Abstract
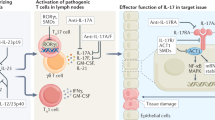
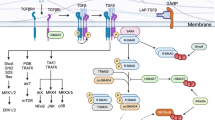
Interleukin (IL)-17, the signature cytokine secreted by T helper (Th) 17 cells, plays important roles in host defense against extracellular bacterial infection and fungal infection and contributes to the pathogenesis of various autoimmune inflammatory diseases. Here we review the recent advances in IL-17-mediated functions with emphasis on the studies of IL-17-mediated signal transduction, providing perspective on potential drug targets for the treatment of autoimmune inflammatory diseases.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mosmann TR, Coffman RL . TH1 and TH2 cells: different patterns of lymphokine secretion lead to different functional properties. Annu Rev Immunol 1989; 7: 145–173.
Glimcher LH, Murphy KM . Lineage commitment in the immune system: the T helper lymphocyte grows up. Genes Dev 2000; 14: 1693–1711.
Krakowski M, Owens T . Interferon-gamma confers resistance to experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Eur J Immunol 1996; 26: 1641–1646.
Gran B, Zhang GX, Yu S, Li J, Chen XH, Ventura ES et al. IL-12p35-deficient mice are susceptible to experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis: evidence for redundancy in the IL-12 system in the induction of central nervous system autoimmune demyelination. J Immunol 2002; 169: 7104–7110.
Korn T, Bettelli E, Oukka M, Kuchroo VK . IL-17 and Th17 cells. Annu Rev Immunol 2009; 27: 485–517.
Stromnes IM, Cerretti LM, Liggitt D, Harris RA, Goverman JM . Differential regulation of central nervous system autoimmunity by T(H)1 and T(H)17 cells. Nat Med 2008; 14: 337–342.
Jager A, Dardalhon V, Sobel RA, Bettelli E, Kuchroo VK . Th1, Th17, and Th9 effector cells induce experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis with different pathological phenotypes. J Immunol 2009; 183: 7169–7177.
O'Connor RA, Prendergast CT, Sabatos CA, Lau CW, Leech MD, Wraith DC et al. Cutting edge: Th1 cells facilitate the entry of Th17 cells to the central nervous system during experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Immunol 2008; 181: 3750–3754.
Axtell RC, Jong BA, Boniface K, Voort LF, Bhat R, Sarno P et al. T helper type 1 and 17 cells determine efficacy of interferon-beta in multiple sclerosis and experimental encephalomyelitis. Nat Med 2010; 16: 406–412.
O'Shea JJ, Steward-Tharp SM, Laurence A, Watford WT, Wei L, Adamson AS et al. Signal transduction and Th17 cell differentiation. Microbes Infect 2009; 11: 599–611.
Dong C . TH17 cells in development: an updated view of their molecular identity and genetic programming. Nat Rev Immunol 2008; 8: 337–348.
Miossec P, Korn T, Kuchroo VK . Interleukin-17 and type 17 helper T cells. N Engl J Med 2009; 361: 888–898.
Ouyang W, Kolls JK, Zheng Y . The biological functions of T helper 17 cell effector cytokines in inflammation. Immunity 2008; 28: 454–467.
Weaver CT, Hatton RD, Mangan PR, Harrington LE . IL-17 family cytokines and the expanding diversity of effector T cell lineages. Annu Rev Immunol 2007; 25: 821–852.
Weaver CT, Hatton RD . Interplay between the TH17 and TReg cell lineages: a (co-)evolutionary perspective. Nat Rev Immunol 2009; 9: 883–889.
Gaffen SL . Structure and signalling in the IL-17 receptor family. Nat Rev Immunol 2009; 9: 556–567.
Hymowitz SG, Filvaroff EH, Yin JP, Lee J, Cai L, Risser P et al. IL-17s adopt a cystine knot fold: structure and activity of a novel cytokine, IL-17F, and implications for receptor binding. EMBO J 2001; 20: 5332–5341.
Chang SH, Dong C . IL-17F: regulation, signaling and function in inflammation. Cytokine 2009; 46: 7–11.
Wright JF, Bennett F, Li B, Brooks J, Luxenberg DP, Whitters MJ et al. The human IL-17F/IL-17A heterodimeric cytokine signals through the IL-17RA/IL-17RC receptor complex. J Immunol 2008; 181: 2799–2805.
