Abstract
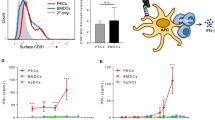
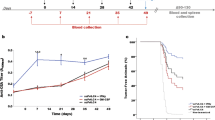
Heat shock proteins (HSPs) have been shown to interact with antigen-presenting cells (APCs), especially dendritic cells (DCs). HSPs act as potent adjuvants, inducing a Th1 response, as well as antigen-specific CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) via cross-presentation. Our previous work has demonstrated that Hsp70-like protein 1 (Hsp70L1), a new member of the Hsp70 subfamily, can act as a powerful Th1 adjuvant in a DC-based vaccine. Here we report the efficient induction of tumor antigen-specific T cell immune response by DCs pulsed with recombinant fusion protein of Hsp70L1 and Her2341–456, the latter of which is a fragment of Her2/neu (Her2) containing E75 (a HLA-A2 restricted CTL epitope). The fusion protein Hsp70L1–Her2341–456 promotes the maturation of DCs and activates them to produce cytokines, such as IL-12 and TNF-α, and chemokines, such as MIP-1α, MIP-1β and RANTES. Taken together, these results indicate that the adjuvant activity of Hsp70L1 is maintained in the fusion protein. Her2-specific HLA-A2.1-restricted CD8+ CTLs can be generated efficiently either from the Peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBL) of healthy donors or from the splenocytes of immunized HLA-A2.1/Kb transgenic mice by in vitro stimulation or immunization with DCs pulsed with the Hsp70L1–Her2341–456 fusion protein. This results in more potent target cell killing in an antigen-specific and HLA-A2.1-restricted manner. Adoptive transfer of splenocytes from transgenic mice immunized with Hsp70L1–Her2341–456-pulsed DCs can markedly inhibit tumor growth and prolong the survival of nude mice with Her2+/HLA-A2.1+ human carcinomas. These results suggest that Hsp70L1–Her2341–456-pulsed DCs could be a new therapeutic vaccine for patients with Her2+ cancer.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Srivastava PK . Therapeutic cancer vaccines. Curr Opin Immunol 2006; 18: 201–205.
Bolhassani A, Rafati S . Heat-shock proteins as powerful weapons in vaccine development. Expert Rev Vaccines 2008; 7: 1185–1199.
Srivastava PK . Interaction of heat shock proteins with peptides and antigen presenting cells: chaperoning of the innate and adaptive immune responses. Annu Rev Immunol 2002; 20: 395–425.
Enomoto Y, Bharti A, Khaleque AA, Song B, Liu C, Apostolopoulos V et al. Enhanced immunogenicity of heat shock protein 70 peptide complexes from dendritic cell–tumor fusion cells. J Immunol 2006; 177: 5946–5955.
Tamura Y, Peng P, Liu K, Daou M, Srivastava PK . Immunotherapy of tumors with autologous tumor derived heat shock protein preparations. Science 1997; 278: 117–120.
Pilla L, Patuzzo R, Rivoltini L, Maio M, Pennacchioli E, Lamaj E et al. A phase II trial of vaccination with autologous, tumor-derived heat-shock protein peptide complexes gp96, in combination with GM-CSF and interferon-α in metastatic melanoma patients. Cancer Immunol Immunother 2006; 55: 958–968.
Wan T, Zhou X, Chen G, An H, Chen T, Zhang W et al. Novel heat shock protein Hsp70L1 activates dendritic cells and acts as a Th1 polarizing adjuvant. Blood 2004; 103: 1747–1754.
Wu Y, Wan T, Zhou X, Wang B, Yang F, Li N et al. Hsp70-like protein 1 fusion protein enhances induction of carcinoembryonic antigen-specific CD8+ CTL response by dendritic cell vaccine. Cancer Res 2005; 65: 4947–4954.
Slamon DJ, Godolphin W, Jones LA, Holt JA, Wong SG, Keith DE et al. Studies of the HER-2/neu proto-oncogene in human breast and ovarian cancer. Science 1989; 244: 707–712.
Pritchard KI, Shepherd LE, O'Malley FP, Andrulis IL, Tu D, Bramwell VH et al. HER2 and responsiveness of breast cancer to adjuvant chemotherapy. N Engl J Med 2006; 354: 2103–2111.
Dhesy-Thind B, Pritchard KI, Messersmith H, O'Malley FP, Elavathil L, Trudeau M . HER2/neu in systemic therapy for women with breast cancer: a systematic review. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2008; 109: 209–229.
Baxevanis CN, Sotiriadou NN, Gritzapis AD, Sotiropoulou PA, Perez SA, Cacoullos NT et al. Immunogenic HER-2/neu peptides as tumor vaccines. Cancer Immunol Immunother 2006; 55: 85–95.
