Abstract
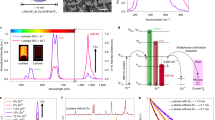
Non-invasive gene monitoring is important for most gene therapy applications to ensure selective gene transfer to specific cells or tissues. We developed a non-invasive imaging system to assess the location and persistence of gene expression by anchoring an anti-dansyl (DNS) single-chain antibody (DNS receptor) on the cell surface to trap DNS-derivatized imaging probes. DNS hapten was covalently attached to cross-linked iron oxide (CLIO) to form a 39±0.5 nm DNS-CLIO nanoparticle imaging probe. DNS-CLIO specifically bound to DNS receptors but not to a control single-chain antibody receptor. DNS-CLIO (100 μM Fe) was non-toxic to both B16/DNS (DNS receptor positive) and B16/phOx (control receptor positive) cells. Magnetic resonance (MR) imaging could detect as few as 10% B16/DNS cells in a mixture in vitro. Importantly, DNS-CLIO specifically bound to a B16/DNS tumor, which markedly reduced signal intensity. Similar results were also shown with DNS quantum dots, which specifically targeted CT26/DNS cells but not control CT26/phOx cells both in vitro and in vivo. These results demonstrate that DNS nanoparticles can systemically monitor the expression of DNS receptor in vivo by feasible imaging systems. This targeting strategy may provide a valuable tool to estimate the efficacy and specificity of different gene delivery systems and optimize gene therapy protocols in the clinic.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Serganova I, Blasberg R . Reporter gene imaging: potential impact on therapy. Nucl Med Biol 2005; 32: 763–780.
Juweid ME, Cheson BD . Positron-emission tomography and assessment of cancer therapy. N Engl J Med 2006; 354: 496–507.
Bell JD, Taylor-Robinson SD . Assessing gene expression in vivo: magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy. Gene Ther 2000; 7: 1259–1264.
Louie A . Design and characterization of magnetic resonance imaging gene reporters. Methods Mol Med 2006; 124: 401–417.
Golzio M, Rols MP, Gabriel B, Teissie J . Optical imaging of in vivo gene expression: a critical assessment of the methodology and associated technologies. Gene Ther 2004; 11 (Suppl 1): S85–S91.
Shah K, Weissleder R . Molecular optical imaging: applications leading to the development of present day therapeutics. NeuroRx 2005; 2: 215–225.
Madsen MT, Park CH . Enhancement of SPECT images by Fourier filtering the projection image set. J Nucl Med 1985; 26: 395–402.
Weissleder R, Ntziachristos V . Shedding light onto live molecular targets. Nat Med 2003; 9: 123–128.
Delikatny EJ, Poptani H . MR techniques for in vivo molecular and cellular imaging. Radiol Clin North Am 2005; 43: 205–220.
Yeung HW, Macapinlac H, Karpeh M, Finn RD, Larson SM . Accuracy of FDG-PET in gastric cancer. Preliminary experience. Clin Positron Imaging 1998; 1: 213–221.
Roffler SR, Wang HE, Yu HM, Chang WD, Cheng CM, Lu YL et al. A membrane antibody receptor for noninvasive imaging of gene expression. Gene Ther 2006; 13: 412–420.
Hogemann D, Josephson L, Weissleder R, Basilion JP . Improvement of MRI probes to allow efficient detection of gene expression. Bioconjug Chem 2000; 11: 941–946.
Hogemann-Savellano D, Bos E, Blondet C, Sato F, Abe T, Josephson L et al. The transferrin receptor: a potential molecular imaging marker for human cancer. Neoplasia 2003; 5: 495–506.
Moore A, Sun PZ, Cory D, Hogemann D, Weissleder R, Lipes MA . MRI of insulitis in autoimmune diabetes. Magn Reson Med 2002; 47: 751–758.
Anderson SA, Shukaliak-Quandt J, Jordan EK, Arbab AS, Martin R, McFarland H et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of labeled T-cells in a mouse model of multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 2004; 55: 654–659.
Gao X, Cui Y, Levenson RM, Chung LW, Nie S . In vivo cancer targeting and imaging with semiconductor quantum dots. Nat Biotechnol 2004; 22: 969–976.
Portney NG, Ozkan M . Nano-oncology: drug delivery, imaging, and sensing. Anal Bioanal Chem 2006; 384: 620–630.
Rotomskis R, Streckyte G, Karabanovas V . [Nanoparticles in diagnostics and therapy: towards nanomedicine]. Medicina (Kaunas) 2006; 42: 542–558.
Pinaud F, Michalet X, Bentolila LA, Tsay JM, Doose S, Li JJ et al. Advances in fluorescence imaging with quantum dot bio-probes. Biomaterials 2006; 27: 1679–1687.
