Abstract
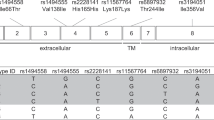
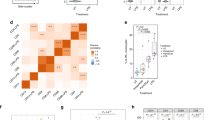
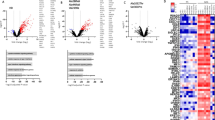
Interleukin-37 (IL-37) is an inhibitory member of the IL-1 family of cytokines. We previously found that balanced selection maintains common variations of the human IL37 gene. However, the functional consequences of this selection have yet to be validated. Here, using cells expressing exogenous IL-37 variants, including IL-37 Ref and IL-37 Var1 and Var2, we found that the three variants of IL-37 exhibited different immunoregulatory potencies in response to immune stimulation. The protein level of IL-37 Var2 was found to be significantly less than that of IL-37 Ref or Var1, despite the comparable mRNA levels of all three variants. Further study showed that IL-37 Var2 was rapidly degraded by a proteasome-dependent mechanism mediated by enhanced polyubiquitination, leading to a transient upregulation of IL-37 Var2 after immune stimulation. Finally, when ectopically expressed in cells, human IL-37 Var2 exerted less inhibition on proinflammatory cytokine production than did other IL-37 variants. Conversely, purified extracellular IL-37 variant proteins demonstrated comparable inhibitory abilities in vitro. In conclusion, our study reveals that common genetic variants of IL37 lead to different immune-inhibitory potencies, primarily as a result of differences in IL-37 protein stability, suggesting the possible involvement of these variants in various human diseases.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nold MF, Nold-Petry CA, Zepp JA, Palmer BE, Bufler P, Dinarello CA . IL-37 is a fundamental inhibitor of innate immunity. Nat Immunol 2010; 11: 1014–1022.
Boraschi D, Lucchesi D, Hainzl S, Leitner M, Maier E, Mangelberger D et al. IL-37: a new anti-inflammatory cytokine of the IL-1 family. Eur Cytokine Netw 2011; 22: 127–147.
Garlanda C, Dinarello CA, Mantovani A . The interleukin-1 family: back to the future. Immunity 2013; 39: 1003–1018.
He L, Liang Z, Zhao F, Peng L, Chen Z . Modulation of IL-37 expression by triptolide and triptonide in THP-1 cells. Cell Mol Immunol 2015; 12: 515–518.
Bulau AM, Nold MF, Li S, Nold-Petry CA, Fink M, Mansell A et al. Role of caspase-1 in nuclear translocation of IL-37, release of the cytokine, and IL-37 inhibition of innate immune responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2014; 111: 2650–2655.
Nold-Petry CA, Lo CY, Rudloff I, Elgass KD, Li S, Gantier MP et al. IL-37 requires the receptors IL-18Ralpha and IL-1R8 (SIGIRR) to carry out its multifaceted anti-inflammatory program upon innate signal transduction. Nat Immunol 2015; 16: 354–365.
Lunding L, Webering S, Vock C, Schroder A, Raedler D, Schaub B et al. IL-37 requires IL-18Ralpha and SIGIRR/IL-1R8 to diminish allergic airway inflammation in mice. Allergy 2015; 70: 366–373.
Li S, Neff CP, Barber K, Hong J, Luo Y, Azam T et al. Extracellular forms of IL-37 inhibit innate inflammation in vitro and in vivo but require the IL-1 family decoy receptor IL-1R8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2015; 112: 2497–2502.
McNamee EN, Masterson JC, Jedlicka P, McManus M, Grenz A, Collins CB et al. Interleukin 37 expression protects mice from colitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2011; 108: 16711–16716.
Ji Q, Zeng Q, Huang Y, Shi Y, Lin Y, Lu Z et al. Elevated plasma IL-37, IL-18, and IL-18BP concentrations in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Mediators Inflamm 2014; 2014: 165742.
Fujita H, Inoue Y, Seto K, Komitsu N, Aihara M . Interleukin-37 is elevated in subjects with atopic dermatitis. J Dermatol Sci 2013; 69: 173–175.
