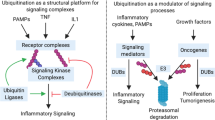
Abstract
The nuclear factor κB (NFκB) transcription factor plays critical roles in inflammation and immunity. The dysregulation of NFκB is associated with inflammatory and autoimmune diseases and cancer. NFκB activation is negatively regulated by the ubiquitin-dependent proteasomal degradation pathway. In the present review, we discuss recent advances in our understanding of how ubiquitin ligases regulate the NFκB degradation pathway.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sen R, Baltimore D . Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell 1986; 46: 705–716.
Chen LF, Greene WC . Shaping the nuclear action of NFkappaB. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2004; 5: 392–401.
Hou Y, Mortimer L, Chadee K . Entamoeba histolytica cysteine proteinase 5 binds integrin on colonic cells and stimulates NFkappaB-mediated pro-inflammatory responses. J Biol Chem 2010; 285: 35497–35504.
Baldwin ASJ . The transcription factor NFκB and human disease. J Clin Invest 2001; 107: 3–6.
Yamamoto Y, Gaynor RB . IkappaB kinases: key regulators of the NFkappaB pathway. Trends Biochem Sci 2004; 29, 72–79.
Solinas G, Germano G, Mantovani A, Allavena P . Tumor-associated macrophages (TAM) as major players of the cancer-related inflammation. J Leukoc Biol 2009; 86: 1065–1073.
Saccani S, Marazzi I, Beg AA, Natoli G . Degradation of promoter-bound p65/RelA is essential for the prompt termination of the nuclear factor KB response. J Exp Med 2004; 200: 107–113.
Hou Y, Moreau F, Chadee K . PPARg is an E3 ligase that induces the degradation of NFkB/p65. Nat Commun 2012; 3: 1300.
Hou Y, Zhang Z, Xu Q, Wang H, Xu Y, Chen KP . Inhibitor of growth 4 induces NF kB/p65 ubiquitin-dependent degradation. Oncogene 2014; 33: 1997–2003.
Deshaies RJ, Joazeiro CA . RING domain E3 ubiquitin ligases. Annu Rev Biochem 2009; 78: 399–434.
Kamizono S, Hanada T, Yasukawa H, Minoguchi S, Kato R, Minoguchi M et al. The SOCS box of SOCS-1 accelerates ubiquitin-dependent proteolysis of TEL-JAK2. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 12530–12538.
Frantsve J, Schwaller J, Sternberg DW, Kutok J, Gilliland DG . Socs-1 inhibits TEL-JAK2-mediated transformation of hematopoietic cells through inhibition of JAK2 kinase activity and induction of proteasome-mediated degradation. Mol Cell Biol 2001; 21: 3547–3557.
Ryo A, Suizu F, Yoshida Y, Perrem K, Liou YC, Wulf G et al. Regulation of NFkappaB signaling by Pin1-dependent prolyl isomerization and ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis of p65/RelA. Mol Cell 2003; 12: 1413–1426
Ganesh L, Burstein E, Guha-Niyogi A, Louder MK, Mascola JR, Klomp LW et al. The gene product Murr1restricts HIV-1 replication in resting CD4+ lympho-cytes. Nature 2003; 426: 853–857.
Marine GN, Mao X, Komarck CM, Burstein E . COMMD1 promotes the ubiquitination of NF-κB subunits through a cullin-containing ubiquitin ligase. EMBO J 2007; 26: 436–447.
Mao X, Gluck N, Li D, Maine GN, Li H, Zaidi IW et al. GCN5 is a required cofactor for a ubiquitin ligase that targets NFkB/RelA. Genes Dev 2009; 23: 849–861.
Rodrigues L, Filipe J, Seldon MP, Fonseca L, Anrather J, Soares MP et al. Termination of NFκB activity through a gammaherpesvirus protein that assembles an EC5S ubiquitin-ligase. EMBO J 2009; 28: 1283–1295.
