Abstract
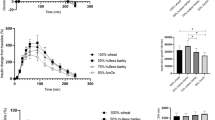
The glycaemic and insulinaemic response to different German honey varieties have not been studied so far. Eight German honey grades differing in their floral source and carbohydrate composition were tested. Isoglucidic test meals (25 g carbohydrate) and a 25 g glucose reference were given to 10 clinically and metabolically healthy, fasting individuals (31.5±8.1 years of age (mean±s.d.), two women). Glycaemic and insulinaemic index were calculated by the recommended FAO/WHO measure. Five of the eight tested honey varieties show a low glycaemic index below 55; for six of the eight tested varieties, the glycaemic load was lower than 10 (portion size of 20 g honey). Glycaemic index and insulinaemic index correlated significantly with the fructose content of honey varieties. The results show that glycaemic index and insulinaemic response depend on the fructose content of honey. Therefore, specific honey varieties may be recommended for subjects with impaired glucose tolerance instead of saccharose in food preparations.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bogdanov S, Jurendic T, Sieber R, Gallmann P (2008). Honey for nutrition and health: a review. J Am Coll Nutr 27, 677–689.
Flint A, Moller BK, Raben A, Sloth B, Pedersen D, Tetens I et al. (2006). Glycemic and insulinemic responses as determinants of appetite in humans. Am J Clin Nutr 84, 1365–1373.
Foster-Powell K, Holt SH, Brand-Miller JC (2002). International table of glycemic index and glycemic load values. Am J Clin Nutr 76, 5–56.
Galgani J, Aguirre C, Diaz E (2006). Acute effect of meal glycemic index and glycemic load on blood glucose and insulin responses in humans. Nutr J 5, 22.
Henry CJ, Lightowler HJ, Strik CM, Renton H, Hails S (2005). Glycaemic index and glycaemic load values of commercially available products in the UK. Br J Nutr 94, 922–930.
Ischayek JI, Kern M (2006). US honeys varying in glucose and fructose content elicit similar glycemic indexes. J Am Diet Assoc 106, 1260–1262.
Samanta A, Burden AC, Jones GR (1985). Plasma glucose responses to glucose, sucrose, and honey in patients with diabetes mellitus: an analysis of glycaemic and peak incremental indices. Diabet Med 2, 371–373.
Wolever TM, Mehling C (2003). Long-term effect of varying the source or amount of dietary carbohydrate on postprandial plasma glucose, insulin, triacylglycerol, and free fatty acid concentrations in subjects with impaired glucose tolerance. Am J Clin Nutr 77, 612–621.
Wolever TM, Yang M, Zeng XY, Atkinson F, Brand-Miller JC (2006). Food glycemic index, as given in glycemic index tables, is a significant determinant of glycemic responses elicited by composite breakfast meals. Am J Clin Nutr 83, 1306–1312.
Acknowledgements
The honey samples tested were provided by the ‘German beekeeper association’ (Deutscher Imkerbund e.V.), Wachtberg, Germany. Food chemistry analyses of the honey varieties tested were performed by the ‘LAVES-Institut für Bienenkunde’, Celle, Germany.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deibert, P., König, D., Kloock, B. et al. Glycaemic and insulinaemic properties of some German honey varieties. Eur J Clin Nutr 64, 762–764 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2009.103
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2009.103
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Symbioses shape feeding niches and diversification across insects
Nature Ecology & Evolution (2023)
-
Short-term effects of six Greek honey varieties on glycemic response: a randomized clinical trial in healthy subjects
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2018)
-
The effect of a cinnamon-, chromium- and magnesium-formulated honey on glycaemic control, weight loss and lipid parameters in type 2 diabetes: an open-label cross-over randomised controlled trial
European Journal of Nutrition (2016)