Abstract
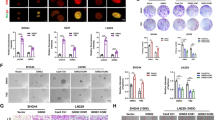
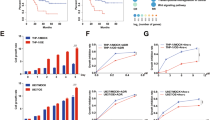
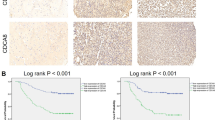
Although temozolomide (TMZ) is the first-line chemotherapeutic agent for glioblastoma, it is often non-curative due to drug resistance. To overcome the resistance of glioblastoma cells to TMZ, it is imperative to identify prognostic markers for outcome prediction and to develop chemo-sensitizing agents. Here, the gene expression profiles of TMZ-resistant and TMZ-sensitive samples were compared by microarray analysis, and mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 2 (MEK2) was upregulated specifically in resistant glioma cells but not in sensitive tumor cells or non-tumor tissues. Moreover, a comprehensive analysis of patient data revealed that the increased level of MEK2 expression correlated well with the advancement of glioma grade and worse prognosis in response to TMZ treatment. Furthermore, reducing the level of MEK2 in U251 glioma cell lines or xenografted glioma models through shRNA-mediated gene knockdown inhibited cell proliferation and enhanced the sensitivity of cells toward TMZ treatment. Further analysis of tumor samples from glioma patients by real-time PCR indicated that an increased MEK2 expression level was closely associated with the activation of many drug resistance genes. Finally, these resistance genes were downregulated after MEK2 was silenced in vitro, suggesting that the mechanism of MEK2-induced chemo-resistance could be mediated by the transcriptional activation of these resistance genes. Collectively, our data indicated that the expression level of MEK2 could serve as a prognostic marker for glioma chemotherapy and that MEK2 antagonists can be used as chemo-sensitizers to enhance the treatment efficacy of TMZ.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Friedmann-Morvinski D, Bushong EA, Ke E, Soda Y, Marumoto T, Singer O et al . Dedifferentiation of neurons and astrocytes by oncogenes can induce gliomas in mice. Science 2012 ; 338 : 1080 – 1084 .
Chen S, Tanaka S, Giannini C, Morris J, Yan ES, Buckner J et al . Gliomatosis cerebri: clinical characteristics, management, and outcomes. J Neurooncol 2013 ; 112 : 267 – 275 .
Zhao J, He H, Zhou K, Ren Y, Shi Z, Wu Z et al . Neuronal transcription factors induce conversion of human glioma cells to neurons and inhibit tumorigenesis. PLoS One 2012 ; 7 : e41506 .
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ et al . Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 2005 ; 352 : 987 – 996 .
Corsa P, Parisi S, Raguso A, Troiano M, Perrone A, Cossa S et al . Temozolomide and radiotherapy as first-line treatment of high-grade gliomas. Tumori 2006 ; 92 : 299 – 305 .
National Cancer Comprehensive Network . NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: central nervous system cancers, v.1.2008 . Available at http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/PDF/cns.pdf ( accessed 7 March 2008 ).
National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) . Carmustine implants and temozolomide for the treatment of newly diagnosed high-grade glioma. Technology Appraisal Guidance No. 121 . London: National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) ; 2007, p . 45 .
Van Meir EG, Hadjipanayis CG, Norden AD, Shu HK, Wen PY, Olson JJ . Exciting new advances in neuro-oncology: the avenue to a cure for malignant glioma. CA Cancer J Clin 2010 ; 60 : 166 – 193 .
Agnihotri S, Gajadhar AS, Ternamian C, Gorlia T, Diefes KL, Mischel PS et al . Alkylpurine-DNA-N-glycosylase confers resistance to temozolomide in xenograft models of glioblastoma multiforme and is associated with poor survival in patients. J Clin Invest 2012 ; 122 : 253 – 266 .
Pan Q, Yang XJ, Wang HM, Dong XT, Wang W, Li Y, Li JM . Chemoresistance to temozolomide in human glioma cell line U251 is associated with increased activity of O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase and can be overcome by metronomic temozolomide regimen. Cell Biochem Biophys 2012 ; 62 : 185 – 191 .