Kolls JK, Linden A . Interleukin-17 family members and inflammation. Immunity 2004; 21: 467–476.
Moseley TA, Haudenschild DR, Rose L, Reddi AH . Interleukin-17 family and IL-17 receptors. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 2003; 14: 155–174.
Wang YH, Liu YJ . The IL-17 cytokine family and their role in allergic inflammation. Curr Opin Immunol 2008; 20: 697–702.
Ely LK, Fischer S, Garcia KC . Structural basis of receptor sharing by interleukin 17 cytokines. Nat Immunol 2009; 10: 1245–1251.
Ye P, Rodriguez FH, Kanaly S, Stocking KL, Schurr J, Schwarzenberger P et al. Requirement of interleukin 17 receptor signaling for lung CXC chemokine and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor expression, neutrophil recruitment, and host defense. J Exp Med 2001; 194: 519–527.
Happel KI, Dubin PJ, Zheng M, Ghilardi N, Lockhart C, Quinton LJ et al. Divergent roles of IL-23 and IL-12 in host defense against Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Exp Med 2005; 202: 761–769.
Conti HR, Shen F, Nayyar N, Stocum E, Sun JN, Lindemann MJ et al. Th17 cells and IL-17 receptor signaling are essential for mucosal host defense against oral candidiasis. J Exp Med 2009; 206: 299–311.
Huang W, Na L, Fidel PL, Schwarzenberger P . Requirement of interleukin-17A for systemic anti-Candida albicans host defense in mice. J Infect Dis 2004; 190: 624–631.
Kelly MN, Kolls JK, Happel K, Schwartzman JD, Schwarzenberger P, Combe C et al. Interleukin-17/interleukin-17 receptor-mediated signaling is important for generation of an optimal polymorphonuclear response against Toxoplasma gondii infection. Infect Immun 2005; 73: 617–621.
Lin Y, Ritchea S, Logar A, Slight S, Messmer M, Rangel-Moreno J et al. Interleukin-17 is required for T helper 1 cell immunity and host resistance to the intracellular pathogen Francisella tularensis. Immunity 2009; 31: 799–810.
Crowe CR, Chen K, Pociask DA, Alcorn JF, Krivich C, Enelow RI et al. Critical role of IL-17RA in immunopathology of influenza infection. J Immunol 2009; 183: 5301–5310.
Wiehler S, Proud D . Interleukin-17A modulates human airway epithelial responses to human rhinovirus infection. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2007; 293: L505–L515.
Grigorian A, Torossian S, Demetriou M . T-cell growth, cell surface organization, and the galectin–glycoprotein lattice. Immunol Rev 2009; 230: 232–246.
Green DR, Ferguson T, Zitvogel L, Kroemer G . Immunogenic and tolerogenic cell death. Nat Rev Immunol 2009; 9: 353–363.
Koenders MI, Kolls JK, Oppers-Walgreen B, van den Bersselaar L, Joosten LA, Schurr JR et al. Interleukin-17 receptor deficiency results in impaired synovial expression of interleukin-1 and matrix metalloproteinases 3, 9, and 13 and prevents cartilage destruction during chronic reactivated streptococcal cell wall-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2005; 52: 3239–3247.
Yu JJ, Ruddy MJ, Wong GC, Sfintescu C, Baker PJ, Smith JB et al. An essential role for IL-17 in preventing pathogen-initiated bone destruction: recruitment of neutrophils to inflamed bone requires IL-17 receptor-dependent signals. Blood 2007; 109: 3794–3802.
Gonzalez-Garcia I, Zhao Y, Ju S, Gu Q, Liu L, Kolls JK et al. IL-17 signaling-independent central nervous system autoimmunity is negatively regulated by TGF-beta. J Immunol 2009; 182: 2665–2671.
Komiyama Y, Nakae S, Matsuki T, Nambu A, Ishigame H, Kakuta S et al. IL-17 plays an important role in the development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Immunol 2006; 177: 566–573.
Burchill MA, Nardelli DT, England DM, DeCoster DJ, Christopherson JA, Callister SM et al. Inhibition of interleukin-17 prevents the development of arthritis in vaccinated mice challenged with Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun 2003; 71: 3437–3442.
