 years and 2–6 years) and Spain (regional only; 4–18 years). Participation rates in these surveys were 46% (Belgium), 42% (Germany), 42% (Dutch survey in adults), 79% (Dutch survey in children) and 77% (Basque survey). Two 24-HDRs were collected by conducting face-to-face interviews in Belgium and Spain, and through telephone interviews in Germany and the Netherlands. Except the Netherlands (19–30 years), where the study was conducted only in autumn, in all other countries the study was conducted throughout the four seasons, including all days of the week. Interviews were conducted by dietitians, except in Germany and Spain. Mean EPIC-Soft interview time was 20–34 min. The dropout rate between the first and second interviews was low (<7.5%) in all surveys.
Conclusion:
EPIC-Soft has been used in different study settings and populations for nutritional exposure assessments. To guarantee the comparability of data across countries, recommendations for the design of future pan-European dietary monitoring surveys using EPIC-Soft should be drawn.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Biro G, Hulshof KF, Ovesen L, Amorim Cruz JA (2002). Selection of methodology to assess food intake. Eur J Clin Nutr 56 (Suppl 2), S25–S32, S25–S32.
Brussaard JH, Lowik MR, Steingrimsdottir L, Moller A, Kearney J, De HS et al. (2002). A European food consumption survey method—conclusions and recommendations. Eur J Clin Nutr 56 (Suppl 2), S89–S94.
Brustad M, Skeie G, Braaten T, Slimani N, Lund E (2003). Comparison of telephone vs face-to-face interviews in the assessment of dietary intake by the 24 h recall EPIC SOFT program--the Norwegian calibration study. Eur J Clin Nutr 57, 107–113.
De Keyzer W, Huybrechts I, De Maeyer M, Ocke M, Slimani N, Van ‘t veer P et al. (2010). Food photographs in nutritional surveillance: errors in portion size estimation using drawings of bread and photographs of margarine and beverages consumption. Br J Nutr 105, 1073–1083.
De Vriese S, Huybrechts I, Moreau M, Van Oyen H (2006). The Belgian Food Consumption Survey 1—2004: report (Enquête de consommation alimentaire Belge 1—2004: Rapport). Scientific Institute of Public Health, Brussels, Belgium. D/2006/2505/16 (http://www.iph.fgov.be/epidemio/epifr/foodfr/table04.htm).
EFSA (2009). General Principles For The Collection Of National Food Consumption Data In The View Of A Pan-European Dietary Survey. European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) 7[12], 1435. European Food Safety Authority (EFSA): Parma, Italy.
Hulshof K, Ocke M, van Rossum C, Buurma E, Brants HA, Drijvers J et al. (2004). Resultaten van de Voedselconsumptiepeiling 2003 (in Dutch). RIVM: Bilthoven. Report 35003002/2004.
Huybrechts I, Geelen A, de Vries JH, Casagrande C, Nicolas G, De Keyzer W et al. (2011). Respondents’ evaluation of the 24-h dietary recall method (EPIC-Soft) in the EFCOVAL Project. Eur J Clin Nutr 65 (Suppl 1), S29–S37.
Larrañaga LN, Amiano EP, Gorostiza GE, Pérez DY, Bidaurrazaga-Van-Dierdonck J, Sarasqueta EC et al. (2006). Encuesta De Nutrición 2005: hábitos alimentarios y estado de salud de la población vasca de 4 a 18 Años. Primeros Resultados. Vitoria-Gasteiz Servicio Central de Publicaciones del Gobierno Vasco: DL.
Max Rubner-Institut (MRI) (2008). Ergebnisbericht der Nationalen Verzehrsstudie II—Teil 1 (in German). Max Rubner-Institut: Germany, Karlsruhe (http://www.was-esse-ich.de/uploads/media/NVS_II_Abschlussbericht_Teil_1.pdf).
Ocke M, Hulshof K, van Rossum C (2005). The Dutch National Food Consumption Survey—2003, methodological issues. Arch Public Health 63, 227–241.
Ocké MC, Slimani N, Brants H, Buurma-Rethans E, Casagrande C, Nicolas G et al. (2011). Potential and requirements for a standardized pan-European food consumption survey using the EPIC-Soft software. Eur J Clin Nutr 65 (Suppl 1), S48–S57.
Ocke M, van Rossum C, Fransen H (2004). Dutch National Food Consumption Survey—Young Children 2005/2006. RIVM: Bilthoven. Report 350070001/2008.
Slimani N, Bingham S, Runswick S, Ferrari P, Day NE, Welch AA et al. (2003). Group level validation of protein intakes estimated by 24-h diet recall and dietary questionnaires against 24-h urinary nitrogen in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC) calibration study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 12, 784–795.
Slimani N, Casagrande C, Nicolas G, Freisling H, Huybrechts I, Ocké MC et al. (2011). The standardized computerized 24-h dietary recall method EPIC-Soft adapted for pan-European dietary monitoring. Eur J Clin Nutr 65 (Suppl 1), S5–S15.
Slimani N, Deharveng G, Charrondiere RU, van Kappel AL, Ocke MC, Welch A et al. (1999). Structure of the standardized computerized 24-h diet recall interview used as reference method in the 22 centers participating in the EPIC project. European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 58, 251–266.
Slimani N, Ferrari P, Ocke M, Welch A, Boeing H, Liere M et al. (2000). Standardization of the 24-h diet recall calibration method used in the European prospective investigation into cancer and nutrition (EPIC): general concepts and preliminary results. Eur J Clin Nutr 54, 900–917.
Slimani N, Valsta L (2002). Perspectives of using the EPIC-SOFT programme in the context of pan-European nutritional monitoring surveys: methodological and practical implications. Eur J Clin Nutr 56 (Suppl 2), S63–S74.
Acknowledgements
The content of this article reflects only our views and the Community is not liable for any use that may be made of the information contained therein. The Community funding under the Sixth Framework Program for the EFCOVAL Project is acknowledged (FOOD-CT-2006-022895).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Contributors: IH, NS, CC and GN contributed to the development and concept of the EPIC-Soft specifications questionnaires. IH was responsible for the statistical analyses. IH, CC, GN, AG, JHdV, WDK, ITL, MDM, CK, PA, EJdB, MCO and NS contributed to the conception of the paper. All of us gave input on the drafting of the manuscript, and read and approved the final version.
Appendix A
Appendix A

Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huybrechts, I., Casagrande, C., Nicolas, G. et al. Inventory of experiences from national/regional dietary monitoring surveys using EPIC-Soft. Eur J Clin Nutr 65 (Suppl 1), S16–S28 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2011.84
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2011.84
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Comparison of meal patterns across five European countries using standardized 24-h recall (GloboDiet) data from the EFCOVAL project
European Journal of Nutrition (2018)
-
Comparison of two food record-based dietary assessment methods for a pan-European food consumption survey among infants, toddlers, and children using data quality indicators
European Journal of Nutrition (2015)
-
Rationale and methods of the European Food Consumption Validation (EFCOVAL) Project
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2011)
-
The standardized computerized 24-h dietary recall method EPIC-Soft adapted for pan-European dietary monitoring
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2011)
-
Potential and requirements for a standardized pan-European food consumption survey using the EPIC-Soft software
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2011)