Abstract
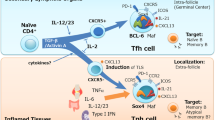
Follicular helper T (TFH) cells represent a distinct subset of CD4+ helper T (TH) cells specialized in providing help to B cells. They are characterized by their unique transcriptional profile (Bcl6), surface marker expression (CXCR5, PD-1, ICOS and CD40L) and cytokine production pattern (IL-21 and IL-6). TFH cells provide help to B cells both to form germinal centers (GCs) and to differentiate into memory B cells and plasma cells for generation of humoral responses. However, there is emerging evidence that implicates TFH cells in the development of various human pathologies, such as autoimmune diseases, immunodeficiency and lymphoma. This review focuses on the current progress in this area including mouse and human studies. A clearer understanding of the mechanisms of TFH cell-mediated immunity and pathology may be exploited for rational development of therapeutic strategies.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Johnston RJ, Poholek AC, DiToro D, Yusuf I, Eto D, Barnett B et al. Bcl6 and Blimp-1 are reciprocal and antagonistic regulators of T follicular helper cell differentiation. Science 2009; 325: 1006–1010.
Nurieva RI, Chung Y, Martinez GJ, Yang XO, Tanaka S, Matskevitch TD et al. Bcl6 mediates the development of T follicular helper cells. Science 2009; 325: 1001–1005.
Yu D, Rao S, Tsai LM, Lee SK, He Y, Sutcliffe EL et al. The transcriptional repressor Bcl-6 directs T follicular helper cell lineage commitment. Immunity 2009; 31: 457–468.
Good-Jacobson KL . PD-1 regulates germinal center B cell survival and the formation and affinity of long-lived plasma cells. Nat Immunol 2010; 11: 535–542.
McHeyzer-Williams LJ, McHeyzer-Williams MG . Antigen-specific memory B cell development. Annu Rev Immunol 2005; 23: 487–513.
Vinuesa CG, Cook MC, Angelucci C, Athanasopoulos V, Rui L, Hill KM . A RING-type ubiquitin ligase family member required to repress follicular helper T cells and autoimmunity. Nature 2005; 435: 452–458.
Gomez-Martin D, Diaz-Zamudio M, Jorge Romo-Tena, Ibarra-Sanchez MJ, Alcocer-Varela J . Follicular helper T cells poise immune responses to the development of autoimmune pathology. Autoimmun Rev 2011; 10: 325–330.
Dong W, Zhu P, Wang Y, Wang Z . Follicular helper T cells in systemic lupus erythematosus: a potential therapeutic target. Autoimmun Rev 2011; 10: 299–304.
Salomonsson S, Jonsson MV, Skarstein K, Brokstad KA, Hjelmstrom P, Wahren-Herlenius M et al. Cellular basis of ectopic germinal center formation and autoantibody production in the target organs of patients with Sjogren's syndrome. Arthritis Rheum 2003; 48: 3187–3201.
Bossaller L, Burger J, Draeger R, Grimbacher B, Knoth R, Plebani A et al. ICOS deficiency is associated with a severe reduction of CXCR5+CD4 germinal center Th cells. J Immunol 2006; 117: 4927–4932.
Rodríguez-Pinilla SM, Atienza L, Murillo C, Pérez-Rodríguez A, Montes-Moreno S, Roncador G et al. Peripheral T-cell lymphoma with follicular T-cell markers. Am J Surg Pathol 2008; 32: 1787–1799.
Crotty S . Follicular helper CD4 T cells (TFH). Annu Rev Immunol 2011; 29: 621–663.
Hardtke S, Ohl L, Forster R . Balanced expression of CXCR5 and CCR7 on follicular T helper cells determines their transient positioning to lymph node follicles and is essential for efficient B-cell help. Blood 2005; 106: 1924–1931.
Haynes NM, Allen CD, Lesley R, Ansel KM, Killeen N, Cyster JG . Role of CXCR5 and CCR7 in follicular Th cell positioning and appearance of a programmed cell death gene-1 high germinal center-associated subpopulation. J Immunol 2007; 179: 5099–5108.
Francisco LM, Sage PT, Sharpe AH . The PD-1 pathway in tolerance and autoimmunity. Immunol Rev 2010; 236: 219–242.
Greenwald RJ, Freeman GJ, Sharpe AH . The B7 family revisited. Annu Rev Immunol 2005; 23: 515–548.
Elgueta R, Benson MJ, de Vries VC, Wasiuk A, Guo Y, Noelle RJ . Molecular mechanism and function of CD40/CD40L engagement in the immune system. Immunol Rev 2009; 229: 152–172.