Park H, Li Z, Yang XO, Chang SH, Nurieva R, Wang YH et al. A distinct lineage of CD4 T cells regulates tissue inflammation by producing interleukin 17. Nat Immunol 2005; 6: 1133–1141.
Wang L, Yi T, Kortylewski M, Pardoll DM, Zeng D, Yu H . IL-17 can promote tumor growth through an IL-6–Stat3 signaling pathway. J Exp Med 2009; 206: 1457–1464.
Kryczek I, Wei S, Szeliga W, Vatan L, Zou W . Endogenous IL-17 contributes to reduced tumor growth and metastasis. Blood 2009; 114: 357–359.
Schwandner R, Yamaguchi K, Cao Z . Requirement of tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor (TRAF)6 in interleukin 17 signal transduction. J Exp Med 2000; 191: 1233–1240.
Novatchkova M, Leibbrandt A, Werzowa J, Neubuser A, Eisenhaber F . The STIR-domain superfamily in signal transduction, development and immunity. Trends Biochem Sci 2003; 28: 226–229.
Chang SH, Park H, Dong C . Act1 adaptor protein is an immediate and essential signaling component of interleukin-17 receptor. J Biol Chem 2006; 281: 35603–35607.
Qian Y, Qin J, Cui G, Naramura M, Snow EC, Ware CF et al. Act1, a negative regulator in CD40- and BAFF-mediated B cell survival. Immunity 2004; 21: 575–587.
Qian Y, Giltiay N, Xiao J, Wang Y, Tian J, Han S et al. Deficiency of Act1, a critical modulator of B cell function, leads to development of Sjögren's syndrome. Eur J Immunol 2008; 38: 2219–2228.
Qian Y, Liu C, Hartupee J, Altuntas CZ, Gulen MF, Jane-Wit D et al. The adaptor Act1 is required for interleukin 17-dependent signaling associated with autoimmune and inflammatory disease. Nat Immunol 2007; 8: 247–256.
Levin SD . IL-17 receptor signaling: ubiquitin gets in on the act. Sci Signal 2009; 2: pe64.
Liu C, Qian W, Qian Y, Giltiay NV, Lu Y, Swaidani S, et al. Act1, a U-box E3 ubiquitin ligase for IL-17 signaling. Sci Signal 2009; 2: ra63.
Huang F, Kao CY, Wachi S, Thai P, Ryu J, Wu R . Requirement for both JAK-mediated PI3K signaling and ACT1/TRAF6/TAK1-dependent NF-kappaB activation by IL-17A in enhancing cytokine expression in human airway epithelial cells. J Immunol 2007; 179: 6504–6513.
Saleh A, Shan L, Halayko AJ, Kung S, Gounni AS . Critical role for STAT3 in IL-17A-mediated CCL11 expression in human airway smooth muscle cells. J Immunol 2009; 182: 3357–3365.
Hartupee J, Liu C, Novotny M, Sun D, Li X, Hamilton TA . IL-17 signaling for mRNA stabilization does not require TNF receptor-associated factor 6. J Immunol 2009; 182: 1660–1666.
Lindemann MJ, Hu Z, Benczik M, Liu KD, Gaffen SL . Differential regulation of the IL-17 receptor by gammac cytokines: inhibitory signaling by the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway. J Biol Chem 2008; 283: 14100–14108.
Shen F, Li N, Gade P, Kalvakolanu DV, Weibley T, Doble B et al. IL-17 receptor signaling inhibits C/EBPbeta by sequential phosphorylation of the regulatory 2 domain. Sci Signal 2009; 2: ra8.
Hurst SD, Muchamuel T, Gorman DM, Gilbert JM, Clifford T, Kwan S et al. New IL-17 family members promote Th1 or Th2 responses in the lung: in vivo function of the novel cytokine IL-25. J Immunol 2002; 169: 443–453.
Wang YH, Angkasekwinai P, Lu N, Voo KS, Arima K, Hanabuchi S et al. IL-25 augments type 2 immune responses by enhancing the expansion and functions of TSLP-DC-activated Th2 memory cells. J Exp Med 2007; 204: 1837–1847.
Angkasekwinai P, Park H, Wang YH, Chang SH, Corry DB, Liu YJ et al. Interleukin 25 promotes the initiation of proallergic type 2 responses. J Exp Med 2007; 204: 1509–1517.
