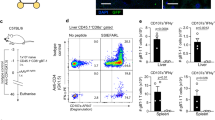
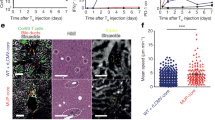
Abstract
CD8+ T cells play a critical role in hepatitis B virus (HBV) pathogenesis. During acute, self-limited infections, these cells are instrumental to viral clearance; in chronic settings, they sustain repetitive cycles of hepatocellular necrosis that promote hepatocellular carcinoma development. Both CD8+ T-cell defensive and destructive functions are mediated by antigen-experienced effector cells and depend on the ability of these cells to migrate to the liver, recognize hepatocellular antigens and perform effector functions. Understanding the signals that modulate the spatiotemporal dynamics of CD8+ T cells in the liver, particularly in the context of antigen recognition, is therefore critical to gaining insight into the pathogenesis of acute and chronic HBV infection. Here, we highlight recent data on how effector CD8+ T cells traffic within the liver, and we discuss the potential for novel imaging techniques to shed light on this important aspect of HBV pathogenesis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Iannacone M, Sitia G, Guidotti LG . Pathogenetic and antiviral immune responses against hepatitis B virus. Future Virol 2006; 1: 189–196.
Iannacone M, Sitia G, Ruggeri ZM, Guidotti LG . HBV pathogenesis in animal models: recent advances on the role of platelets. J Hepatol 2007; 46: 719–726.
Guidotti LG, Chisari FV . Immunobiology and pathogenesis of viral hepatitis. Annu Rev Pathol 2006; 1: 23–61.
Springer TA . Traffic signals for lymphocyte recirculation and leukocyte emigration: the multistep paradigm. Cell 1994; 76: 301–314.
von Andrian UH, Mackay CR . T-cell function and migration. Two sides of the same coin. N Engl J Med 2000; 343: 1020–1034.
Kansas GS . Selectins and their ligands: current concepts and controversies. Blood 1996; 88, 3259–3287.
Hynes RO . Integrins: versatility, modulation, and signaling in cell adhesion. Cell 1992; 69, 11–25.
Hynes RO . Integrins: bidirectional, allosteric signaling machines. Cell 2002; 110: 673–687.
Lee WY, Kubes P . Leukocyte adhesion in the liver: distinct adhesion paradigm from other organs. J Hepatol 2008; 48: 504–512.
Guidotti LG, Iannacone M . Effector CD8 T cell trafficking within the liver. Mol Immunol 2013; 55: 94–99.
Wong J, Johnston B, Lee SS, Bullard DC, Smith CW, Beaudet AL et al. A minimal role for selectins in the recruitment of leukocytes into the inflamed liver microvasculature. J Clin Invest 1997; 99: 2782–2790.
Wisse E, de Zanger RB, Charels K, van der Smissen P, McCuskey RS . The liver sieve: considerations concerning the structure and function of endothelial fenestrae, the sinusoidal wall and the space of Disse. Hepatology 1985; 5: 683–692.
Warren A, Le Couteur DG, Fraser R, Bowen DG, McCaughan GW, Bertolino P . T lymphocytes interact with hepatocytes through fenestrations in murine liver sinusoidal endothelial cells. Hepatology 2006; 44: 1182–1190.
Iannacone M, Sitia G, Isogawa M, Marchese P, Castro MG, Lowenstein PR et al. Platelets mediate cytotoxic T lymphocyte-induced liver damage. Nat Med 2005; 11: 1167–1169.
Iannacone M, Sitia G, Narvaiza I, Ruggeri ZM, Guidotti LG . Antiplatelet Drug therapy moderates immune-mediated liver disease and inhibits viral clearance in mice infected with a replication-deficient adenovirus. Clin Vaccine Immunol 2007; 14: 1532–1535.
Iannacone M, Sitia G, Guidotti LG . On the role of platelets in the pathogenesis of viral hepatitis. J Hepatol 2009; 51: 599–600.
Lang PA, Contaldo C, Georgiev P, El-Badry AM, Recher M, Kurrer M et al. Aggravation of viral hepatitis by platelet-derived serotonin. Nat Med 2008; 14: 756–761.
Sitia G, Aiolfi R, Di Lucia P, Mainetti M, Fiocchi A, Mingozzi F et al. Antiplatelet therapy prevents hepatocellular carcinoma and improves survival in a mouse model of chronic hepatitis B. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2012; 109: E2165–E2172.
Cattaneo M . Aspirin and clopidogrel: efficacy, safety, and the issue of drug resistance. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2004; 24: 1980–1987.
Mcdonald B, McAvoy EF, Lam F, Gill V, de la Motte C, Savani RC et al. Interaction of CD44 and hyaluronan is the dominant mechanism for neutrophil sequestration in inflamed liver sinusoids. J Exp Med 2008; 205: 915–927.