Chtanova T, Tangye SG, Newton R, Frank N, Hodge MR, Rolph MS et al. T follicular helper cells express a distinctive transcriptional profile, reflecting their role as non-Th1/Th2 effector cells that provide help for B cells. J Immunol 2004; 173: 68–78.
Nurieva RI, Chung Y, Hwang D, Yang XO, Kang HS, Ma L et al. Generation of T follicular helper cells is mediated by interleukin-21 but independent of T helper 1, 2, or 17 cell lineages. Immunity 2008; 29: 138–149.
Suto A, Kashiwakuma D, Kagami S, Hirose K, Watanabe N, Yokote K et al. Development and characterization of IL-21-producing CD4+ T cells. J Exp Med 2008; 205: 1369–1379.
Eto D, Lao C, DiToro D, Barnett B, Escobar TC, Kageyama R et al. IL-21 and IL-6 are critical for different aspects of B cell immunity and redundantly induce optimal follicular helper CD4 T cell (Tfh) differentiation. PLoS ONE 2011; 6: 17739.
Ozaki K, Spolski R, Feng CG, Qi CF, Cheng J, Sher A et al. A critical role for IL-21 in regulating immunoglobulin production. Science 2004; 298: 1630–1634.
Johnston RJ, Poholek AC, DiToro D, Yusuf I, Eto D, Barnett B et al. Bcl6 and Blimp-1 are reciprocal and antagonistic regulators of T follicular helper cell differentiation. Science 2009; 325: 1006–1010.
Chang PP, Barral P, Fitch J, Pratama A, Ma CS, Kallies A et al. Identification of Bcl-6-dependent follicular helper NKT cells that provide cognate help for B cell responses. Nat Immunol 2011; 13: 35–43.
Linterman MA, Pierson W, Lee SK, Kallies A, Kawamoto S, Rayner TF et al. Foxp3+ follicular regulatory T cells control the germinal center response. Nat Med 2011; 17: 975–982.
Wollenberg I, Agua-Doce A, Hernández A, Almeida C, Oliveira VG, Faro J et al. Regulation of the germinal center reaction by Foxp3+ follicular regulatory T cells. J Immunol 2011; 187: 4553–4560.
Chung Y, Tanaka S, Chu F, Nurieva RI, Martinez GJ, Rawal S et al. Follicular regulatory T cells expressing Foxp3 and Bcl-6 suppress germinal center reactions. Nat Med 2011; 17: 983–988.
Vinuesa CG, Tangye SG, Moser B, Mackay CR . Follicular B helper T cells in antibody responses and autoimmunity. Nat Rev Immunol 2005; 5: 853–865.
Luzina IG, Atamas SP, Storrer CE, daSilva LC, Kelsoe G, Papadimitriou JC et al. Spontaneous formation of germinal centers in autoimmune mice. J Leukoc Biol 2001; 70: 578–584.
Vinuesa CG, Sanz I, Cook MC . Dysregulation of germinal centres in autoimmune disease. Nat Rev Immunol 2009; 9: 845–857.
Cappione A 3rd, Anolik JH, Pugh-Bernard A, Barnard J, Dutcher P, Silverman G et al. Germinal center exclusion of autoreactive B cells is defective in human systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest 2005; 115: 3205–3216.
Linterman MA, Rigby RJ, Wong RK, Yu D, Brink R, Cannons JL et al. Follicular helper T cells are required for systemic autoimmunity. J Exp Med 2009; 206: 561–576.
Yu D, Tan AH, Hu X, Athanasopoulos V, Simpson N, Silva DG et al. Roquin represses autoimmunity by limiting inducible T-cell co-stimulator messenger RNA. Nature 2007; 450: 299–303.
Glasmacher E, Hoefig KP, Vogel KU, Rath N, Du L, Wolf C et al. Roquin binds inducible costimulator mRNA and effectors of mRNA decay to induce microRNA-independent post-transcriptional repression. Nat Immunol 2010; 11: 725–733.
Bertossi A, Aichinger M, Sansonetti P, Lech M, Neff F, Pal M et al. Loss of Roquin induces early death and immune deregulation but not autoimmunity. J Exp Med 2011; 208: 1749–1756.
Feng J, Lu L, Hua C, Qin L, Zhao P, Wang J et al. High frequency of CD4+CXCR5+ TFH cells in patients with immune-active chronic hepatitis B. PLoS ONE 2011; 6: e21698.
Fahey LM, Wilson EB, Elsaesser H, Fistonich CD, McGavern DB, Brooks DG . Viral persistence redirects CD4 T cell differentiation toward T follicular helper cells. J Exp Med 2011; 208: 987–999.
Ko HJ, Yang H, Yang JY, Seo SU, Chang SY, Seong JK et al. Expansion of Tfh-like cells during chronic Salmonella exposure mediates the generation of autoimmune hypergammaglobulinemia in MyD88-deficient mice. Eur J Immunol 2012; 42: 618–628.