Fallon PG, Ballantyne SJ, Mangan NE, Barlow JL, Dasvarma A, Hewett DR et al. Identification of an interleukin (IL)-25-dependent cell population that provides IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 at the onset of helminth expulsion. J Exp Med 2006; 203: 1105–1116.
Owyang AM, Zaph C, Wilson EH, Guild KJ, McClanahan T, Miller HR et al. Interleukin 25 regulates type 2 cytokine-dependent immunity and limits chronic inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract. J Exp Med 2006; 203: 843–849.
Maezawa Y, Nakajima H, Suzuki K, Tamachi T, Ikeda K, Inoue J et al. Involvement of TNF receptor-associated factor 6 in IL-25 receptor signaling. J Immunol 2006; 176: 1013–1018.
Rickel EA, Siegel LA, Yoon BR, Rottman JB, Kugler DG, Swart DA et al. Identification of functional roles for both IL-17RB and IL-17RA in mediating IL-25-induced activities. J Immunol 2008; 181: 4299–4310.
Swaidani S, Bulek K, Kang Z, Liu C, Lu Y, Yin W et al. The critical role of epithelial-derived Act1 in IL-17- and IL-25-mediated pulmonary inflammation. J Immunol 2009; 182: 1631–1640.
Claudio E, Sonder SU, Saret S, Carvalho G, Ramalingam TR, Wynn TA et al. The adaptor protein CIKS/Act1 is essential for IL-25-mediated allergic airway inflammation. J Immunol 2009; 182: 1617–1630.
Rong Z, Wang A, Li Z, Ren Y, Cheng L, Li Y et al. IL-17RD (Sef or IL-17RLM) interacts with IL-17 receptor and mediates IL-17 signaling. Cell Res 2009; 19: 208–215.
Li TS, Li XN, Chang ZJ, Fu XY, Liu L . Identification and functional characterization of a novel interleukin 17 receptor: a possible mitogenic activation through ras/mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway. Cell Signal 2006; 18: 1287–1298.
Kang Z, Altuntas CZ, Gulen MF, Liu C, Giltiay N, Qin H et al. Astrocyte-restricted ablation of interleukin-17-induced Act1-mediated signaling ameliorates autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Immunity 2010; 32: 414–425.
Zhang Z, Zheng M, Bindas J, Schwarzenberger P, Kolls JK . Critical role of IL-17 receptor signaling in acute TNBS-induced colitis. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2006; 12: 382–388.
Ito R, Kita M, Shin-Ya M, Kishida T, Urano A, Takada R et al. Involvement of IL-17A in the pathogenesis of DSS-induced colitis in mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2008; 377: 12–16.
O'Connor W Jr, Kamanaka M, Booth CJ, Town T, Nakae S, Iwakura Y et al. A protective function for interleukin 17A in T cell-mediated intestinal inflammation. Nat Immunol 2009; 10: 603–609.
Awasthi A, Kuchroo VK . IL-17A directly inhibits TH1 cells and thereby suppresses development of intestinal inflammation. Nat Immunol 2009; 10: 568–570.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the American Asthma Foundation and the Multiple Sclerosis Society to Xiaoxia Li, and by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 30930084, 30871298 and 30928025), 973 Program (No. 2010CB529705), Chinese Academy of Sciences (Nos. KSCX2-YW-R-146 and KSCX1-YW-22) and Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (No. 08PJ14110).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qian, Y., Kang, Z., Liu, C. et al. IL-17 signaling in host defense and inflammatory diseases. Cell Mol Immunol 7, 328–333 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2010.27
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2010.27
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Transcriptional changes in the peripheral blood leukocytes from Brangus cattle before and after tick challenge with Rhipicephalus australis
BMC Genomics (2022)
-
Levels of Peripheral Th17 Cells and Th17-Related Cytokines in Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis: A Meta-analysis
Advances in Therapy (2022)
-
A critical role for Th17 cell-derived TGF-β1 in regulating the stability and pathogenicity of autoimmune Th17 cells
Experimental & Molecular Medicine (2021)
-
Repurposing of Secukinumab as Neuroprotective in Cuprizone-Induced Multiple Sclerosis Experimental Model via Inhibition of Oxidative, Inflammatory, and Neurodegenerative Signaling
Molecular Neurobiology (2020)
-
Preparation of a novel monoclonal antibody against caprine interleukin-17A and its applications in immunofluorescence and immunohistochemistry assays
BMC Biotechnology (2019)