Mccuskey RS . The hepatic microvascular system in health and its response to toxicants. Anat Rec (Hoboken) 2008; 291: 661–671.
Klugewitz K, Adams DH, Emoto M, Eulenburg K, Hamann A . The composition of intrahepatic lymphocytes: shaped by selective recruitment? Trends Immunol 2004; 25: 590–594.
Egen JG, Rothfuchs AG, Feng CG, Winter N, Sher A, Germain RN . Macrophage and T cell dynamics during the development and disintegration of mycobacterial granulomas. Immunity 2008; 28: 271–284.
Jenne CN, Kubes P . Immune surveillance by the liver. Nat Immunol 2013; 14: 996–1006.
Halin C, Mora JR, Sumen C, von Andrian UH . In vivo imaging of lymphocyte trafficking. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 2005; 21: 581–603.
Sitia G, Iannacone M, Aiolfi R, Isogawa M, van Rooijen N, Scozzesi C et al. Kupffer cells hasten resolution of liver immunopathology in mouse models of viral hepatitis. PLoS Pathog 2011; 7: e1002061.
Zhang P . Correlative cryo-electron tomography and optical microscopy of cells. Curr Opin Struct Biol 2013; 23: 763–770.
Briers JD . Laser Doppler, speckle and related techniques for blood perfusion mapping and imaging. Physiol Meas 2001; 22: R35–R66.
Briers JD, Fercher AF . Retinal blood-flow visualization by means of laser speckle photography. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1982; 22: 255–259.
Wang L, Xu W, Bachman M, Li GP, Chen Z . Phase-resolved optical Doppler tomography for imaging flow dynamics in microfluidic channels. Appl Phys Lett 2004; 85: 1855–1857.
Wang XJ, Milner TE, Nelson JS . Characterization of fluid flow velocity by optical Doppler tomography. Opt Lett 1995; 20: 1337–1339.
Grant I . Particle image velocimetry: a review. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part C J Mech Eng Sci 1997; 211: 55–76.
Lima R, Wada S, Tsubota KI, Yamaguchi T . Confocal micro-PIV measurements of three-dimensional profiles of cell suspension flow in a square microchannel. Meas Sci Technol 2006; 17: 797.
Magde D, Webb WW, Elson EL . Fluorescence correlation spectroscopy. III. Uniform translation and laminar flow. Biopolymers 1978; 17: 361–376.
Haustein E, Schwille P . Single-molecule spectroscopic methods. Curr Opin Struct Biol 2004; 14: 531–540.
Dittrich PS, Schwille P . Spatial two-photon fluorescence cross-correlation spectroscopy for controlling molecular transport in microfluidic structures. Anal Chem 2002; 74: 4472–4479.
Elson EL, Magde D . Fluorescence correlation spectroscopy. I. Conceptual basis and theory. Biopolymers 1974; 13: 1–27.
Brister PC, Kuricheti KK, Buschmann V, Weston KD . Fluorescence correlation spectroscopy for flow rate imaging and monitoring — optimization, limitations and artifacts. Lab Chip 2005; 5: 785–791.
Collini M, D'Alfonso L, Caccia M, Sironi L, Panzica M, Chirico G et al. In vitro–in vivo fluctuation spectroscopies. Opt Fluoresc Microsc 2011; 2011: 165–181.
Arbour TJ, Enderlein J . Application of dual-focus fluorescence correlation spectroscopy to microfluidic flow-velocity measurement. Lab Chip 2010; 10: 1286.
Pozzi P, Sironi L, D'Alfonso L, Bouzin M, Collini M, Chirico G et al. Electron multiplying charge-coupled device-based fluorescence cross-correlation spectroscopy for blood velocimetry on zebrafish embryos. J Biomed Opt 2014; 19: 067007.
Rossow MJ, Mantulin WW, Gratton E . Scanning laser image correlation for measurement of flow. J Biomed Opt 2010; 15: 026003.
Acknowledgements
We thank R Serra for secretarial assistance; L Ganzer, D Inverso and L G Guidotti for help with the preparation of Figures and Movies; and L Sironi, G Chirico and all the members of the Iannacone laboratory for helpful discussions. This work was supported by ERC (grant 281648), Italian Association for Cancer Research (grant 9965) and a Career Development Award from the Giovanni Armenise-Harvard Foundation. Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Cellular & Molecular Immunology's website (http://www.nature.com/cmi).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Cellular & Molecular Immunology's website. (http://www.nature.com/cmi).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iannacone, M. Hepatic effector CD8+ T-cell dynamics. Cell Mol Immunol 12, 269–272 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2014.78
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2014.78
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Immunobiology and pathogenesis of hepatitis B virus infection
Nature Reviews Immunology (2022)
-
Overview of the special issue on HBV immunity
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2015)