Abstract
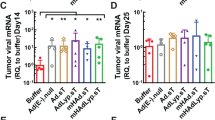
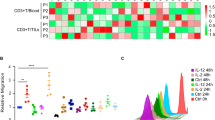
Interleukin (IL)-24, a promising therapeutic gene, has been widely used for Cancer Targeting Gene-Viro-Therapy (CTGVT). In this study, IL-24 was inserted into an oncolytic adenovirus in which the E1A gene is driven by an enhanced, short α-fetoprotein (AFP) promoter and the E1B gene is completely deleted to form Ad.enAFP-E1A-ΔE1B-IL-24. This construct has a potent antitumor effect on liver cancer cell lines in vitro, but little or no effect on normal cell lines, such as L-02 and QSG-7701. In vivo, the complete elimination of Huh-7 liver cancer in nude mice with Ad.enAFP-E1A-ΔE1B-IL-24 intratumor injection was observed. The design of Ad.enAFP-E1A-ΔE1B-IL-24 and its potent antitumor effect on liver cancer have not been published previously. The mechanism of the potent antitumor effect of Ad.enAFP-E1A-ΔE1B-IL-24 is due to the upregulation of GADD34 and intrinsic and extrinsic apoptotic signaling.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bosch FX, Ribes J, Diaz M, Cleries R . Primary liver cancer: worldwide incidence and trends. Gastroenterology 2004; 127: S5–S16.
Carr BI . Hepatocellular carcinoma: current management and future trends. Gastroenterology 2004; 127: S218–S224.
Liu XY . A new anticancer strategy: gene-virotherapy therapy of cancer. Chin J Cancer Biother 2001; 8: 1.
Zhang ZL, Zou WG, Luo CX, Li BH, Wang JH, Sun LY et al. An armed oncolytic adenovirus system, ZD55-gene, demonstrating potent antitumoral efficacy. Cell Res 2003; 13: 481–489.
Davydova J, Le LP, Gavrikova T, Wang M, Krasnykh V, Yamamoto M . Infectivity-enhanced cyclooxygenase-2-based conditionally replicative adenoviruses for esophageal adenocarcinoma treatment. Cancer Res 2004; 64: 4319–4327.
Nicklin SA, Von Seggern DJ, Work LM, Pek DC, Dominiczak AF, Nemerow GR et al. Ablating adenovirus type 5 fiber-CAR binding and HI loop insertion of the SIGYPLP peptide generate an endothelial cell-selective adenovirus. Mol Ther 2001; 4: 534–542.
Okada Y, Okada N, Nakagawa S, Mizuguchi H, Takahashi K, Mizuno N et al. Tumor necrosis factor alpha-gene therapy for an established murine melanoma using RGD (Arg-Gly-Asp) fiber-mutant adenovirus vectors. Jpn J Cancer Res 2002; 93: 436–444.
O’Shea CC, Johnson L, Bagus B, Choi S, Nicholas C, Shen A et al. Late viral RNA export, rather than p53 inactivation, determines ONYX-015 tumor selectivity. Cancer Cell 2004; 6: 611–623.
Sauthoff H, Heitner S, Rom WN, Hay JG . Deletion of the adenoviral E1b-19kD gene enhances tumor cell killing of a replicating adenoviral vector. Hum Gene Ther 2000; 11: 379–388.
Rodriguez R, Schuur ER, Lim HY, Henderson GA, Simons JW, Henderson DR . Prostate attenuated replication competent adenovirus (ARCA) CN706: a selective cytotoxic for prostate-specific antigen-positive prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res 1997; 57: 2559–2563.
Adachi Y, Reynolds PN, Yamamoto M, Wang M, Takayama K, Matsubara S et al. A midkine promoter-based conditionally replicative adenovirus for treatment of pediatric solid tumors and bone marrow tumor purging. Cancer Res 2001; 61: 7882–7888.
Nettelbeck DM, Rivera AA, Balague C, Alemany R, Curiel DT . Novel oncolytic adenoviruses targeted to melanoma: specific viral replication and cytolysis by expression of E1A mutants from the tyrosinase enhancer/promoter. Cancer Res 2002; 62: 4663–4670.