Lee ES, Ko KK, Joe YA, Kang SG, Hong YK . Inhibition of STAT3 reverses drug resistance acquired in temozolomide-resistant human glioma cells. Oncol Lett 2011 ; 2 : 115 – 121 .
Lu XY, Cao K, Li QY, Yuan ZC, Lu PS . The synergistic therapeutic effect of temozolomide and hyperbaric oxygen on glioma U251 cell lines is accompanied by alterations in vascular endothelial growth factor and multidrug resistance-associated protein-1 levels. J Int Med Res 2012 ; 40 : 995 – 1004 .
Munoz JL, Rodriguez-Cruz V, Greco SJ, Ramkissoon SH, Ligon KL, Rameshwar P . Temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma cells occurs partly through epidermal growth factor receptor-mediated induction of connexin 43. Cell Death Dis 2014 ; 5 : e1145 .
Poteet E, Choudhury GR, Winters A, Li W, Ryou MG, Liu R et al . Reversing the Warburg effect as a treatment for glioblastoma. J Biol Chem 2013 ; 288 : 9153 – 9164 .
Hegi ME, Diserens AC, Gorlia T, Hamou MF, de Tribolet N, Weller M et al . MGMT gene silencing and benefit from temozolomide in glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 2005 ; 352 : 997 – 1003 .
Tao BB, He H, Shi XH, Wang CL, Li WQ, Li B et al . Up-regulation of USP2a and FASN in gliomas correlates strongly with glioma grade. J Clin Neurosci 2013 ; 20 : 717 – 720 .
Okabe H, Lee SH, Phuchareon J, Albertson DG, McCormick F, Tetsu O . A critical role for FBXW8 and MAPK in cyclin D1 degradation and cancer cell proliferation. PLoS One 2006 ; 1 : e128 .
Basto D, Trovisco V, Lopes JM, Martins A, Pardal F, Soares P, Reis RM . Mutation analysis of B-RAF gene in human gliomas. Acta Neuropathol 2005 ; 109 : 207 – 210 .
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network . Comprehensive genomic characterization defines human glioblastoma genes and core pathways. Nature 2008 ; 455 : 1061 – 1068 .
MacDonald TJ, Brown KM, LaFleur B, Peterson K, Lawlor C, Chen Y et al . Expression profiling of medulloblastoma: PDGFRA and the RAS/MAPK pathway as therapeutic targets for metastatic disease. Nat Genet 2001 ; 29 : 143 – 152 .
Ding X, He Z, Zhou K, Cheng J, Yao H, Lu D et al . Essential role of TRPC6 channels in G2/M phase transition and development of human glioma. J Natl Cancer Inst 2010 ; 102 : 1052 – 1068 .
Li B, He H, Tao BB, Zhao ZY, Hu GH, Luo C et al . Knockdown of CDK6 enhances glioma sensitivity to chemotherapy. Oncol Rep 2012 ; 28 : 909 – 914 .
Zhao Z, Liu Y, He H, Chen X, Chen J, Lu YC . Candidate genes influencing sensitivity and resistance of human glioblastoma to Semustine. Brain Res Bull 2011 ; 86 : 189 – 194 .
Guo G, Yao W, Zhang Q, Bo Y . Oleanolic acid suppresses migration and invasion of malignant glioma cells by inactivating MAPK/ERK signaling pathway. PLoS One 2013 ; 8 : e72079 .
Roskoski R Jr, MEK1/2 dual-specificity protein kinases: structure and regulation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2012 ; 417 : 5 – 10 .
Zhang L, Shi R, He C, Cheng C, Song B, Cui H et al . Oncogenic B-Raf(V600E) abrogates the AKT/B-Raf/Mps1 interaction in melanoma cells. Cancer Lett 2013 ; 337 : 125 – 132 .
Chen Z, Zhang L, Xia L, Jin Y, Wu Q, Guo H et al . Genomic analysis of drug resistant gastric cancer cell lines by combining mRNA and microRNA expression profiling. Cancer Lett 2014 ; 350 : 43 – 51 .
Infante JR, Fecher LA, Falchook GS, Nallapareddy S, Gordon MS, Becerra C et al . Safety, pharmacokinetic, pharmacodynamic, and efficacy data for the oral MEK inhibitor trametinib: a phase 1 dose-escalation trial. Lancet Oncol 2012 ; 13 : 773 – 781 .