Nurieva R, Yang XO, Martinez G, Zhang Y, Panopoulos AD, Ma L et al. Essential autocrine regulation by IL-21in the generation of inflammatory T cells. Nature 2007; 448: 480–483.
Vogelzang A, McGuire HM, Yu D, Sprent J, Mackay CR, King C . A fundamental role for interleukin-21 in the generation of T follicular helper cells. Immunity 2008; 29: 127–137.
Ozaki K, Spolski R, Ettinger R, Kim HP, Wang G, Qi CF et al. Regulation of B cell differentiation and plasma cell generation by IL-21, a novel inducer of Blimp-1 and Bcl-6. J Immunol 2004; 173: 5361–5371.
Herber D, Brown TP, Liang S, Young DA, Collins M, Dunussi-Joannopoulos K . IL-21 has a pathogenic role in a lupus-prone mouse model and its blockade with IL-21R.Fc reduces disease progression. J Immunol 2007; 178: 3822–3830.
Rankin AL, Guay H, Herber D, Bertino SA, Duzanski TA, Carrier Y et al. IL-21 receptor is required for the systemic accumulation of activated B and T lymphocytes in MRL/MpJ-Fas(lpr/lpr)/J mice. J Immunol 2012; 188: 1656–1667.
Andrews BS, Eisenberg RA, Theofilopoulos AN, Izui S, Wilson CB, McConahey PJ et al. Spontaneous murine lupus-like syndromes. Clinical and immunopathological manifestations in several strains. J Exp Med 1978; 148: 1198–1215.
Wu HY, Quintana FJ, Weiner HL . Nasal anti-CD3 antibody ameliorates lupus by inducing an IL-10-secreting CD4+CD25−LAP+ regulatory T cell and is associated with down-regulation of IL-17+CD4+ICOS+CXCR5+ follicular helper T cells. J Immunol 2008; 181: 6038–6050.
Batten M, Ramamoorthi N, Kljavin NM, Ma CS, Cox JH, Dengler HS et al. IL-27 supports germinal center formation by enhancing IL-21 production and the function of T follicular helper cells. J Exp Med 2010; 207: 2895–2906.
Lim HW, Hillsamer P, Kim CH . Regulatory T cells can migrate to follicles upon T cell activation and suppress GC-Th cells and GC-Th cell-driven B cell responses. J Clin Invest 2004; 114: 1640–1649.
Mietzner B, Tsuiji M, Scheid J, Velinzon K, Tiller T, Abraham K et al. Autoreactive IgG memory antibodies in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus arise from nonreactive and polyreactive precursors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105: 9727–9732.
Chang A, Henderson SG, Brandt D, Liu N, Guttikonda R, Hsieh C et al. In situ B cell-mediated immune responses and tubuleinterstitial inflammation in human lupus nephritis. J Immunol 2011; 186: 1849–1860.
Grammer AC, Slota R, Fischer R, Gur H, Girschick H, Yarboro C et al. Abnormal germinal center reactions in systemic lupus erythematosus demonstrated by blockade of CD154−CD40 interactions. J Clin Invest 2003; 112: 1506–1520.
Simpson N, Gatenby PA, Wilson A, Malik S, Fulcher DA, Tangye SG et al. Expansion of circulating T cells resembling follicular helper T cells is a fixed phenotype that identifies a subset of severe systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 2010; 62: 234–244.
Morita R, Schmitt N, Bentebibel SE, Ranganathan R, Bourdery L, Zurawski G et al. Human blood CXCR5+CD4+ T cells are counterparts of T follicular cells and contain specific subsets that differentially support antibody secretion. Immunity 2011; 34: 108–121.
Ma J, Zhu C, Ma B, Tian J, Baidoo SE, Mao C et al. Increased frequency of circulating follicular helper T cells in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Dev Immunol 2012; 2012: 827480.
Zhu C, Ma J, Liu Y, Tong J, Tian J, Chen J et al. Increased frequency of follicular helper T cells in patients with autoimmune thyroid disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2012; 97: 943–950.
Li XY, Wu ZB, Ding J, Zheng ZH, Li XY, Chen LN et al. Role of the frequency of blood CD4+CXCR5+CCR6+ T cells in autoimmunity in patients with sjogren's syndrome. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2012; 422: 238–244.
Kitano M, Moriyama S, Ando Y, Hikida M, Mori Y, Kurosaki T et al. Bcl6 protein expression shapes pre-germinal center B cell dynamics and follicular helper T cell heterogeneity. Immunity 2011; 34: 961–972.