Cheng TL, Liao KW, Tzou SC, Cheng CM, Chen BM, Roffler SR . Hapten-directed targeting to single-chain antibody receptors. Cancer Gene Ther 2004; 11: 380–388.
Chuang KH, Cheng CM, Roffler SR, Lu YL, Lin SR, Wang JY et al. Combination cancer therapy by hapten-targeted prodrug-activating enzymes and cytokines. Bioconjug Chem 2006; 17: 707–714.
Molday RS, MacKenzie D . Immunospecific ferromagnetic iron-dextran reagents for the labeling and magnetic separation of cells. J Immunol Methods 1982; 52: 353–367.
Will O, Purkayastha S, Chan C, Athanasiou T, Darzi AW, Gedroyc W et al. Diagnostic precision of nanoparticle-enhanced MRI for lymph-node metastases: a meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol 2006; 7: 52–60.
Boerman OC, Kranenborg MH, Oosterwijk E, Griffiths GL, McBride WJ, Oyen WJ et al. Pretargeting of renal cell carcinoma: improved tumor targeting with a bivalent chelate. Cancer Res 1999; 59: 4400–4405.
Kranenborg MH, Boerman OC, Oosterwijk-Wakka JC, de Weijert MC, Corstens FH, Oosterwijk E . Development and characterization of anti-renal cell carcinoma x antichelate bispecific monoclonal antibodies for two-phase targeting of renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res 1995; 55: 5864s–5867s.
Goel A, Baranowska-Kortylewicz J, Hinrichs SH, Wisecarver J, Pavlinkova G, Augustine S et al. 99mTc-labeled divalent and tetravalent CC49 single-chain Fv's: novel imaging agents for rapid in vivo localization of human colon carcinoma. J Nucl Med 2001; 42: 1519–1527.
Thorek DL, Chen AK, Czupryna J, Tsourkas A . Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle probes for molecular imaging. Ann Biomed Eng 2006; 34: 23–38.
Santra S, Dutta D, Walter GA, Moudgil BM . Fluorescent nanoparticle probes for cancer imaging. Technol Cancer Res Treat 2005; 4: 593–602.
Sun EY, Josephson L, Kelly KA, Weissleder R . Development of nanoparticle libraries for biosensing. Bioconjug Chem 2006; 17: 109–113.
Hussain SM, Hess KL, Gearhart JM, Geiss KT, Schlager JJ . In vitro toxicity of nanoparticles in BRL 3A rat liver cells. Toxicol In Vitro 2005; 19: 975–983.
Kircher MF, Allport JR, Graves EE, Love V, Josephson L, Lichtman AH et al. In vivo high resolution three-dimensional imaging of antigen-specific cytotoxic T-lymphocyte trafficking to tumors. Cancer Res 2003; 63: 6838–6846.
Harisinghani MG, Saini S, Weissleder R, Hahn PF, Yantiss RK, Tempany C et al. MR lymphangiography using ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide in patients with primary abdominal and pelvic malignancies: radiographic-pathologic correlation. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1999; 172: 1347–1351.
Semelka RC, Helmberger TK . Contrast agents for MR imaging of the liver. Radiology 2001; 218: 27–38.
Bhushan R, Reddy GP . Thin layer chromatography of dansyl and dinitrophenyl derivatives of amino acids. A review. Biomed Chromatogr 1989; 3: 233–240.
Walker JM . The Dansyl-Edman method for manual peptide sequencing. Methods Mol Biol 1997; 64: 183–187.
O’Connor NA, Sakata ST, Zhu H, Shea KJ . Chemically modified dansyl probes: a fluorescent diagnostic for ion and proton detection in solution and in polymers. Org Lett 2006; 8: 1581–1584.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Research Program for Genomic Medicine (NRPGM), National Science Council, Taipei, Taiwan (NSC95-3112-B-037-001, NSC 95-2627-M-037-001) and the National Health Research Institutes (NHRI-EX96-9624SI). We acknowledge technical support from the Functional and Micro-Magnetic Resonance Imaging Center supported by the National Research Program for Genomic Medicine, National Science Council, Taiwan (NSC95-3112-B-001-009) and the National Sun Yat-Sen University-Kaohsiung Medical University Joint Research Center.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, CM., Chu, PY., Chuang, KH. et al. Hapten-derivatized nanoparticle targeting and imaging of gene expression by multimodality imaging systems. Cancer Gene Ther 16, 83–90 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/cgt.2008.50
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cgt.2008.50
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Humanized bispecific antibody (mPEG × HER2) rapidly confers PEGylated nanoparticles tumor specificity for multimodality imaging in breast cancer
Journal of Nanobiotechnology (2020)