Hui K, Yang Y, Shi K, Luo H, Duan J, An J et al . The p38 MAPK-regulated PKD1/CREB/Bcl-2 pathway contributes to selenite-induced colorectal cancer cell apoptosis in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Lett 2014 ; 354 : 189 – 199 .
Boeckx C, Op de Beeck K, Wouters A, Deschoolmeester V, Limame R, Zwaenepoel K et al . Overcoming cetuximab resistance in HNSCC: The role of AURKB and DUSP proteins. Cancer Lett 2014 ; 354 : 365 – 377 .
Ito M, Ohba S, Gaensler K, Ronen SM, Mukherjee J, Pieper RO . Early Chk1 phosphorylation is driven by temozolomide-induced, DNA double strand break- and mismatch repair-independent DNA damage. PLoS One 2013 ; 8 : e62351 .
Tomiyasu H, Watanabe M, Sugita K, Goto-Koshino Y, Fujino Y, Ohno K et al . Regulations of ABCB1 and ABCG2 expression through MAPK pathways in acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell lines. Anticancer Res 2013 ; 33 : 5317 – 5323 .
Barancik M, Bohacova V, Kvackajova J, Hudecova S, Krizanova O, Breier A . SB203580, a specific inhibitor of p38-MAPK pathway, is a new reversal agent of P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance. Eur J Pharm Sci 2001 ; 14 : 29 – 36 .
Graziosi L, Mencarelli A, Santorelli C, Renga B, Cipriani S, Cavazzoni E et al . Mechanistic role of p38 MAPK in gastric cancer dissemination in a rodent model peritoneal metastasis. Eur J Pharmacol 2012 ; 674 : 143 – 152 .
Guo X, Ma N, Wang J, Song J, Bu X, Cheng Y et al . Increased p38-MAPK is responsible for chemotherapy resistance in human gastric cancer cells. BMC Cancer 2008 ; 8 : 375 .
Shen H, Xu W, Luo W, Zhou L, Yong W, Chen F et al . Upregulation of mdr1 gene is related to activation of the MAPK/ERK signal transduction pathway and YB-1 nuclear translocation in B-cell lymphoma. Exp Hematol 2011 ; 39 : 558 – 569 .
Gong X, Schwartz PH, Linskey ME, Bota DA . Neural stem/progenitors and glioma stem-like cells have differential sensitivity to chemotherapy. Neurology 2011 ; 76 : 1126 – 1134 .
Skarpen E, Flinder LI, Rosseland CM, Orstavik S, Wierod L, Oksvold MP et al . MEK1 and MEK2 regulate distinct functions by sorting ERK2 to different intracellular compartments. FASEB J 2008 ; 22 : 466 – 476 .
Lu Y, Wang L, He M, Huang W, Li H, Wang Y et al . Nix protein positively regulates NF-kappaB activation in gliomas. PLoS One 2012 ; 7 : e44559 .
Jameson KL, Mazur PK, Zehnder AM, Zhang J, Zarnegar B, Sage J, Khavari PA . IQGAP1 scaffold-kinase interaction blockade selectively targets RAS-MAP kinase-driven tumors. Nat Med 2013 ; 19 : 626 – 630 .
Sato A, Sunayama J, Matsuda K, Seino S, Suzuki K, Watanabe E et al . MEK-ERK signaling dictates DNA-repair gene MGMT expression and temozolomide resistance of stem-like glioblastoma cells via the MDM2-p53 axis. Stem Cells 2011 ; 29 : 1942 – 1951 .
Stewart S, Sundaram M, Zhang Y, Lee J, Han M, Guan KL . Kinase suppressor of Ras forms a multiprotein signaling complex and modulates MEK localization. Mol Cell Biol 1999 ; 19 : 5523 – 5534 .
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by NSFC81302187 and CWS14C063.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest in this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, H., Yao, M., Zhang, W. et al. MEK2 is a prognostic marker and potential chemo-sensitizing target for glioma patients undergoing temozolomide treatment. Cell Mol Immunol 13, 658–668 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2015.46
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2015.46