Abstract
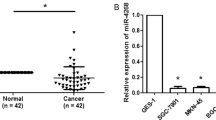
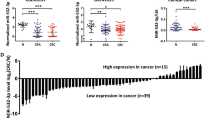
Colorectal carcinoma (CRC) is known as the most common cancer. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) have been proven to have important roles in human carcinogenesis by regulating various target genes. Recently, the downregulation of miR-582-5p had been demonstrated in CRC. However, its function and the underlying mechanism in CRC remains unknown. In this study, we found that miR-582-5p was frequently downregulated in CRC tissues compared with corresponding noncancerous tissues, as well as in CRC cell lines. Transfection with miR-582-5p mimics significantly inhibited CRC cell proliferation, invasion and arrested cell cycle at the G1/S phase, but promoted cell apoptosis. Further analysis demonstrated that miR-582-5p attenuated the expression of RAS-related GTP-binding protein (Rab27a). Luciferase reporter assay confirmed that Rab27a was a target of miR-582-5p. Mechanism analyses revealed that Rab27a overexpression significantly attenuated the inhibitory effect of miR-582-5p on CRC cell growth, invasion and cell cycle progression. Our data suggest that miR-582-5p may function as a tumor suppressor in the development of CRC by targeting Rab27a, indicating a novel therapeutic strategy for patients with CRC.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang Y, He X, Liu Y, Ye Y, Zhang H, He P et al. MicroRNA-320a inhibits tumor invasion by targeting neuropilin I and is associated with liver metastasis in colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep 2012; 27: 685.
Pericleous M, Mandair D, Caplin ME . Diet and supplements and their impact on colorectal cancer. J Gastrointest Oncol 2013; 4: 409.
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D . Global cancer statistics. Cancer J Clin 2011; 61: 69–90.
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Murray T et al. Cancer statistics, 2008. Cancer J Clin 2008; 58: 71–96.
Baraniskin A, Birkenkamp-Demtroder K, Maghnouj A, Zöllner H, Munding J, Klein-Scory S et al. MiR-30a-5p suppresses tumor growth in colon carcinoma by targeting DTL. Carcinogenesis 2012; 33: 732–739.
Braconi C, Kogure T, Valeri N, Huang N, Nuovo G, Costinean S et al. MicroRNA-29 can regulate expression of the long non-coding RNA gene MEG3 in hepatocellular cancer. Oncogene 2011; 30: 4750–4756.
Chang Y, Yan W, He X, Zhang L, Li C, Huang H et al. miR-375 inhibits autophagy and reduces viability of hepatocellular carcinoma cells under hypoxic conditions. Gastroenterology 2012; 143: 177–187 e178.
Bartel DP . MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004; 116: 281–297.
Bartel DP . MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009; 136: 215–233.
Brennecke J, Hipfner DR, Stark A, Russell RB, Cohen SM . Bantam encodes a developmentally regulated microRNA that controls cell proliferation and regulates the proapoptotic gene hid in Drosophila. Cell 2003; 113: 25–36.
Xu P, Vernooy SY, Guo M, Hay BA . The Drosophila microRNA Mir-14 suppresses cell death and is required for normal fat metabolism. Curr Biol 2003; 13: 790–795.
Ambros V . The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 2004; 431: 350–355.
Chen C-Z, Li L, Lodish HF, Bartel DP . MicroRNAs modulate hematopoietic lineage differentiation. Science 2004; 303: 83–86.
Ma Y, Zhang P, Wang F, Zhang H, Yang Y, Shi C et al. Elevated oncofoetal miR-17-5p expression regulates colorectal cancer progression by repressing its target gene P130. Nat Commun 2012; 3: 1291.
Wu J, Wu G, Lv L, Ren Y-F, Zhang X-J, Xue Y-F et al. MicroRNA-34a inhibits migration and invasion of colon cancer cells via targeting to Fra-1. Carcinogenesis 2011; 33: 519–528.
Yang I-P, Tsai H-L, Hou M-F, Chen K-C, Tsai P-C, Huang S-W et al. MicroRNA-93 inhibits tumor growth and early relapse of human colorectal cancer by affecting genes involved in the cell cycle. Carcinogenesis 2012; 33: 1522–1530.
Chen D-L, Wang D-S, Wu W-J, Zeng Z-L, Luo H-Y, Qiu M-Z et al. Overexpression of paxillin induced by miR-137 suppression promotes tumor progression and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Carcinogenesis 2013; 34: 803–811.
Pagliuca A, Valvo C, Fabrizi E, di Martino S, Biffoni M, Runci D et al. Analysis of the combined action of miR-143 and miR-145 on oncogenic pathways in colorectal cancer cells reveals a coordinate program of gene repression. Oncogene 2012; 32: 4806–4813.
