Abstract
Background/Objectives:
Increasing evidence suggests that altered methionine/folate metabolism may contribute to the development of hepatic injury. We addressed the question of whether folic acid (FA) supplementation can affect serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) level in hypertensive Chinese adults.
Subjects/Methods:
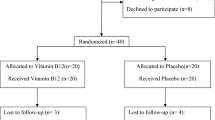
A total of 480 participants with mild or moderate essential hypertension and without known hepatic disease were randomly assigned to three treatment groups: (1) enalapril only (10 mg, control group); (2) enalapril–FA tablet (10 mg enalapril combined with 0.4 mg of FA, low FA group); and (3) enalapril–FA tablet (10 mg enalapril combined with 0.8 mg of FA, high FA group), once daily for 8 weeks.
Results:
This report included 455 participants in the final analysis according to the principle of intention to treat. We found a significant reduction in ALT level in the high FA group (median (25th percentile, 75th percentile), −0.6 (−6.9, 2.0)IU/l, P=0.0008). Compared with the control group, the high FA group showed a significantly greater ALT-lowering response in men (median ALT ratio (ALT at week 8 to ALT at baseline; 25th percentile, 75th percentile): 0.93 (0.67, 1.06) vs 1.00 (0.91, 1.21), P=0.032), and in participants with elevated ALT (ALT>40 IU/l) at baseline. There was no difference in ALT lowering between the control and the low FA group.
Conclusions:
Compared with treatment using 10 mg of enalapril alone, a daily dose of 10 mg enalapril combined with 0.8 mg of FA showed a beneficial effect on serum ALT level, particularly in men and in participants with elevated (>40 IU/l) ALT.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Björck J, Hellgren M, Råstam L, Lindblad U (2006). Associations between serum insulin and homocysteine in a Swedish population-a potential link between the metabolic syndrome and hyperhomocysteinemia: the Skaraborg project. Metabolism 55, 1007–1013.
Charatcharoenwitthaya P, Levy C, Angulo P, Keach J, Jorgensen R, Lindor KD (2007). Open-label pilot study of folic acid in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Liver Int 27, 220–226.
Ford ES, Schulze MB, Bergmann MM, Thamer C, Joost HG, Boeing H (2008). Liver enzymes and incident diabetes: findings from the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC)-Potsdam Study. Diabetes Care 31, 1138–1143.
Gulsen M, Yesilova Z, Bagci S, Uygun A, Ozcan A, Ercin CN et al. (2005). Elevated plasma homocysteine concentrations as a predictor of steatohepatitis inpatients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 20, 1448–1455.
Goessling W, Massaro JM, Vasan RS, D’Agostino Sr RB, Ellison RC, Fox CS (2008). Aminotransferase levels and 20-year risk of metabolic syndrome, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. Gastroenterology 135, 1935–1944.
Homocysteine Lowering Trialists’ Collaboration. (2005). Dose-dependent effects of folic acid on blood concentrations of homocysteine: a meta-analysis of the randomized trials. Am J Clin Nutr 82, 806–812.
Ioannou GN, Boyko EJ, Lee SP (2006). The prevalence and predictors of elevated serum aminotransferase activity in the United States in 1999–2002. Am J Gastroenterol 101, 76–82.
Kim HC, Kang DR, Nam CM, Hur NW, Shim JS, Jee SH et al. (2005). Elevated serum aminotransferase level as a predictor of intracerebral hemorrhage: Korea Medical Insurance Corporation Study. Stroke 36, 1642–1647.
Kim HC, Nam CM, Jee SH, Han KH, Oh DK, Sun I (2004). Normal serum aminotransferase concentration and risk of mortality from liver diseases: prospective cohort study. BMJ 328, 983–988.
Kim WR, Flamm SL, Di Bisceglie AM, Bodenheimer HC, Public Policy Committee of the American Association for the Study of Liver Disease. (2008). Serum activity of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) as an indicator of health and disease. Hepatology 47, 1363–1370.
Liao D, Tan H, Hui R, Li Z, Jiang X, Gaubatz J et al. (2006). Hyperhomocysteinemia decreases circulating high-density lipoprotein by inhibiting apolipoprotein A-I protein synthesis and enhancing HDL cholesterol clearance. Circ Res 99, 598–606.
Li JP, Huo Y, Liu P (2007). Efficacy and safety of Enalapril-Folate acid tablets in lowering blood pressure and plasma homocysteine. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao 39, 614–618.