Xie X, Xia W, Li Z, Kuo HP, Liu Y, Ding Q et al. Targeted expression of BikDD eradicates pancreatic tumors in noninvasive imaging models. Cancer Cell 2007; 12: 52–65.
Cao X, Yang M, Wei RC, Zeng Y, Gu JF, Huang WD et al. Cancer targeting Gene-Viro-Therapy of liver carcinoma by dual-regulated oncolytic adenovirus armed with TRAIL gene. Gene Therapy 2011; 18: 765–777.
Hallenbeck PL, Chang YN, Hay C, Golightly D, Stewart D, Lin J et al. A novel tumor-specific replication-restricted adenoviral vector for gene therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hum Gene Ther 1999; 10: 1721–1733.
Tangkijvanich P, Anukulkarnkusol N, Suwangool P, Lertmaharit S, Hanvivatvong O, Kullavanijaya P et al. Clinical characteristics and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: analysis based on serum alpha-fetoprotein levels. J Clin Gastroenterol 2000; 31: 302–308.
Li Y, Yu DC, Chen Y, Amin P, Zhang H, Nguyen N et al. A hepatocellular carcinoma-specific adenovirus variant, CV890, eliminates distant human liver tumors in combination with doxorubicin. Cancer Res 2001; 61: 6428–6436.
Arbuthnot P, Bralet MP, Thomassin H, Danan JL, Brechot C, Ferry N . Hepatoma cell-specific expression of a retrovirally transferred gene is achieved by alpha-fetoprotein but not insulinlike growth factor II regulatory sequences. Hepatology 1995; 22: 1788–1796.
Arbuthnot PB, Bralet MP, Le Jossic C, Dedieu JF, Perricaudet M, Brechot C et al. In vitro and in vivo hepatoma cell-specific expression of a gene transferred with an adenoviral vector. Hum Gene Ther 1996; 7: 1503–1514.
Zhao L, Gu J, Dong A, Zhang Y, Zhong L, He L et al. Potent antitumor activity of oncolytic adenovirus expressing mda-7/IL-24 for colorectal cancer. Hum Gene Ther 2005; 16: 845–858.
Zhang KJ, Wang YG, Cao X, Zhong SY, Wei RC, Wu YM et al. Potent antitumor effect of interleukin-24 gene in the survivin promoter and retinoblastoma double-regulated oncolytic adenovirus. Hum Gene Ther 2009; 20: 818–830.
Fan JK, Wei N, Ding M, Gu JF, Liu XR, Li BH et al. Targeting Gene-ViroTherapy for prostate cancer by DD3-driven oncolytic virus-harboring interleukin-24 gene. Int J Cancer 2010; 127: 707–717.
Zhao L, Dong A, Gu J, Liu Z, Zhang Y, Zhang W et al. The antitumor activity of TRAIL and IL-24 with replicating oncolytic adenovirus in colorectal cancer. Cancer Gene Ther 2006; 13: 1011–1022.
Wu YM, Zhang KJ, Yue XT, Wang YQ, Yang Y, Li GC et al. Enhancement of tumor cell death by combining cisplatin with an oncolytic adenovirus carrying MDA-7/IL-24. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2009; 30: 467–477.
Zhong S, Yu D, Wang Y, Qiu S, Wu S, Liu XY . An armed oncolytic adenovirus ZD55-IL-24 combined with ADM or DDP demonstrated enhanced antitumor effect in lung cancer. Acta Oncol 2010; 49: 91–99.
Xiao L, Li X, Niu N, Qian J, Xie G, Wang Y . Dichloroacetate (DCA) enhances tumor cell death in combination with oncolytic adenovirus armed with MDA-7/IL-24. Mol Cell Biochem 2010; 340: 31–40.
Liu XR, Cai Y, Cao X, Wei RC, Li HL, Zhou XM et al. A new oncolytic adenoviral vector carrying dual tumor suppressor genes shows potent antitumor effect. J Cell Mol Med 2011; 16: 1298–1309.