Tanaka T, Grusby MJ, Kaisho T . PDLIM2-mediated termination of transcription factor NF-kappaB activation by intranuclear sequestration and degradation of the p65 subunit. Nat Immunol 2007; 8: 584–591.
Fan Y, Mao R, Zhao Y, Yu Y, Sun W, Song P et al. Tumor necrosis factor-α induces RelA degradation via ubiquitination at lysine 195 to prevent excessive nuclear factor-kB activation. J Biol Chem 2009; 284: 29290–28297.
Greene ME, Blumberg B, McBride OW, Yi HF, Kronquist K, Kwan K et al. Isolation of the human peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma cDNA: expression in hematopoietic cells and chromosomal mapping. Gene Express 1995; 4: 281–299.
Girnun GD, Naseri E, Vafai SB, Qu L, Szwaya JD, Bronson R et al. Synergy between PPARgamma ligands and platinum-based drugs in cancer. Cancer Cell 2007; 11: 395–406.
Zhang Z, Xu Y, Xu Q, Hou Y . PPARγ against tumors by different signaling pathways. Onkologie 2013; 36: 598–601.
Hou Y, Gao J, Xu H, Xu Y, Zhang Z, Xu Q et al. PPARγ E3 ubiquitin ligase regulates MUC1-C oncoprotein stability. Oncogene 2013; in press.
Kelly D, Campbell JI, King TP, Grant G, Jansson EA, Coutts AG et al. Commensal anaerobic gut bacteria attenuate inflammation by regulating nuclear-cytoplasmic shuttling of PPAR-gamma and RelA. Nat Immunol 2004; 5: 104–112.
Chung SW, Kang BY, Kim SH, Pak YK, Cho D, Trinchieri G et al. Oxidized low-density lipoprotein inhibits interleukin-12 production in lipopolysaccharide-activated mouse macrophages via direct interactions between peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma and nuclear factor-kappa B. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 32681–3267.
Ruan H, Pownall HJ, Lodish HF . Troglitazone antagonizes tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced reprogramming of adipocyte gene expression by inhibiting the transcriptional regulatory functions of NF-kappaB. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 28181–28192.
Garkavtsev I, Kozin SV, Chernova O, Xu L, Winkler F, Brown E et al. The candidate tumour suppressor protein ING4 regulates brain tumour growth and angiogenesis. Nature 2004; 428: 328–332.
Coles AH, Gannon H, Cerny A, Kurt-Jones E, Jones SN . Inhibitor of growth-4 promotes IkappaB promoter activation to suppress NF-kappaB signaling and innate immunity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010; 107: 11423–11428.
Ivanov AV, Peng H, Yurchenko V, Yap KL, Negorev DG, Schultz DC et al. PHD domain-mediated E3 ligase activity directs intramolecular sumoylation of an adjacent bromodomain required for gene silencing. Mol Cell 2007; 28: 823–837.
Coscoy L, Ganem D . PHD domains and E3 ubiquitin ligases: viruses make the connection. Trends Cell Biol 2003; 13: 7–12.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Jiangsu Province Natural Science Foundation (SBK201320232); the National Science Foundation of China (31271272, 31071030); and the Scientific Research Foundation for Returned Overseas Chinese Scholars, State Education Ministry.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, H., You, M., Shi, H. et al. Ubiquitin-mediated NFκB degradation pathway. Cell Mol Immunol 12, 653–655 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2014.99
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2014.99
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Dual function of activated PPARγ by ligands on tumor growth and immunotherapy
Medical Oncology (2024)
-
TRIMs: selective recruitment at different steps of the NF-κB pathway—determinant of activation or resolution of inflammation
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2021)
-
The ubiquitin–proteasome system in kidney physiology and disease
Nature Reviews Nephrology (2019)
-
STAT3 and NF-κB are Simultaneously Suppressed in Dendritic Cells in Lung Cancer
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Cellular and molecular regulation of innate inflammatory responses
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2016)