Kiessling R, Wei WZ, Herrmann F, Lindencrona JA, Choudhury A, Kono K et al. Cellular immunity to the HER-2/neu protooncogene. Adv Cancer Res 2002; 85: 101–144.
Voutsas IF, Gritzapis AD, Mahaira LG, Salagianni M, von Hofe E, Kallinteris NL et al. Peptide vaccine given with a Toll-like receptor agonist is effective for the treatment and prevention of spontaneous breast tumors. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 1326–1334.
Kawashima I, Tsai V, Southwood S, Takesako K, Sette A, Celis E . Identification of HLA-A3-restricted cytotoxic T lymphocyte epitopes from carcinoembryonic antigen and HER-2/neu by primary in vitro immunization with peptide-pulsed dendritic cells. Cancer Res 1999; 59: 431–435.
Gritzapis AD, Voutsas IF, Lekka E, Tsavaris N, Missitzis I, Sotiropoulou P et al. Identification of a novel immunogenic HLA-A*0201-binding epitope of HER-2/neu with potent antitumor properties. J Immunol 2008; 181: 146–154.
Ambrosino E, Spadaro M, Iezzi M, Curcio C, Forni G, Musiani P et al. Immunosurveillance of Erbb2 carcinogenesis in transgenic mice is concealed by a dominant regulatory T-cell self-tolerance. Cancer Res 2006; 66: 7734–7740.
Gritzapis AD, Mahaira LG, Perez SA, Cacoullos NT, Papamichail M, Baxevanis CN . Vaccination with human HER-2/neu435–443 CTL peptide induces effective antitumor immunity against HER-2/neu-expressing tumor cells in vivo. Cancer Res 2006; 66: 5452–5460.
Baxevanis CN . Induction of potent CD4+ T cell-mediated antitumor responses by a helper HER-2/neu peptide linked to the Ii-Key moiety of the invariant chain. Int J Cancer 2007; 121: 2031–2041.
Brossart P, Wirths S, Stuhler G, Reichardt VL, Kanz K, Brugger W . Induction of cytotoxic T-lymphocyte responses in vivo after vaccinations with peptide-pulsed dendritic cells. Blood 2000; 96: 3102–3108.
Disis ML, Gooley TA, Rinn K, Davis D, Piepkorn M, Cheever MA et al. Generation of T-cell immunity to the HER-2/neu protein after active immunization with HER-2/neu peptide-based vaccines. J Clin Oncol 2002; 20: 2624–2632.
Disis ML, Grabstein KH, Sleath PR, Cheever MA . Generation of immunity to the HER-2/neu oncogenic protein in patients with breast and ovarian cancer using a peptide-based vaccine. Clin Cancer Res 1999; 5: 1289–1297.
Knutson KL, SchiVman K, Cheever MA, Disis ML . Immunization of cancer patients with a HER-2/neu, HLA-A2 peptide, p369–377, results in short-lived peptide-specific immunity. Clin Cancer Res 2002; 8: 1014–1018.
Kono K, Takahashi A, Sugai H, Fujii H, Choudhury AR, Kiessling R et al. Dendritic cells pulsed with HER-2/neu derived peptides can induce specific T-cell responses in patients with gastric cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2002; 8: 3394–3400.
Murray JL, Gillogly ME, Przepiorka D, Brewer H, Ibrahim NK, Booser DJ et al. Toxicity, immunogenicity, and induction of E75-specific tumor-lytic CTLs by HER-2 peptide E75 (369–377) combined with granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in HLA-A2+ patients with metastatic breast and ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2002; 8: 3407–3418.
Zaks TZ, Rosenberg SA . Immunization with a peptide epitope (p369–377) from HER-2/neu leads to peptide-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes that fail to recognize HER-2/neu+ tumors. Cancer Res 1998; 58: 4902–4908.
Liu S, Yu Y, Zhang M, Wang W, Cao X . The involvement of TNF-α-related apoptosis-inducing ligand in the enhanced cytotoxicity of IFN-β-stimulated human dendritic cells to tumor cells. J Immunol 2001; 166: 5407–5415.
Wang B, Chen H, Jiang X, Zhang M, Wan T, Li N et al. Identification of an HLA-A*0201-restricted CD8+ T-cell epitope SSp-1 of SARS-CoV spike protein. Blood 2004; 104: 200–206.
Cao X, Zhang W, He L, Xie Z, Ma S, Tao Q et al. Lymphotactin genemodified bone marrow dendritic cells act as more potent adjuvants for peptide delivery to induce specific antitumor immunity. J Immunol 1998; 161: 6238–6244.