Li Y, Jiang C, Xu G, Wang N, Zhu Y, Tang C et al. (2008). Homocysteine upregulates resistin production from adipocytes in vivo and in vitro. Diabetes 57, 817–827.
Mao G, Hong X, Xing H, Liu P, Liu H, Yu Y et al. (2008). Efficacy of folic acid and enalapril combined therapy on reduction of blood pressure and plasma glucose: a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, parallel-controlled, clinical trial. Nutrition 24, 1088–1096.
Pratt DS, Kaplan MM (2000). Evaluation of abnormal liver-enzyme results in asymptomatic patients. N Engl J Med 342, 1266–1271.
Purohit V, Abdelmalek MF, Barve S, Benevenga NJ, Halsted CH, Kaplowitz N et al. (2007). Role of S-adenosylmethionine, folate, and betaine in the treatment of alcoholic liver disease: summary of a symposium. Am J Clin Nutr 86, 14–24.
Sato KK, Hayashi T, Nakamura Y, Harita N, Yoneda T, Endo G et al. (2008). Liver enzymes compared with alcohol consumption in predicting the risk of type 2 diabetes: the Kansai Healthcare Study. Diabetes Care 31, 1230–1236.
Schindhelm RK, Dekker JM, Nijpels G, Bouter LM, Stehouwer CD, Heine RJ et al. (2007). Alanine aminotransferase predicts coronary heart disease events: a 10-year follow-up of the Hoorn Study. Atherosclerosis 191, 391–396.
Schulz KF, Altman DG, Moher D, CONSORT Group. (2010). CONSORT 2010 statement: updated guidelines for reporting parallel group randomized trials. Ann Intern Med 152, 726–732.
Wald DS, Law M, Morris JK (2002). Homocysteine and cardiovascular disease: evidence on causality from a meta-analysis. BMJ 325, 1202–1206.
Wang X, Qin X, Demirtas H, Li J, Mao G, Huo Y et al. (2007). Efficacy of folic acid supplementation in stroke prevention: a meta-analysis. Lancet 369, 1876–1882.
Welzel TM, Katki HA, Sakoda LC, Evans AA, London WT, Chen G et al. (2007). Blood folate levels and risk of liver damage and hepatocellular carcinoma in a prospective high-risk cohort. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 16, 1279–1282.
Woo CW, Prathapasinghe GA, Siow YL, Kaimin O (2006). Hyperhomocysteinemia induces liver injury in rat: protective effect of folic acid supplementation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1762, 656–665.
Yun KE, Shin CY, Yoon YS, Park HS (2009). Elevated alanine aminotransferase levels predict mortality from cardiovascular disease and diabetes in Koreans. Atherosclerosis 205, 533–537.
Yang Q, Botto LD, Erickson JD, Berry RJ, Sambell C, Johansen H et al. (2006). Improvement in stroke mortality in Canada and the United States, 1990–2002. Circulation 113, 1335–1343.
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the assistance and cooperation of the faculty and staff of the Anhui Medical University and thank all of the participants in our study. This study was conducted in accordance with the current regulations of People‘s Republic of China. The study was supported by Beijing Huaanfo Biomedical Research Center Inc. Beijing, China and in part by a grant from Anhui Provincial Ministry of Education (No. 2002kj174ZC), Anhui Provincial Ministry of Science and Technology, Anhui Medical University Biomedical Institute.
The sponsors did not participate in the design and conduct of the study; collection, management, analysis, and interpretation of the data; and preparation, review, and approval of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Contributors: Study concept and design: XQ, JL, YC, ZL, ZZ, JG, DG, JH, YW, FZ, XX, XW, XX, YH. Acquisition of data: JL, YC, ZL, JG, DG, JH, YW, FZ, YH. Analysis of data: XQ, JL, XX, XW, XX, HY. Interpretation of Data: XQ, L, YC, ZL, ZZ, JG, DG, JH, YW, FZ, XX, XW, XX, YH. Drafting and critical review of manuscript for important intellectual content: XQ, JL, YC, ZL, ZZ, JG, DG, JH, YW, FZ, XX, XW, XX, YH.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, X., Li, J., Cui, Y. et al. Effect of folic acid intervention on ALT concentration in hypertensives without known hepatic disease: a randomized, double-blind, controlled trial. Eur J Clin Nutr 66, 541–548 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2011.192
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2011.192
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Safety assessment of genetically modified rice expressing Cry1Ab protein in Sprague–Dawley rats
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Eating a healthy lunch improves serum alanine aminotransferase activity
Lipids in Health and Disease (2013)