Notarangelo LD, Fischer A, Geha RS, Casanova JL, Chapel H, Conley ME et al. Primary immunodeficiencies: 2009 update. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2009; 124: 1161–1178.
Tangye SG, Deenick EK, Palendira U, Ma CS . T cell–B cell interactions in primary immunodeficiencies. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2012; 1250: 1–13.
van Zelm MC, Reisli I, van der Burg M, Castaño D, van Noesel CJ, van Tol MJ et al. An antibody-deficiency syndrome due to mutations in the CD19 gene. N Engl J Med 2006; 354: 1901–1912.
Nichols KE, Ma CS, Cannons JL, Schwartzberg PL, Tangye SG . Molecular and cellular pathogenesis of X-linked lymphoproliferative disease. Immunol Rev 2005; 203: 180–199.
Ma CS, Hare NJ, Nichols KE, Dupré L, Andolfi G, Roncarolo MG et al. Impaired humoral immunity in X-linked lymphoproliferative disease is associated with defective IL-10 production by CD4+ T cells. J Clin Invest 2005; 115: 1049–1059.
Crotty S, Kersh EN, Cannons J, Schwartzberg PL, Ahmed R . SAP is required for generating long-term humoral immunity. Nature 2003; 412: 282–287.
Korthäuer U, Graf D, Mages HW, Brière F, Padayachee M, Malcolm S et al. Defective expression of T-cell CD40 ligand causes X-lined immunodeficiency with hyper IgM. Nature 1993; 361: 539–541.
Dorfman DM, Brown JA, Shahsafaei A, Freeman GJ . Programmed death-1 (PD-1) is a marker of germinal center-associated T cells and angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma. Am J Surg Pathol 2006; 30: 802–810.
Dupuis J, Boye K, Martin N, Copie-Bergman C, Plonquet A, Fabiani B et al. Expression of CXCL13 by neoplastic cells in angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma (AITL): a new diagnostic marker providing evidence that AITL derives from follicular helper T cells. Am J Surg Pathol 2006; 30: 490–494.
Grogg KL, Attygalle AD, Macon WR, Remstein ED, Kurtin PJ, Dogan A . Angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma: a neoplasm of germinal-center T-helper cells? Blood 2005; 106: 1501–1502.
Grogg KL, Jung S, Erickson LA, McClure RF, Dogan A . Primary cutaneous CD4-positive small/medium-sized pleomorphic T-cell lymphoma: a clonal T-cell lymphoproliferative disorder with indolent behavior. Mod Pathol 2008; 21: 708–715.
Yu H, Shahsafaei A, Dorfman DM . Germinal-center T-helper-cell markers PD-1 and CXCL13 are both expressed by neoplastic cells in angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma. Am J Clin Pathol 2009; 131: 33–41.
de Leval L, Rickman DS, Thielen C, Reynies A, Huang YL, Delsol G et al. The gene expression profile of nodal peripheral T-cell lymphoma demonstrates a molecular link between angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma (AITL) and follicular helper T (TFH) cells. Blood 2007; 109: 4952–4963.
Rodríguez Pinilla SM, Roncador G, Rodríguez-Peralto JL, Mollejo M, García JF, Montes-Moreno S et al. Primary cutaneous CD4+ small/medium-sized pleomorphic T-cell lymphoma expresses follicular T-cell markers. Am J Surg Pathol 2009; 33: 81–90.
Amé-Thomas P, le Priol J, Yssel H, Caron G, Pangault C, Jean R et al. Characterization of intratumoral follicular helper T cells in follicular lymphoma: role in the survival of malignant B cells. Leukemia 2012; 26: 1053–1063.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from Canadian Institutes of Health Research and Manitoba Health Research Council (to XY). SS was a recipient of Dr Allan R. Ronald Studentship and Manitoba Health Research Council PhD Studentship. XY is Canada Research Chair in Infection and Immunity. The authors would like to thank Ms Ying Peng for her assistance in figure drawing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shekhar, S., Yang, X. The darker side of follicular helper T cells: from autoimmunity to immunodeficiency. Cell Mol Immunol 9, 380–385 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2012.26
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2012.26
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
A follicular regulatory Innate Lymphoid Cell population impairs interactions between germinal center Tfh and B cells
Communications Biology (2021)
-
A Critical Role for IL-21 Receptor Signaling in the Coxsackievirus B3-Induced Myocarditis
Inflammation (2017)
-
IL-21 acts as a promising therapeutic target in systemic lupus erythematosus by regulating plasma cell differentiation
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2015)
-
High-throughput detection of miRNAs and gene-specific mRNA at the single-cell level by flow cytometry
Nature Communications (2014)
-
Follicular helper T cells in immune homeostasis
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2012)