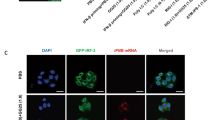
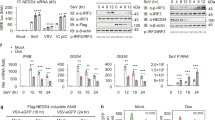
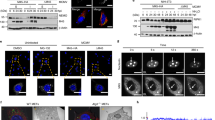
Abstract
Interferon regulatory factor (IRF) 7 has been demonstrated to be a master regulator of virus-induced type I interferon production (IFN), and it plays a central role in the innate immune response against viruses. Here, we identified death-associated protein kinase 1 (DAPK1) as an IRF7-interacting protein by tandem affinity purification (TAP). Viral infection induced DAPK1–IRF7 and DAPK1–IRF3 interactions and overexpression of DAPK1 enhanced virus-induced activation of the interferon-stimulated response element (ISRE) and IFN-β promoters and the expression of the IFNB1 gene. Knockdown of DAPK1 attenuated the induction of IFNB1 and RIG-I expression triggered by viral infection or IFN-β, and they were enhanced by viral replication. In addition, viral infection or IFN-β treatment induced the expression of DAPK1. IFN-β treatment also activated DAPK1 by decreasing its phosphorylation level at serine 308. Interestingly, the involvement of DAPK1 in virus-induced signaling was independent of its kinase activity. Therefore, our study identified DAPK1 as an important regulator of the cellular antiviral response.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Takeuchi O, Akira S . Pattern recognition receptors and inflammation. Cell 2010; 140: 805–820.
Akira S, Uematsu S, Takeuchi O . Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell 2006; 124: 783–801.
Garcia-Sastre A, Biron CA . Type 1 interferons and the virus-host relationship: a lesson in detente. Science 2006; 312: 879–882.
O'Neill LA, Bowie AG . The family of five: TIR-domain-containing adaptors in Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat Rev Immunol 2007; 7: 353–364.
Oshiumi H, Matsumoto M, Funami K, Akazawa T, Seya T . TICAM-1, an adaptor molecule that participates in Toll-like receptor 3-mediated interferon-beta induction. Nat Immunol 2003; 4: 161–167.
Yamamoto M, Sato S, Hemmi H, Hoshino K, Kaisho T, Sanjo H et al. Role of adaptor TRIF in the MyD88-independent Toll-like receptor signaling pathway. Science 2003; 301: 640–643.
Xu LG, Wang YY, Han KJ, Li LY, Zhai Z, Shu HB . VISA is an adapter protein required for virus-triggered IFN-beta signaling. Mol Cell 2005; 19: 727–740.
O'Neill LA, Bowie AG . Sensing and signaling in antiviral innate immunity. Curr Biol 2010; 20: R328–R333.
Fitzgerald KA, McWhirter SM, Faia KL, Rowe DC, Latz E, Golenbock DT et al. IKKepsilon and TBK1 are essential components of the IRF3 signaling pathway. Nat Immunol 2003; 4: 491–496.
Sharma S, tenOever BR Grandvaux N, Zhou GP, Lin R, Hiscott J . Triggering the interferon antiviral response through an IKK-related pathway. Science 2003; 300: 1148–1151.
Ermolaeva MA, Michallet MC Papadopoulou N Utermöhlen O Kranidioti K, Kollias G et al. Function of TRADD in tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 signaling and in TRIF-dependent inflammatory responses. Nat Immunol 2008; 9: 1037–1046.
Michallet MC, Meylan E, Ermolaeva MA, Vazquez J, Rebsamen M, Curran J et al. TRADD protein is an essential component of the RIG-like helicase antiviral pathway. Immunity 2008; 28: 651–661.
Balachandran S, Venkataraman T, Fisher PB, Barber GN . Fas-associated death domain-containing protein-mediated antiviral innate immune signaling involves the regulation of Irf7. J Immunol 2007; 178: 2429–2439.
Zhong B, Yang Y, Li S, Wang YY, Li Y, Diao F et al. The adaptor protein MITA links virus-sensing receptors to IRF3 transcription factor activation. Immunity 2008; 29: 538–550.
Lei CQ, Zhong B, Zhang Y, Zhang J, Wang S, Shu HB et al. Glycogen synthase kinase 3beta regulates IRF3 transcription factor-mediated antiviral response via activation of the kinase TBK1. Immunity 2010; 33: 878–889.
Tamura T, Yanai H, Savitsky D, Taniguchi T . The IRF family transcription factors in immunity and oncogenesis. Annu Rev Immunol 2008; 26: 535–584.
Hiscott J . Triggering the innate antiviral response through IRF-3 activation. J Biol Chem 2007; 282: 15325–15329.
Honda K, Yanai H, Negishi H, Asagiri M, Sato M, Mizutani T et al. IRF-7 is the master regulator of type-I interferon-dependent immune responses. Nature 2005; 434: 772–777.
Lu R, Au WC, Yeow WS, Hageman N, Pitha PM . Regulation of the promoter activity of interferon regulatory factor-7 gene. Activation by interferon snd silencing by hypermethylation. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 31805–31812.
Litvak V, Ratushny AV, Lampano AE, Schmitz F, Huang AC, Raman A et al. A FOXO3-IRF7 gene regulatory circuit limits inflammatory sequelae of antiviral responses. Nature 2012; 490: 421–425.
Wang RP, Zhang M, Li Y, Diao FC, Chen D, Zhai Z et al. Differential regulation of IKK alpha-mediated activation of IRF3/7 by NIK. Mol Immunol 2008; 45: 1926–1934.