Wei RC, Cao X, Gui JH, Zhou XM, Yan QL, Huang WD et al. Augmenting the antitumor effect of TRAIL by SOCS3 with double-regulated replicating oncolytic adenovirus in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hum Gene Ther 2011; 22: 1109–1119.
Liu X, Cao X, Wei R, Cai Y, Li H, Gui J et al. Gene-viro-therapy targeting liver cancer by a dual-regulated oncolytic adenoviral vector harboring IL-24 and TRAIL. Cancer Gene Ther 2011; 19: 49–57.
Li B, Liu X, Fan J, Qi R, Bo L, Gu J et al. A survivin-mediated oncolytic adenovirus induces non-apoptotic cell death in lung cancer cells and shows antitumoral potential in vivo. J Gene Med 2006; 8: 1232–1242.
Narayanan V, Gaudiani JL, Harris RH, Mehler PS . Liver function test abnormalities in anorexia nervosa—cause or effect. Int J Eat Disord 2010; 43: 378–381.
Kaufman HL, Bines SD . OPTIM trial: a phase III trial of an oncolytic herpes virus encoding GM-CSF for unresectable stage III or IV melanoma. Fut Oncol 2010; 6: 941–949.
Schmidt C . Amgen spikes interest in live virus vaccines for hard-to-treat cancers. Nat Biotechnol 2011; 29: 295–296.
Breitbach CJ, Burke J, Jonker D, Stephenson J, Haas AR, Chow LQ et al. Intravenous delivery of a multi-mechanistic cancer-targeted oncolytic poxvirus in humans. Nature 2011; 477: 99–102.
Lei N, Shen FB, Chang JH, Wang L, Li H, Yang C et al. An oncolytic adenovirus expressing granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor shows improved specificity and efficacy for treating human solid tumors. Cancer Gene Ther 2009; 16: 33–43.
Cunningham CC, Chada S, Merritt JA, Tong A, Senzer N, Zhang Y et al. Clinical and local biological effects of an intratumoral injection of mda-7 (IL24; INGN 241) in patients with advanced carcinoma: a phase I study. Mol Ther 2005; 11: 149–159.
Eager R, Harle L, Nemunaitis J . Ad-MDA-7; INGN 241: a review of preclinical and clinical experience. Expert Opin Biol Ther 2008; 8: 1633–1643.
White E, Cipriani R . Role of adenovirus E1B proteins in transformation: altered organization of intermediate filaments in transformed cells that express the 19-kilodalton protein. Mol Cell Biol 1990; 10: 120–130.
White E, Sabbatini P, Debbas M, Wold WS, Kusher DI, Gooding LR . The 19-kilodalton adenovirus E1B transforming protein inhibits programmed cell death and prevents cytolysis by tumor necrosis factor alpha. Mol Cell Biol 1992; 12: 2570–2580.
Subramanian T, Boyd JM, Chinnadurai G . Functional substitution identifies a cell survival promoting domain common to adenovirus E1B 19 kDa and Bcl-2 proteins. Oncogene 1995; 11: 2403–2409.
Telling GC, Perera S, Szatkowski-Ozers M, Williams J . Absence of an essential regulatory influence of the adenovirus E1B 19-kilodalton protein on viral growth and early gene expression in human diploid WI38, HeLa, and A549 cells. J Virol 1994; 68: 541–547.
Schmitz M, Graf C, Gut T, Sirena D, Peter I, Dummer R et al. Melanoma cultures show different susceptibility towards E1A-, E1B-19 kDa- and fiber-modified replication-competent adenoviruses. Gene Therapy 2006; 13: 893–905.
Pan QW, Zhong SY, Liu BS, Liu J, Cai R, Wang YG et al. Enhanced sensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma cells to chemotherapy with a Smac-armed oncolytic adenovirus. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2007; 28: 1996–2004.
Kim J, Cho JY, Kim JH, Jung KC, Yun CO . Evaluation of E1B gene-attenuated replicating adenoviruses for cancer gene therapy. Cancer Gene Ther 2002; 9: 725–736.
Yoon AR, Kim JH, Lee YS, Kim H, Yoo JY, Sohn JH et al. Markedly enhanced cytolysis by E1B-19kD-deleted oncolytic adenovirus in combination with cisplatin. Hum Gene Ther 2006; 17: 379–390.
