Abstract
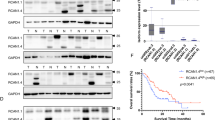
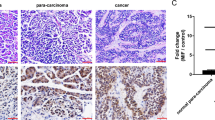
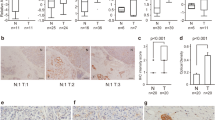
Cytokine-induced antiapoptotic molecule (CIAPIN1), a newly identified apoptosis inhibitor, has been found to participate in the process of proliferation and tumorigenicity for several cancers. The aim of this study was to evaluate the prognostic value of CIAPIN1 in pancreatic cancer and to probe its function in pancreatic carcinogenesis. We found that CIAPIN1 protein was absent or reduced in pancreatic cancer cell lines. There was also a loss or decrease in CIAPIN1 expression in 118 cases of pancreatic cancer tissues as compared with that in 82 cases of normal pancreatic tissues. In a Cox proportional hazards model, CIAPIN1 expression independently predicted better survival (P<0.0001). Adenoviral-mediated restoration of CIAPIN1 expression greatly repressed the proliferation of pancreatic cancer cell in vitro and suppressed the tumorigenicity of pancreatic cancer cell in Balb/c nude mice. Our data also revealed that inhibition of pancreatic cancer cells proliferation by enforcing CIAPIN1 expression at least partly through delaying cell cycle progression and inducing cell apoptosis. In summary, our work revealed a novel function of CIAPIN1, which might possibly be used as an independent prognostic factor and a potential therapeutic target for pancreatic cancer.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Thun MJ . Cancer statistics, 20CA. Cancer J Clin 2009; 59: 225–249.
Li D, Xie K, Wolff R, Abbruzzese JL . Pancreatic cancer. Lancet 2004; 363: 1049–1057.
Scotti ML, Bamlet WR, Smyrk TC, Fields AP, Murray NR . Protein kinase Ciota is required for pancreatic cancer cell transformed growth and tumorigenesis. Cancer Res 2010; 70: 2064–2074.
Shibayama H, Takai E, Matsumura I, Kouno M, Morii E, Kitamura Y et al. Identification of a cytokine-induced antiapoptotic molecule anamorsin essential for definitive hematopoiesis. J Exp Med 2004; 199: 581–592.
Li X, Hong L, Zhao Y, Jin H, Fan R, Du R et al. A new apoptosis inhibitor, CIAPIN1 (cytokine-induced apoptosis inhibitor 1), mediates multidrug resistance in leukemia cells by regulating MDR-1, Bcl-2, and Bax. Biochem Cell Biol 2007; 85: 741–750.
Hao Z, Li X, Qiao T, Du R, Hong L, Fan D . CIAPIN1 confers multidrug resistance by upregulating the expression of MDR-1 and MRP-1 in gastric cancer cells. Cancer Biol Ther 2006; 5: 261–266.
Li X, Hao Z, Fan R, Zou X, Jin H, Pan Y et al. CIAPIN1 inhibits gastric cancer cell proliferation and cell cycle progression by downregulating cyclinD1 and upregulating P. Cancer Biol Ther 2007; 6: 1539–1545.
Hao Z, Li X, Qiao T, Li S, Lv Y, Fan D . Downregulated expression of CIAPIN1 may contribute to gastric carcinogenesis by accelerating cell proliferation and promoting cell cycle progression. Cancer Biol Ther 2009; 8: 1064–1070.
Yan K, He LJ, Cheng W, Ji ZZ, Zhao BX, Hui XL et al. Inhibiting gastric cancer-associated angiogenesis by CIAPIN1 siRNA. Cancer Biol Ther 2009; 8: 1058–1063.
Li X, Pan Y, Fan R, Jin H, Han S, Liu J et al. Adenovirus-delivered CIAPIN1 small interfering RNA inhibits HCC growth in vitro and in vivo. Carcinogenesis 2008; 29: 1587–1593.
Shizusawa T, Shibayama H, Murata S, Saitoh Y, Sugimoto Y, Matsumura I et al. The expression of anamorsin in diffuse large B cell lymphoma: possible prognostic biomarker for low IPI patients. Leuk Lymphoma 2008; 49: 113–121.
Wang Y, Qi HW, Li XH, Chen XX, Liu J . CIAPIN1 expression in human lung cancer tissues and inhibitory effects of the gene on human pulmonary carcinoma NCI-H446 cells]. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi 2008; 24: 434–437.
Zheng X, Zhao Y, Wang X, Li Y, Wang R, Jiang Y et al. Decreased expression of CIAPIN1 is correlated with poor prognosis in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Dig Dis Sci 2010; 55: 3408–3414.