Ning S, Campos AD, Darnay BG, Bentz GL, Pagano JS . TRAF6 and the three C-terminal lysine sites on IRF7 are required for its ubiquitination-mediated activation by the tumor necrosis factor receptor family member latent membrane protein 1. Mol Cell Biol 2008; 28: 6536–6546.
Yu Y, Hayward GS . The ubiquitin E3 ligase RAUL negatively regulates type i interferon through ubiquitination of the transcription factors IRF7 and IRF3. Immunity 2010; 33: 863–877.
Mao AP, Li S, Zhong B, Li Y, Yan J, Li Q et al. Virus-triggered ubiquitination of TRAF3/6 by cIAP1/2 is essential for induction of interferon-beta (IFN-beta) and cellular antiviral response. J Biol Chem 2010; 285: 9470–9476.
Li Y, Li C, Xue P, Zhong B, Mao AP, Ran Y et al. ISG56 is a negative-feedback regulator of virus-triggered signaling and cellular antiviral response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009; 106: 7945–7950.
Diao F, Li S, Tian Y, Zhang M, Xu LG, Zhang Y et al. Negative regulation of MDA5- but not RIG-I-mediated innate antiviral signaling by the dihydroxyacetone kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104: 11706–11711.
Huang J, Liu T, Xu LG, Chen D, Zhai Z, Shu HB . SIKE is an IKK epsilon/TBK1-associated suppressor of TLR3- and virus-triggered IRF-3 activation pathways. EMBO J 2005; 24: 4018–4028.
Chuang YT, Fang LW, Lin-Feng MH, Chen RH, Lai MZ . The tumor suppressor death-associated protein kinase targets to TCR-stimulated NF-kappa B activation. J Immunol 2008; 180: 3238–3249.
Wang YY, Liu LJ, Zhong B Liu TT, Li Y, Yang Y et al. WDR5 is essential for assembly of the VISA-associated signaling complex and virus-triggered IRF3 and NF-kappaB activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010; 107: 815–820.
Deiss LP, Feinstein E, Berissi H, Cohen O, Kimchi A . Identification of a novel serine/threonine kinase and a novel 15-kD protein as potential mediators of the gamma interferon-induced cell death. Genes Dev 1995; 9: 15–30.
Levine B, Klionsky DJ . Development by self-digestion: molecular mechanisms and biological functions of autophagy. Dev Cell 2004; 6: 463–477.
Bialik S, Kimchi A . The death-associated protein kinases: structure, function, and beyond. Annu Rev Biochem 2006; 75: 189–210.
Kuo JC, Wang WJ, Yao CC, Wu PR, Chen RH . The tumor suppressor DAPK inhibits cell motility by blocking the integrin-mediated polarity pathway. J Cell Biol 2006; 172: 619–631.
Harrison B, Kraus M, Burch L, Stevens C, Craig A, Gordon-Weeks P et al. DAPK-1 binding to a linear peptide motif in MAP1B stimulates autophagy and membrane blebbing. J Biol Chem 2008; 283: 9999–10014.
Kang BN, Ahmad AS, Saleem S, Patterson RL, Hester L, Doré S et al. Death-associated protein kinase-mediated cell death modulated by interaction with DANGER. J Neurosci 2010; 30: 93–98.
Zidi I, Mestiri S, Bartegi A, Amor NB . TNF-alpha and its inhibitors in cancer. Med Oncol 2009; 27: 185–198.
Perry AK, Chow EK, Goodnough JB, Yeh WC, Cheng G . Differential requirement for TANK-binding kinase-1 in type I interferon responses to Toll-like receptor activation and viral infection. J Exp Med 2004; 199: 1651–1658.
Tenoever BR, Ng SL, Chua MA, McWhirter SM, García-Sastre A, Maniatis T . Multiple functions of the IKK-related kinase IKKepsilon in interferon-mediated antiviral immunity. Science 2007; 315: 1274–1278.
Shohat G, Spivak-Kroizman T, Cohen O, Bialik S, Shani G, Berrisi H et al. The pro-apoptotic function of death-associated protein kinase is controlled by a unique inhibitory autophosphorylation-based mechanism. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 47460–47467.
Hsu H, Huang J, Shu HB, Baichwal V, Goeddel DV . TNF-dependent recruitment of the protein kinase RIP to the TNF receptor-1 signaling complex. Immunity 1996; 4: 387–396.
Ea CK, Deng L, Xia ZP, Pineda G, Chen ZJ . Activation of IKK by TNFalpha requires site-specific ubiquitination of RIP1 and polyubiquitin binding by NEMO. Mol Cell 2006; 22: 245–257.
Acknowledgements
We thank the members of our laboratory for their technical help and stimulating discussions. This work was supported by grants from the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2012CB910201, 2010CB911802) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31221061, 31130020, 31101019 and 91029302).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Cellular & Molecular Immunology's website. (http://www.nature.com/cmi).
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Hu, MM., Shu, HB. et al. Death-associated protein kinase 1 is an IRF3/7-interacting protein that is involved in the cellular antiviral immune response. Cell Mol Immunol 11, 245–252 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2013.65
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2013.65
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
SNX8 modulates the innate immune response to RNA viruses by regulating the aggregation of VISA
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2020)
-
IFITM3 inhibits virus-triggered induction of type I interferon by mediating autophagosome-dependent degradation of IRF3
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2018)
-
Krüppel-like factor 4 negatively regulates cellular antiviral immune response
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2016)
-
Innate recognition of microbial-derived signals in immunity and inflammation
Science China Life Sciences (2016)