Xia L, Shen H, Lu J . Elevated serum and synovial fluid levels of interleukin-37 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: Attenuated the production of inflammatory cytokines. Cytokine 2015; 76: 553–557.
Ye L, Jiang B, Deng J, Du J, Xiong W, Guan Y et al. IL-37 alleviates rheumatoid arthritis by suppressing IL-17 and IL-17-triggering cytokine production and limiting Th17 cell proliferation. J Immunol 2015; 194: 5110–5119.
Kang B, Cheng S, Peng J, Yan J, Zhang S . Interleukin-37 gene variants segregated anciently coexist during hominid evolution. Eur J Hum Genet 2015; 23: 1392–1398.
Bufler P, Gamboni-Robertson F, Azam T, Kim SH, Dinarello CA . Interleukin-1 homologues IL-1F7b and IL-18 contain functional mRNA instability elements within the coding region responsive to lipopolysaccharide. Biochem J 2004; 381: 503–510.
Quintana-Murci L, Clark AG . Population genetic tools for dissecting innate immunity in humans. Nat Rev Immunol 2013; 13: 280–293.
Leffler EM, Gao Z, Pfeifer S, Segurel L, Auton A, Venn O et al. Multiple instances of ancient balancing selection shared between humans and chimpanzees. Science 2013; 339: 1578–1582.
Quirk S, Agrawal DK . Immunobiology of IL-37: mechanism of action and clinical perspectives. Expert Rev Clin Immunol 2014; 10: 1703–1709.
Newman TL, Tuzun E, Morrison VA, Hayden KE, Ventura M, McGrath SD et al. A genome-wide survey of structural variation between human and chimpanzee. Genome Res 2005; 15: 1344–1356.
Huang Z, Gao C, Chi X, Hu YW, Zheng L, Zeng T et al. IL-37 expression is upregulated in patients with tuberculosis and induces macrophages towards an M2-like phenotype. Scand J Immunol 2015; 82: 370–379.
Ge R, Pan F, Liao F, Xia G, Mei Y, Shen B et al. Analysis on the interaction between IL-1F7 gene and environmental factors on patients with ankylosing spondylitis: a case-only study. Mol Biol Rep 2011; 38: 2281–2284.
Pei B, Xu S, Liu T, Pan F, Xu J, Ding C . Associations of the IL-1F7 gene polymorphisms with rheumatoid arthritis in Chinese Han population. Int J Immunogenet 2013; 40: 199–203.
Naggie S, Osinusi A, Katsounas A, Lempicki R, Herrmann E, Thompson AJ et al. Dysregulation of innate immunity in hepatitis C virus genotype 1 IL28B-unfavorable genotype patients: impaired viral kinetics and therapeutic response. Hepatology 2012; 56: 444–454.
Sharma S, Jin Z, Rosenzweig E, Rao S, Ko K, Niewold TB . Widely divergent transcriptional patterns between SLE patients of different ancestral backgrounds in sorted immune cell populations. J Autoimmun 2015; 60: 51–58.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81371823 to SZ and No. 31500697 to JS), by the 973 Project (No. 2015CB554300 to SZ) and by the Shanghai Pujiang Program (No. 15PJ1407300 to JS). We wish to thank Biogot Technology for kindly providing us with the pCMV-Myc-Ub plasmid. We thank Dr. Daqiang Li (Fudan University) for technical advice.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information for this article can be found on the Cellular & Molecular Immunology website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, J., Zhang, Y., Cheng, S. et al. Common genetic heterogeneity of human interleukin-37 leads to functional variance. Cell Mol Immunol 14, 783–791 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2016.48
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2016.48
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Parallel selection on ecologically relevant gene functions in the transcriptomes of highly diversifying salmonids
BMC Genomics (2019)
-
Cynomolgus macaque IL37 polymorphism and control of SIV infection
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
IL-37 isoform D downregulates pro-inflammatory cytokines expression in a Smad3-dependent manner
Cell Death & Disease (2018)