Tacken PJ, de Vries IJ, Torensma R, Figdor CG . Dendritic-cell immunotherapy: from ex vivo loading to in vivo targeting. Nat Rev Immunol 2007; 7: 790–802.
Banchereau J, Palucka AK . Dendritic cells as therapeutic vaccines against cancer. Nat Rev Immunol 2005; 5: 296–306.
Tagliabue E, Balsari A, Campiglio M, Pupa SM . HER2 as a target for breast cancer therapy. Expert Opin Biol Ther 2010; 10: 711–724.
Nahta R, Esteva FJ . Herceptin: mechanisms of action and resistance. Cancer Lett 2006; 232: 123–138.
Berns K, Horlings HM, Hennessy BT, Madiredjo M, Hijmans EM, Beelen K et al. A functional genetic approach identifies the PI3K pathway as a major determinant of trastuzumab resistance in breast cancer. Cancer Cell 2007; 12: 395–402.
Cobleigh MA, Vogel CL, Tripathy D, Robert NJ, Scholl S, Fehrenbacher L et al. Multinational study of the efficacy and safety of humanized anti-HER2 monoclonal antibody in women who have HER2-overexpressing metastatic breast cancer that has progressed after chemotherapy for metastatic disease. J Clin Oncol 1999; 17: 2639–2648.
Bengala C, Zamagni C, Pedrazzoli P, Matteucci P, Ballestrero A, da Prada G et al. Cardiac toxicity of trastuzumab in metastatic breast cancer patients previously treated with high-dose chemotherapy: a retrospective study. Br J Cancer 2006; 94: 1016–1020.
Banchereau J, Steinman RM . Dendritic cells and the control of immunity. Nature 1998; 392: 245–252.
Chen Y, Sun H, Liu GY, Wang B, Wang F, Sun BC et al. EBV LMP2A-specific T cell immune responses elicited by dendritic cells loaded with LMP2A protein. Cell Mol Immunol 2009; 6: 269–276.
Kantoff PW, Higano CS, Shore ND, Berger ER, Small EJ, Penson DF et al. Sipuleucel-T immunotherapy for castration-resistant prostate cancer. N Engl J Med 2010; 363: 411–422.
Ladjemi MZ, Jacot W, Chardès T, Pèlegrin A, Navarro-Teulon I . Anti-HER2 vaccines: new prospects for breast cancer therapy. Cancer Immunol Immunother 2010; 59: 1295–1312.
Kono K, Takahashi A, Sugai H, Fujii H, Choudhury AR, Kiessling R et al. Dendritic cells pulsed with HER-2/neu-derived peptides can induce specific T-cell responses in patients with gastric cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2002; 8: 3394–3400.
Czerniecki BJ, Koski GK, Koldovsky U, Xu S, Cohen PA, Mick R et al. Targeting HER-2/neu in early breast cancer development using dendritic cells with staged interleukin-12 burst secretion. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 1842–1852.
Liu G, Yao K, Wang B, Chen Y, Zhou F, Guo Y et al. Immunotherapy of Epstein-Barr virus associated malignancies using mycobacterial HSP70 and LMP2A356–364 epitope fusion protein. Cell Mol Immunol 2009; 6: 423–431.
Wood C, Srivastava P, Bukowski R, Lacombe L, Gorelov AI, Gorelov S et al. An adjuvant autologous therapeutic vaccine (HSPPC-96; vitespen) versus observation alone for patients at high risk of recurrence after nephrectomy for renal cell carcinoma: a multicentre, open-label, randomised phase III trial. Lancet 2008; 372: 145–154.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Major Program of the Shanghai Committee of Science and Technology Development (QF, 06DZ19010), the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (YFW, 2009AA02Z102), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (YFW, 30872296) and the National Science and Technology Major Project of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (TWan, 2008ZX09101-043).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, Q., Wu, Y., Yan, F. et al. Efficient induction of a Her2-specific anti-tumor response by dendritic cells pulsed with a Hsp70L1–Her2341–456 fusion protein. Cell Mol Immunol 8, 424–432 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2011.21
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2011.21
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Intracellular HSP70L1 inhibits human dendritic cell maturation by promoting suppressive H3K27me3 and H2AK119Ub1 histone modifications
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2020)
-
HSP70L1-mediated intracellular priming of dendritic cell vaccination induces more potent CTL response against cancer
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2018)
-
TLR4 is essential for dendritic cell activation and anti-tumor T-cell response enhancement by DAMPs released from chemically stressed cancer cells
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2014)
-
Immunization with a HSP65–HER2 fusion peptide selectively eliminates HER2+ B16 melanoma cells in a xenograft tumor mouse model
Tumor Biology (2013)