Doloff JC, Waxman DJ, Jounaidi Y . Human telomerase reverse transcriptase promoter-driven oncolytic adenovirus with E1B-19 kDa and E1B-55 kDa gene deletions. Hum Gene Ther 2008; 19: 1383–1400.
Jiang H, Lin JJ, Su ZZ, Goldstein NI, Fisher PB . Subtraction hybridization identifies a novel melanoma differentiation associated gene, mda-7, modulated during human melanoma differentiation, growth and progression. Oncogene 1995; 11: 2477–2486.
Sarkar D, Su ZZ, Lebedeva IV, Sauane M, Gopalkrishnan RV, Valerie K et al. Mda-7 (IL-24) mediates selective apoptosis in human melanoma cells by inducing the coordinated overexpression of the GADD family of genes by means of p38 MAPK. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 10054–10059.
Saeki T, Mhashilkar A, Swanson X, Zou-Yang XH, Sieger K, Kawabe S et al. Inhibition of human lung cancer growth following adenovirus-mediated mda-7 gene expression in vivo. Oncogene 2002; 21: 4558–4566.
Pataer A, Vorburger SA, Barber GN, Chada S, Mhashilkar AM, Zou-Yang H et al. Adenoviral transfer of the melanoma differentiation-associated gene 7 (mda7) induces apoptosis of lung cancer cells via up-regulation of the double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase (PKR). Cancer Res 2002; 62: 2239–2243.
Caudell EG, Mumm JB, Poindexter N, Ekmekcioglu S, Mhashilkar AM, Yang XH et al. The protein product of the tumor suppressor gene, melanoma differentiation-associated gene 7, exhibits immunostimulatory activity and is designated IL-24. J Immunol 2002; 168: 6041–6046.
Sarkar D, Su ZZ, Vozhilla N, Park ES, Gupta P, Fisher PB . Dual cancer-specific targeting strategy cures primary and distant breast carcinomas in nude mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 14034–14039.
Ramesh R, Ito I, Gopalan B, Saito Y, Mhashilkar AM, Chada S . Ectopic production of MDA-7/IL-24 inhibits invasion and migration of human lung cancer cells. Mol Ther 2004; 9: 510–518.
Nakabayashi H, Hashimoto T, Miyao Y, Tjong KK, Chan J, Tamaoki T . A position-dependent silencer plays a major role in repressing alpha-fetoprotein expression in human hepatoma. Mol Cell Biol 1991; 11: 5885–5893.
Acknowledgements
We thank YanLing Ren and LanYing Sun for kind help in cell culture, and we also thank Prof YouChen Xu for good comments for writing. This work was supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (No. 30623003), the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program) (No. 2010CB529901), Important National Science and Technology Specific Project of Hepatitis and Hepatoma Related Program (2008ZX10002-023), the National Basic Research Committee of Science and Technology (Nos. 06ZR14072 and 074119508); and the ZheJiang Sci-Tech University Grant No.1016819-Y.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Cancer Gene Therapy website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, KJ., Zhang, J., Wu, YM. et al. Complete eradication of hepatomas using an oncolytic adenovirus containing AFP promoter controlling E1A and an E1B deletion to drive IL-24 expression. Cancer Gene Ther 19, 619–629 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/cgt.2012.40
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cgt.2012.40
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Natural Killer Cells Recruitment in Oncolytic Virotherapy: A Mathematical Model
Bulletin of Mathematical Biology (2021)
-
RGD-modified oncolytic adenovirus-harboring shPKM2 exhibits a potent cytotoxic effect in pancreatic cancer via autophagy inhibition and apoptosis promotion
Cell Death & Disease (2017)
-
A combinatory use of adenoviruses expressing melanoma differentiation-associated gene-7 and replication-competent adenoviruses produces synergistic effects on pancreatic carcinoma cells
Tumor Biology (2015)
-
Combination of hepatocyte specific delivery and transformation dependent expression of shRNA inducing transcriptional gene silencing of c-Myc promoter in hepatocellular carcinoma cells
BMC Cancer (2014)