He L, Wang H, Jin H, Guo C, Xie H, Yan K et al. CIAPIN1 inhibits the growth and proliferation of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Lett 2009; 276: 88–94.
Shi H, Zhou Y, Liu H, Chen C, Li S, Li N et al. Expression of CIAPIN1 in human colorectal cancer and its correlation with prognosis. Bmc Cancer 2010; 10: 477.
Sobin LH, Greene FL . TNM classification: clarification of number of regional lymph nodes for pNo. Cancer 2001; 92: 452.
Huang J, Che MI, Huang YT, Shyu MK, Huang YM, Wu YM et al. Overexpression of MUC15 activates extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 and promotes the oncogenic potential of human colon cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 2009; 30: 1452–1458.
Chen X, Mo P, Li X, Zheng P, Zhao L, Xue Z et al. CacyBP/SIP protein promotes proliferation and G1/S transition of human pancreatic cancer cells. Mol Carcinog 2011; 50: 804–810.
He TC, Zhou S, Da CL, Yu J, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B . A simplified system for generating recombinant adenoviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998; 95: 2509–2514.
Raghu H, Lakka SS, Gondi CS, Mohanam S, Dinh DH, Gujrati M et al. Suppression of uPA and uPAR attenuates angiogenin mediated angiogenesis in endothelial and glioblastoma cell lines. PLoS One 2010; 5: e12458.
Morgans CW, Kensel-Hammes P, Hurley JB, Burton K, Idzerda R, McKnight GS et al. Loss of the synaptic vesicle protein SV2B results in reduced neurotransmission and altered synaptic vesicle protein expression in the retina. PLoS One 2009; 4: e5230.
Yang X, Yang S, McKimmey C, Liu B, Edgerton SM, Bales W et al. Genistein induces enhanced growth promotion in ER-positive/erbB-2-overexpressing breast cancers by ER-erbB-2 cross talk and p27/kip1 downregulation. Carcinogenesis 2010; 31: 695–702.
Perez M, Regan T, Pflug B, Lynch J, Djakiew D . Loss of low-affinity nerve growth factor receptor during malignant transformation of the human prostate. Prostate 1997; 30: 274–279.
Geldof AA, Van Haarst EP, Newling DW . Neurotrophic factors in prostate and prostatic cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 1998; 1: 236–241.
Miller FD, Kaplan DR . Neurotrophin signalling pathways regulating neuronal apoptosis. Cell Mol Life Sci 2001; 58: 1045–1053.
Khwaja F, Tabassum A, Allen J, Djakiew D . The p75(NTR) tumor suppressor induces cell cycle arrest facilitating caspase mediated apoptosis in prostate tumor cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2006; 341: 1184–1192.
Sherr CJ, Roberts JM . CDK inhibitors: positive and negative regulators of G1-phase progression. Genes Dev 1999; 13: 1501–1512.
Kinsey M, Smith R, Lessnick SL . NR0B1 is required for the oncogenic phenotype mediated by EWS/FLI in Ewing's sarcoma. Mol Cancer Res 2006; 4: 851–859.
Majeti R, Becker MW, Tian Q, Lee TL, Yan X, Liu R et al. Dysregulated gene expression networks in human acute myelogenous leukemia stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009; 106: 3396–3401.
Vincent-Salomon A, Lucchesi C, Gruel N, Raynal V, Pierron G, Goudefroye R et al. Integrated genomic and transcriptomic analysis of ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast. Clin Cancer Res 2008; 14: 1956–1965.
Garman KS, Acharya CR, Edelman E, Grade M, Gaedcke J, Sud S et al. A genomic approach to colon cancer risk stratification yields biologic insights into therapeutic opportunities. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105: 19432–19437.
Jazdzewski K, Liyanarachchi S, Swierniak M, Pachucki J, Ringel MD, Jarzab B et al. Polymorphic mature microRNAs from passenger strand of pre-miR-146a contribute to thyroid cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009; 106: 1502–1505.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Zengfu Xue and Technician Zheng Chen for excellent experimental assistant and constructive advice. This work was funded by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30471989).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, X., Li, X., Chen, J. et al. Overexpression of CIAPIN1 inhibited pancreatic cancer cell proliferation and was associated with good prognosis in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Gene Ther 19, 538–544 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/cgt.2012.28
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cgt.2012.28
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
MiRNA-195-5p Functions as a Tumor Suppressor and a Predictive of Poor Prognosis in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer by Directly Targeting CIAPIN1
Pathology & Oncology Research (2019)