Uchino K, Takeshita F, Takahashi RU, Kosaka N, Fujiwara K, Naruoka H et al. Therapeutic effects of microRNA-582-5p and -3p on the inhibition of bladder cancer progression. Mol Ther 2013; 21: 610–619.
Yang L, Belaguli N, Berger DH . MicroRNA and colorectal cancer. World J Surg 2009; 33: 638–646.
Di Leva G, Garofalo M, Croce CM . MicroRNAs in cancer. Annu Rev Pathol 2014; 9: 287.
Huang Z, Huang S, Wang Q, Liang L, Ni S, Wang L et al. MicroRNA-95 promotes cell proliferation and targets sorting Nexin 1 in human colorectal carcinoma. Cancer Res 2011; 71: 2582–2589.
Wang Q, Huang Z, Guo W, Ni S, Xiao X, Wang L et al. MicroRNA-202-3p inhibits cell proliferation by targeting ADP-ribosylation factor-like 5A in human colorectal carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 2014; 20: 1146–1157.
Zhang Y, Huang W, Ran Y, Xiong Y, Zhong Z, Fan X et al. miR-582-5p inhibits proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting CDK1 and AKT3. Tumour Biol 2015. (doi:10.1007/s13277-015-3582-0; e-pub ahead of print).
Floyd DH, Zhang Y, Dey BK, Kefas B, Breit H, Marks K et al. Novel anti-apoptotic microRNAs 582-5p and 363 promote human glioblastoma stem cell survival via direct inhibition of caspase 3, caspase 9, and Bim. PLoS One 2014; 9: e96239.
Maeno A, Terada N, Uegaki M, Goto T, Okada Y, Kobayashi T et al. Up-regulation of miR-582-5p regulates cellular proliferation of prostate cancer cells under androgen-deprived conditions. Prostate 2014; 74: 1604–1612.
Liu Y, Jiang J, Wang X, Zhai F, Cheng X . miR-582-5p is upregulated in patients with active tuberculosis and inhibits apoptosis of monocytes by targeting FOXO1. PLoS One 2013; 8: e78381.
Recchi C, Seabra MC . Rab GTPases and their interacting proteins in health and disease: novel functions for Rab GTPases in multiple aspects of tumour progression. Biochem Soc Trans 2012; 40 (Part 6): 1398.
Wang J-S, Wang F-B, Zhang Q-G, Shen Z-Z, Shao Z-M . Enhanced expression of Rab27A gene by breast cancer cells promoting invasiveness and the metastasis potential by secretion of insulin-like growth factor-II. Mol Cancer Res 2008; 6: 372–382.
Akavia UD, Litvin O, Kim J, Sanchez-Garcia F, Kotliar D, Causton HC et al. An integrated approach to uncover drivers of cancer. Cell 2010; 143: 1005–1017.
Ostrowski M, Carmo NB, Krumeich S, Fanget I, Raposo G, Savina A et al. Rab27a and Rab27b control different steps of the exosome secretion pathway. Nat Cell Biol 2009; 12: 19–30.
Silva J, Garcia V, Rodriguez M, Compte M, Cisneros E, Veguillas P et al. Analysis of exosome release and its prognostic value in human colorectal cancer. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2012; 51: 409–418.
Ki DH, Jeung HC, Park CH, Kang SH, Lee GY, Lee WS et al. Whole genome analysis for liver metastasis gene signatures in colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer 2007; 121: 2005–2012.
Wu X, Hu A, Zhang M, Chen Z . Effects of Rab27a on proliferation, invasion, and anti-apoptosis in human glioma cell. Tumor Biol 2013; 34: 2195–2203.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Zhang, Y., Yang, J. et al. Upregulation of miR-582-5p inhibits cell proliferation, cell cycle progression and invasion by targeting Rab27a in human colorectal carcinoma. Cancer Gene Ther 22, 475–480 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/cgt.2015.44
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cgt.2015.44
This article is cited by
-
miR-582 negatively regulates pre-B cell proliferation and survival through targeting Hif1α and Rictor
Cell Death & Disease (2022)
-
miR-582-5p inhibits migration and chemo-resistant capabilities of colorectal cancer cells by targeting TNKS2
Genes & Genomics (2022)
-
Exogenous delivery of microRNA-134 (miR-134) using α-tocopherol-based PEGylated liposome for effective treatment in skin squamous cell carcinoma
Drug Delivery and Translational Research (2021)
-
MiR-924 as a tumor suppressor inhibits non-small cell lung cancer by inhibiting RHBDD1/Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
Cancer Cell International (2020)
-
Cell Cycle Regulation by Berberine in Human Melanoma A375 Cells
Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine (2020)